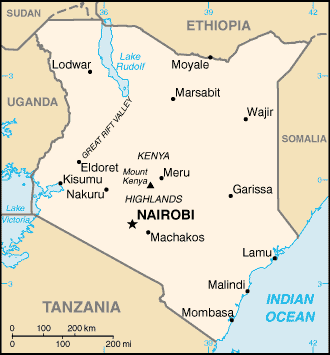
Geography of Kenya
|
|
This article describes the geography of Kenya.
- Location
- Eastern Africa, bordering the Indian Ocean, between Somalia and Tanzania
- Geographic coordinates
- Template:Coor dm
- Map references
- Africa
- Area
-
- Total: 582,650 km²
- Land: 569,250 km²
- Water: 13,400 km²
- Land boundaries
- Coastline
- 536 km
- Maritime claims
- Climate
- Varies from tropical along coast to arid in interior
- Terrain
- Low plains rise to central highlands bisected by Great Rift Valley; fertile plateau in west
- Elevation extremes
-
- Lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
- Highest point: Mount Kenya 5,199 m
- Natural resources
- Gold, limestone, soda ash, salt barites, rubies, fluorspar, garnets, wildlife, hydropower
- Land use
-
- Arable land: 7%
- Permanent crops: 1%
- Permanent pastures: 37%
- Forests and woodland: 30%
- Other: 25% (1993 est.)
- Irrigated land
- 660 km² (1993 est.)
- Natural hazards
- Recurring drought in northern and eastern regions; flooding during rainy seasons
- Environment--current issues
- Water pollution from urban and industrial wastes; degradation of water quality from increased use of pesticides and fertilizers; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; poaching
- Environment--international agreements
-
- Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
- Signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
- Geography--note
- The Kenyan Highlands comprise one of the most successful agricultural production regions in Africa; glaciers on Mt. Kenya; unique physiography supports abundant and varied wildlife of scientific and economic value