Geography of Azerbaijan
|
|
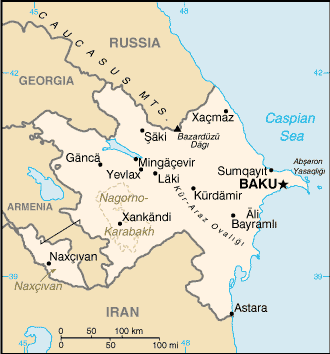
This article describes the geography of Azerbaijan.
- Location
- Southwestern Asia, bordering the Caspian Sea, between Iran and Russia
- Geographic coordinates
- Template:Coor dm
- Map references
- Commonwealth of Independent States
- Area
-
- Total: 86,600 km²
- Land: 86,100 km²
- Water: 500 km²
- Note: Includes the exclave of Naxcivan Autonomous Republic and the Nagorno-Karabakh region; the region's autonomy was abolished by Azerbaijani Supreme Soviet on November 26, 1991.
Historical Azerbaijan and today's area populated by ethnic Azeris is much larger than the independent country: the whole Northwestern part of Iran forms the so called "South Azerbaijan".
- Area comparative
- Australia comparative: slightly smaller than Tasmania
- Canada comparative: larger than New Brunswick
- United Kingdom comparative: slightly larger than Scotland
- United States comparative: slightly smaller than Maine
- Land boundaries
- Coastline
- 0 km (landlocked). Azerbaijan borders the Caspian Sea. (800 km, est.)
- Maritime claims
- None (landlocked)
- Climate
- Dry, semiarid steppe
- Terrain
- Large, flat Kur-Araz Ovaligi (Kura-Araks Lowland) (much of it below sea level) with Great Caucasus Mountains to the north, Qarabag Yaylasi (Karabakh Upland) in west; Baky lies on Abseron Yasaqligi (Apsheron Peninsula) that juts into Caspian Sea
- Elevation extremes
-
- Lowest point: Caspian Sea -28 m
- Highest point: Bazarduzu Dagi 4,485 m (on border with Russia)
- Highest peak entirely within Azeri territory: Shah Dagi 4,243 m
- Natural resources
- Petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, nonferrous metals, alumina.
- Land use
-
- Arable land: 18%
- Permanent crops: 5%
- Permanent pastures: 25%
- Forests and woodland: 11%
- Other: 41% (1993 est.)
- Irrigated land
- 10,000 sq km (1993 est.)
- Natural hazards
- Droughts; some lowland areas threatened by rising levels of the Caspian Sea
- Environment--current issues
- Local scientists consider the Abseron Yasaqligi (Apsheron Peninsula) (including Baky and Sumqayit) and the Caspian Sea to be the ecologically most devastated area in the world because of severe air, water, and soil pollution; soil pollution results from the use of DDT as a pesticide and also from toxic defoliants used in the production of cotton.
- Environment - international agreements
-
- Party to: Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection
- Signed, but not ratified: Biodiversity
- Geography--note
- Semi-landlocked (the Caspian basin is accessible from the oceans through the Volga-Don Canal system, allowing transportation of dimension-restricted sea freight).