Eicosanoid
|
|
In biochemistry, eicosanoids are a class of oxygenated hydrophobic cytokines that largely function as a autocrine and paracrine mediators. All eicosanoids derive from arachidonic acid, a polyunsaturated fatty acid.
| Contents |
Nomenclature
Eicosa (Greek: twenty, see eicosahedron) denotes the amount of C atoms in arachidonic acid. The numbering of eicosanoids is used to denote the number of double bonds. The prostanoids generally have two, while the leukotrienes have four.
Synthesis
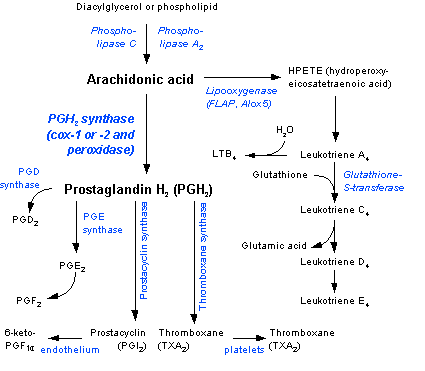
The first step of eicosanoid biosynthesis is the release of arachidonic acid from phospholipids (by phospholipase A2) or diacylglycerol (by phospholipase C).Arachidonic acid has two possible fates:
- 5-lipoxygenase pathway:
- Cyclooxygenase pathway ("prostanoids"):
Leukotrienes
5-lipoxygenase uses the nuclear-membrane protein cofactor 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein (FLAP) to sequentially convert arachidonic acid, first into 5-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-HPETE), and then 5-HPETE into leukotriene A4 (LTA4). LTA4 may be converted into LTB4 by the enzyme leukotriene A4 epoxide hydrolase. Eosinophils, mast cells, and alveolar macrophages use the enzyme leukotriene C4 synthase to conjugate glutathione with LTA4 to make leukotriene C4 (LTC4). LTC4 is transported out of the cell, where a glutamic acid moiety is removed from it to make leukotriene D4 (LTD4). LTD4 is cleaved by dipeptidases to make leukotriene E4 (LTE4).
LTC4, LTD4 and LTE4 all contain cysteine and are collectively known as the cysteinyl leukotrienes.
Prostanoids
All prostanoids originate from prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), which is converted by different enzymes into the various compounds. The enzyme PGH2-synthase is in fact a combination of a peroxidase and a cyclooxygenase (Cox-1 or Cox-2). The Cox enzymes are the molecular target of the NSAIDs, such as aspirin (see below).
PGH2 is converted:
- By PGE synthetase into PGE (which in turn is converted into PGF)
- By PGD synthetase into PGD
- By Prostacyclin synthase into prostacyclin (PGI2)
- By Thromboxane synthase into thromboxanes
Receptors
There are specific receptors for all eicosanoids (see also specific articles):
- Leukotrienes:
- CysLT1 (Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor type 1)
- CysLT2 (Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor type 2)
- BLT1 (Leukotriene B4 receptor)
- Prostanoids:
- PGD2: DP-(PGD2)
- PGE2:
- EP1-(PGE2)
- EP2-(PGE2)
- EP3-(PGE2)
- EP4-(PGE2)
- PGF2α: FP-(PGF2α)
- PGI2 (prostacyclin): IP-(PGI2)
- TXA2 (thromboxane): TP-(TXA2)
Function and pharmacology
Leukotrienes
Leukotrienes play an important role in inflammation, and blocking leukotriene receptors can play a role in the management of asthma (montelukast, zafirlukast).
Prostanoids
See also the main article prostaglandin
Prostanoids mediate local symptoms of inflammation: vasoconstriction or vasodilation, coagulation, pain and fever. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase, specifically the inducible COX II isoform, is the hallmark of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), such as aspirin. COX II is responsible for pain and inflammation, while COX I is responsible for platelet clotting actions.fr:E´cosano´de