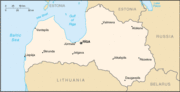
Geography of Latvia
|
|
Between 55.40 and 58.05 latitude and 20.58 and 28.14 longitude, Latvia lies on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea on the level northwestern part of the rising East European platform. About 98% of the country lie under 200m elevation (640 ft.). The damp climate resembles New England's. With the exception of the coastal plains, the ice age divided Latvia into three main regions: the morainic Western and Eastern uplands and the Middle lowlands. Latvia holds over 12,000 rivers, only 17 of which are longer than 60 miles, and over 3,000 small lakes, most of which are eutrophic. The major rivers include Daugava, Lielupe, and Gauja. Woodlands, more than half of which are pine woods, cover around 41% of the country. Other than peat, dolomite, and limestone, natural resources are scarce. Latvia has 531km (329 mi.) of sandy coastline, and the ports of Liepaja and Ventspils provide important warm-water harbors for the Baltic littoral.
Latvia is slightly larger than Denmark, Estonia, the Netherlands, or Switzerland. Its strategic location has instigated many wars between rival powers on its territory. As recently as 1944, the U.S.S.R. granted Russia the Abrene region on the Livonian frontier, which Latvia still contests.
Location: Northern Europe, on the Baltic Sea coast between Estonia and Lithuania.
Geographic coordinates: Template:Coor dm
Map references: Europe
Area:
total:
64,588 sq km
land:
64,588 sq km
water:
0 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly larger than West Virginia
Land boundaries:
total:
1,150 km
border countries:
Belarus 141 km, Estonia 339 km, Lithuania 453 km, Russia 217 km
Coastline: 531 km
Maritime claims:
continental shelf:
200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
exclusive economic zone:
200 nautical miles
territorial sea:
12 nautical miles
Climate: maritime; wet, moderate winters
Terrain: low plain
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
Baltic Sea 0 m
highest point:
Gaizinkalns 312 m
Natural resources: minimal; amber, peat, limestone, dolomite, hydropower, arable land
Land use:
arable land:
27%
permanent crops:
0%
permanent pastures:
13%
forests and woodland:
46%
other:
14% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 160 sq km (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: NA
Environment - current issues: air and water pollution because of a lack of waste conversion equipment; Gulf of Riga and Daugava River heavily polluted; contamination of soil and groundwater with chemicals and petroleum products at military bases
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol