Flowchart
|
|
LampFlowchart.png
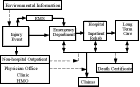
A flowchart (also spelled flow-chart and flow chart) is a schematic representation of a process. They are commonly used in business/economic presentations to help the audience visualize the content better, or to find flaws in the process.
Examples include instructions for a bicycle's assembly, an attorney outlining a case's timeline, diagram of an automobile plant's work flow, the decisions to be taken on a tax form, et cetera.
Generally the start point, end points, inputs, outputs, possible paths and the decisions that lead to these possible paths are included.
Many humorous flowcharts exist, e.g. one that outlines how to pass the blame if something goes wrong.
Flow-charts can be created by hand or manually in most office software, but lately specialized diagram drawing software has emerged that can also be used for the purpose, such as Visio, OpenOffice.org Draw and Dia.
Programs have been written to create flowcharts directly from computer program source.
| Contents |
Applications in computer science
Flowcharts were used historically in computer science to represent algorithms, which are themselves instructions for a sequence of operations. Today, however, the trend is towards the use of pseudocode to represent algorithms. Flowcharts are, however, more visual, and are often used in presentations.
Creating flowcharts on a computer
There are various packages for creating flowcharts, according to different standards. The most common is UML, for which there are abundant packages for various platforms. See UML article for list. The creation of simple flowcharts on a computer is fairly easy with any vector-based drawing program, but Microsoft Word (versions 97 through 2003) and Openoffice.org (Draw app) both have specialized tools for making consistent charts.
When in Word, enable the Drawing toolbar and click Autoshapes then Flowcharts and finally on the appropriate shape you would like. Right-click on a shape and then click Add Text to do so. The Arrow or Line tool is used to manually draw links.
When in Draw, enable the Flowchart pallette and click a shape to add it in. Double-clicking a shape will add text to it within appropriate boundaries. Connections can be automatically made between shapes using Connectors and Glue Points - click on the Connector arrow to see a selection of them before dragging from a Glue Point on a shape to another. Draw will maintain the link and automatically redraw the connector if you resize or move any shape.
See also
External links
- Flowcharting Techniques, an IBM manual from 1969 (http://www.fh-jena.de/~kleine/history/software/IBM-FlowchartingTechniques-GC20-8152-1.pdf) (5MB PDF format)
- Tools of Flowcharting (http://www.tpub.com/neets/book22/93c.htm)
- Scott W. Ambler, The Object Primer 3rd Edition: Agile Model Driven Development with UML 2 (http://www.agilemodeling.com/artifacts/flowChart.htm)
- Flowcharting Basics (http://www.nos.org/htm/basic2.htm) - from the National Institute of Open Schooling. Contains info on standard symbols
Agile Model Driven Development with UML 2, Copyright 2003-2005]de:Programmablaufplan it:Diagramma a blocchi ja:フローチャート he:תרשים זרימה nl:Stroomdiagram