Ancient Egypt Facts for Students | Pharaohs, Pyramids, and Daily Life
Discover Ancient Egypt through this student-friendly article. Learn about pharaohs, pyramids, hieroglyphics, daily life, gods, and mummies. Includes vocabulary, fun facts, and a quiz—perfect for middle school learners and classrooms

Introduction: Why Is Ancient Egypt Important?
Ancient Egypt is one of the world’s oldest and most famous civilizations. Located in northeastern Africa along the Nile River, it lasted for over 3,000 years! The Egyptians built massive pyramids, developed a system of writing called hieroglyphics, and worshipped a large number of gods and goddesses. Their culture continues to amaze historians, archaeologists, and students all over the world.
This article explores Ancient Egyptian geography, society, religion, daily life, writing, and achievements—and why their legacy still matters today
🗺️ Geography and the Nile River
The Nile River was the lifeline of Ancient Egypt. It flows from south to north and empties into the Mediterranean Sea.
- Every year, the Nile flooded, leaving behind rich soil for farming.
- Most Egyptian cities and farms were located along the river.
- The desert around the Nile helped protect Egypt from invaders.
Because of the Nile, Egypt was called the “Gift of the Nile” by the Greek historian Herodotus.
🏛️ Pharaohs and Government
Egypt was ruled by a pharaoh, who was both the king and considered a god.
- Pharaohs wore crowns and symbols like the crook and flail.
- They were buried in grand tombs, including pyramids and underground chambers.
- Some famous pharaohs include:
- King Tutankhamun (King Tut) – Became pharaoh at age 9; his tomb was found nearly untouched in 1922.
- Ramses II – Ruled for 66 years and built many temples.
- Hatshepsut – A female pharaoh known for peaceful trade and building projects.
Egypt’s government was highly organized. Officials, scribes, tax collectors, and generals helped the pharaoh run the country.
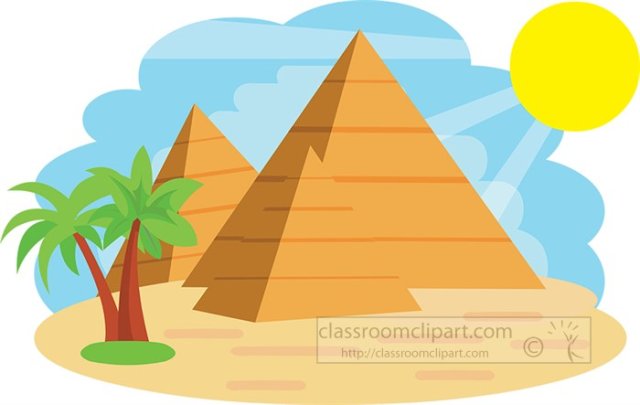
🧱 Pyramids and Monuments
Ancient Egyptians are famous for their incredible stone structures.
Pyramids
- Built as tombs for pharaohs during the Old Kingdom.
- The most famous is the Great Pyramid of Giza, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
Temples
- Built to honor gods and pharaohs.
- Decorated with hieroglyphs, carvings, and statues.
- Examples include Karnak and Abu Simbel.
📜 Hieroglyphics and Writing
- Egyptians used a picture-writing system called hieroglyphics.
- It included over 700 symbols representing sounds or ideas.
- Writing was used on temple walls, tombs, and papyrus scrolls.
- Only scribes—specially trained men—could read and write.
The key to understanding hieroglyphics was found in 1799 with the discovery of the Rosetta Stone, which had the same message written in Greek, Demotic, and hieroglyphics.
☥ Religion and Gods
Ancient Egyptians were polytheistic—they believed in many gods and goddesses.
Important Gods:
Ra: The sun god and king of the gods.
- Osiris: God of the afterlife.
- Isis: Goddess of magic and motherhood.
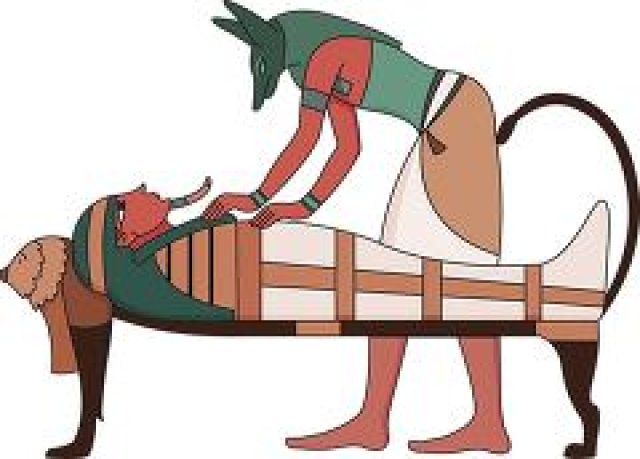
- Anubis: God of mummification and the dead.
- Horus: Sky god, shown with a falcon head.
They believed in life after death. That’s why they built tombs and practiced mummification to preserve bodies for the afterlife.
🏺 Daily Life in Ancient Egypt
Jobs
Most Egyptians were farmers. Others were:
- Builders
- Craftspeople
- Merchants
- Soldiers
- Priests
- Scribes
Homes and Food
- Houses were made of mud bricks.
- Meals included bread, fish, dates, beer, and vegetables.
Clothing
- Made from linen.
- Men wore kilts; women wore dresses.
- Both men and women wore jewelry and makeup!
Children
- Played games with dolls, balls, and toys.
- Many didn’t go to school unless they trained to be scribes.
⚰️ Mummies and the Afterlife
Egyptians believed the soul needed the body after death. They used mummification to preserve the dead.
Steps of Mummification:
- Remove internal organs and dry the body.
- Wrap it in linen bandages.
- Place in a decorated coffin or sarcophagus.
Tombs were filled with treasures, food, and items for the next world. The Book of the Dead was a guide for the journey to the afterlife.
🧠 Vocabulary Word List: Ancient Egypt
Pharaoh - Ruler of Ancient Egypt, considered a god-king.
Hieroglyphics - Picture-based writing system used in Ancient Egypt.
Mummification - A process to preserve dead bodies for the afterlife.
Papyrus - A plant used to make paper-like scrolls.
Sarcophagus - A decorated coffin used for wealthy or royal Egyptians.
Polytheistic - Believing in many gods and goddesses.
Scribe - A trained person who could read and write.
Afterlife - Life believed to occur after death.
Pyramid - A large triangular tomb built for pharaohs.
Nile River - The river that made civilization in Egypt possible.
💡 Interesting Facts About Ancient Egypt
- The Great Pyramid was the tallest building in the world for over 3,800 years!
- Ancient Egyptians invented toothpaste and breath mints.
- Cleopatra, the last Egyptian ruler, was actually Greek by blood.
- Egyptians used calendar systems based on the stars.
- Cats were sacred and often mummified like people.
- The Nile flows north, one of the few major rivers to do so.
📚 Kid-Friendly Summary: What You Should Remember
Ancient Egypt was a powerful and fascinating civilization that grew along the Nile River. The Egyptians built pyramids, used hieroglyphics to write, believed in many gods, and created amazing art and mummies. Pharaohs ruled the land, and religion played a big part in daily life. They believed in life after death and worked hard to prepare for it. Their inventions and ideas still amaze people today!