International Commission on Illumination
|
|
The International Commission on Illumination (usually known as the CIE for its French-language name Commission Internationale de l'Eclairage) is the international authority on light, illumination, colour, and colour spaces.
The CIE has its headquarters in Vienna, Austria.
The CIE's chromaticity diagram (shown below), developed in 1931, is still used as a standard reference for defining colours, and as a reference for other colour spaces. The diagram is a two-dimensional plot of colours of constant intensity based on the visual response of the CIE-1931 standard observer, which was determined by physiological measurements of human colour vision. Since the human eye has three types of colour sensor that respond to different ranges of wavelengths, a full plot of all visible colours is a three-dimensional figure. This is inconvenient to draw on a two-dimensional sheet of paper, so for convenience the CIE transformed the three-dimensional colour space into two artificial dimensions of colour (collectively called chromaticity) and one of intensity, and then took a two-dimensional slice through this space at the level of maximum intensity. This slice became the chromaticity diagram. Incidentally, this technique of converting a three-dimensional colour space to a combination of chromaticity and intensity is also used in colour television.
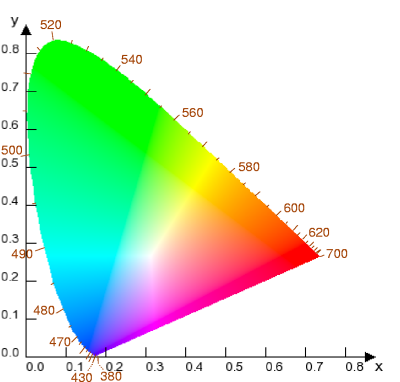
The gamut of all visible colours on the CIE plot is a tongue-shaped or horseshoe-shaped figure, with the curved edge corresponding to the colours of the visible spectrum and the straight edge (the purple line) corresponding to non-spectral shades of purple. Less saturated colours appear in the interior of the figure, with white at the centre.
A three-dimensional figure can be made by plotting the CIE's chromaticity on two axes and intensity on the third axis. It is a roughly pyramidal solid that is informally called the colour bag.
Note that the chromaticity diagram is a tool to specify how the human eye will experience light with a given spectrum. It cannot specify colours of objects (or printing inks), since the chromaticity observed while looking at an object depends on the light source as well.
The cut-offs at the short- and long-wavelength side of the diagram are chosen somewhat arbitrarily; the human eye can actually see light with wavelengths up to about 810 nm, but with a sensitivity that is many thousand times lower than for green light.
Background
The human eye has receptors for short (S), middle (M), and long (L) wavelengths, also known as blue, green, and red receptors. That means that one, in principle, needs three parameters to describe a color sensation. In the CIE diagram, those parameters are not the M, S, and L stimuli, but rather a more abstract x and y parameter, and an implicit luminosity (brightness) parameter, that is not shown.
External links
- http://www.cie.co.at/cie/
- List of CIE publications and standards (http://www.cie.co.at/framepublications.html)
- http://www.cox-internet.com/ast305/color.html More information with tons of useful linksde:Internationale Beleuchtungskommission
