Diene
|
|
Dienes are hydrocarbons which contain two double bonds.
Classes
Dienes can divided into three classes:
- Unconjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by two or more single bonds.
- Conjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by one single bond.
- Cumulated dienes have the double bonds sharing a common atom.
Common examples
The simplest conjugated diene is 1,3-butadiene:
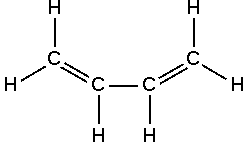
The 1,3 configuration of double bonds found in 1,3-butadiene (conjugated double bonds) make these types of dienes capable of participating in more reaction types than is the case for molecules with either just a single alkene functional group or with multiple, but non-alternating, alkene groups. One possible reaction for such dienes is the Diels-Alder reaction.
A compound in which two double bonds exist but are immediate adjacent to each other is, in contrast, called an allene.
Cyclopentadiene is another example of a diene.
Template:Organic-compound-stubde:Polyene
fr:Diène
pl:Dien
ru:Диены
sv:Dien
