Basilar membrane
|
|
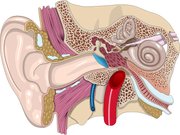
The basilar membrane within the cochlea of the inner ear is the part of the auditory system that decomposes incoming auditory signals into their frequency components. This allows higher neural processing of sound information to focus on the frequency spectrum of input, rather than just the time domain waveform.
In brief, the membrane is tapered and is stiffer at one end than the other. This causes sound input of a certain frequency to vibrate a particular location of the membrane more than other locations due to the physical property of resonance. As shown in experiments by Nobel Prize laureate Georg von B髩sy, high frequencies will lead to vibrations at the narrow, basal end of the membrane, low frequencies will lead to vibrations at the wide, apical end of the membrane. The localized vibration of the basilar membrane is then transduced into neural signals by the inner hair cells of the Organ of Corti, which sits on top of the basilar membrane. The hair cells above the most resonating segment of the membrane will fire the most signals, thus the neural code leaving the ear through the auditory nerve is frequency coded.
Anatomy Clipart and Pictures
- Clip Art (http://classroomclipart.com)
- Anatomy Clip Art (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Anatomy)
- Anatomy Clip Art (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Clipart/Anatomy)
- Anatomy Animations (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Animations/Anatomy)
- Anatomy Illustrations (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Illustrations/Anatomy)
| Sensory system - Auditory system | Edit (http://en.wikipedia.org/w/wiki.phtml?title=Template:Auditory_system&action=edit) |
| Pinna - Ear canal - Eardrum - Ossicles - Cochlea - Basilar membrane - Organ of Corti - Hair cells - Auditory nerve - Primary auditory cortex |