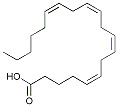
Arachidonic acid
|
|
It is present in the membranes of the body's cells, and is highly enriched in the brain. It is a precursor in the production of eicosanoids: the prostaglandins, thromboxanes, prostacyclin and the leukotrienes.
Arachidonic acid is one of the essential fatty acids required by most mammals. Some mammals lack the ability to—or have a very limited capacity to—convert linoleic acid into arachidonic acid, making it an essential part of their diet. Since little or no arachidonic acid is found in plants, such animals are obligatory carnivors; the cat is a common example.
See also
External links
- Arachidonic Acid (http://www.acnp.org/g4/GN401000059/Default.htm)
- Special Dietary Requirements of Cats (http://www.speedyvet.com/nutrition/default.asp?module=6&page=specialrequirements)de:Arachidonsäure