The Brain: How Your Body’s Command Center Works
Learn what the brain does, how it controls your body, and why it’s one of the most powerful organs. Explore its parts and how it keeps you alive and thinking.
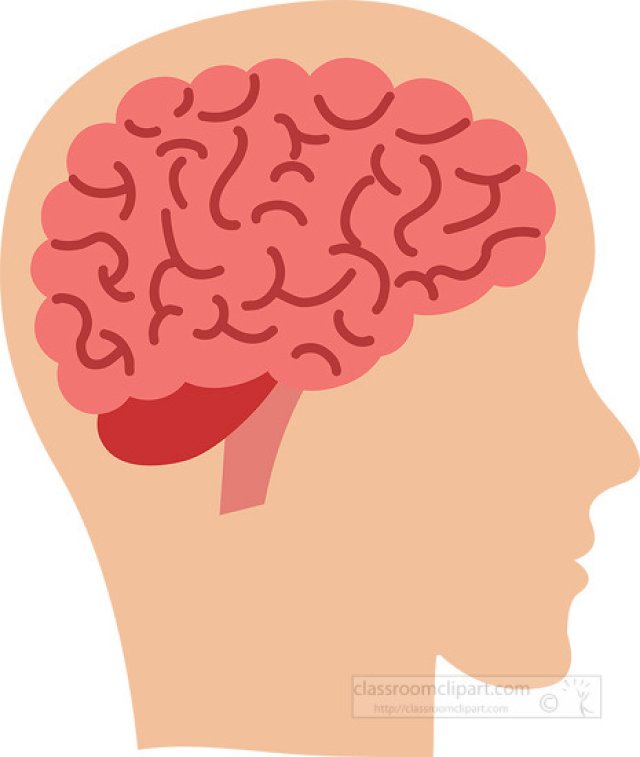
🧠 Introduction: Your Most Powerful Organ
The brain is the most powerful and complex organ in the human body. Even though it weighs only about three pounds, it acts as the control center for everything you think, feel, and do. It works nonstop—from the moment you’re born to the moment you go to sleep, and even while you're asleep. It helps you breathe, move, talk, solve problems, and experience emotions. It also stores your memories, allows you to dream, and keeps your body in balance.
Made up of billions of cells called neurons, the brain communicates with the rest of the body by sending and receiving messages through the nervous system. These messages travel in split seconds and help you react to the world around you. Whether you're playing a video game, riding a bike, or remembering your best friend’s name, your brain is behind it all.
🧩 What Does the Brain Do?
The brain is responsible for both voluntary actions—like choosing to move your hand—and involuntary actions, like your heartbeat and breathing, which happen automatically.
Some of the brain’s most important jobs include:
Thinking and learning: solving problems, understanding ideas, and remembering information
Controlling movement: sending signals to your muscles to move your body
Regulating senses: processing everything you see, hear, smell, touch, and taste
Managing emotions: helping you feel happy, sad, scared, or excited
Keeping you alive: running basic life functions like breathing, digestion, and body temperature
Your brain is constantly working, even when you’re resting. It never truly turns off.
🧠 The Three Main Parts of the Brain
Although the brain is one organ, it’s divided into three major parts, each with its own job. These parts work together to help your body run smoothly and respond to the world.
1. Cerebrum – The Thinker
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. It sits at the top and looks like a wrinkled walnut. This part of the brain helps you:
Think and make decisions
Speak and understand language
Control voluntary movements, like walking or writing
Feel emotions and store memories
The cerebrum is divided into two halves, called hemispheres:
The left hemisphere helps with logic, language, and math
The right hemisphere handles creativity, imagination, and music
These two sides work together but also control opposite sides of your body. For example, the left brain controls your right hand, and the right brain controls your left hand.
2. Cerebellum – The Balancer
Located underneath the cerebrum at the back of the brain, the cerebellum is smaller but still very important. It helps:
Control balance and coordination
Fine-tune your movements, so they’re smooth and not shaky
Support posture and muscle memory (like riding a bike)
Without the cerebellum, your movements would be clumsy, and it would be hard to stay upright or catch a ball.
3. Brainstem – The Lifeline
The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord. It’s located at the base of the brain and is responsible for automatic body functions that happen without thinking. These include:
Breathing
Heart rate
Digestion
Blinking
Sleeping and waking
The brainstem is always active, even when you're unconscious. It keeps your body functioning and alive, even while you sleep.
🔁 How the Brain Sends Messages
Your brain works closely with the spinal cord and nerves to send messages throughout the body. These messages travel as electrical signals through neurons—tiny cells that act like messengers.
Here’s how it works:
The brain decides what needs to happen (like moving your hand)
The message travels down the spinal cord
The nerves carry the signal to the muscles or organs
Your body responds almost instantly
If you touch something hot, for example, your skin sends a message through your nerves to your brain. In less than a second, your brain responds by telling your hand to pull away.
This communication system works faster than any computer!
🧠 Vocabulary List
Term Definition
Brain The control center of the body that manages thinking, movement, and senses
Neuron A nerve cell that sends and receives messages in the brain and body
Cerebrum The largest part of the brain responsible for thinking and movement
Cerebellum The part of the brain that controls balance and coordination
Brainstem The lower part of the brain that controls automatic body functions
Spinal cord A bundle of nerves that connects the brain to the rest of the body
Nerves Wires that carry messages between the brain and body
Hemisphere One half of the brain (left or right)
Reflex A quick, automatic action controlled by the brain and spinal cord
Nervous system The body system that includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
❓ Interactive Quiz: Test Your Brain Knowledge
1. What does the brain do?
A. Only controls sleep
B. Only stores memories
C. Controls almost everything in the body
D. Only helps you breathe
2. What part of the brain helps you think and make decisions?
A. Cerebellum
B. Brainstem
C. Spinal cord
D. Cerebrum
3. What part of the brain helps with balance?
A. Left hemisphere
B. Brainstem
C. Cerebellum
D. Neuron
4. Which part controls automatic actions like breathing?
A. Cerebrum
B. Nerves
C. Brainstem
D. Right hemisphere
5. What is a neuron?
A. A brain muscle
B. A hair cell
C. A nerve cell
D. A blood vessel
⭐ Kid-Friendly Summary
Your brain is the command center of your body. It helps you think, move, breathe, feel, and remember. The cerebrum helps you think and talk, the cerebellum helps you balance and move smoothly, and the brainstem keeps you alive by controlling your heartbeat and breathing. Your brain works with your spinal cord and nerves to send messages to every part of your body—and it never takes a break!
🤯 Fun and Interesting Facts
The brain has about 86 billion neurons!
Your brain uses about 20% of the oxygen your body takes in.
The left side of your brain controls the right side of your body (and vice versa).
A human brain can process thoughts faster than any computer.
Your brain keeps working even while you’re asleep—especially to help you dream!