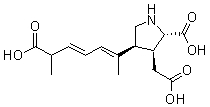
Domoic acid
|
|
Domoic acid, also called Amnesic Shellfish Poison (ASP), is an amino acid phycotoxin (algal toxin) found associated with certain algal blooms [1] (http://www.glf.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/pls/inter/dapr_view_intro?langE=en:Cite_sources).
1958, domoic acid was originally isolated from the Red alga called "Doumoi" or "Hanayanagi" (Chondria armata[2] (http://www.usep.edu.ph/smarrdec/macrobenthic%20algae/Chondria%20armata.JPG)) in Japan;"Doumoi" is used as an anthelmintic in Tokunoshima, Kagoshima.
Domoic acid is also produced by diatoms of the genus Pseudo-nitzschia. The chemical can bioaccumulate in marine organisms that feed on the phytoplankton, such as shellfish, anchovies, and sardines. In mammals, including humans, domoic acid acts as a neurotoxin, causing short-term memory loss, brain damage, and death in severe cases. Red tides are associated with the phenomenon of ASP.
In the brain, domoic acid especially damages the hippocampus and amygdaloid nucleus. It damages the neurons by activating AMPA and kainate receptors, causing an influx of calcium. Although calcium flowing into cells is a normal event, the uncontrolled increase of calcium causes the cell to degenerate.