Zond 1
|
|
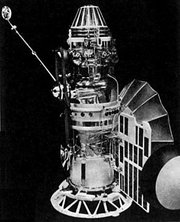
Zond 1, a member of the Soviet Zond program, was the second Soviet research spacecraft to successfully reach position Venus. A slow leak from a cracked sensor window caused the spacecraft to depressurize. An ill-timed command from ground control turned on its radio system while there was still a rarefied atmosphere inside, causing the electronics to short out by corona discharge. Communication was subsequently maintained via the transmitter in the landing capsule, and space radiation and atomic-hydrogen spectrometer measurements were performed.
Zond-1 was designed to carry a 90 cm spherical landing capsule to Venus. It contained experiments for chemical analysis of the atmosphere, gamma-ray measurments of surface rocks, a photometer, temperature and pressure gauges, and a motion/rocking sensor in case it landed in water.
The spacecraft, a Venera 3MV-1, was launched on April 4, 1964 from Tyuratam, communications failed by May 14, and it achieved orbit around the sun 100,000km from Venus on July 14 of that year.
External links
Astrolink description of spacecraft and payload (http://www.astrolink.de/m052/m052001/) NSSDC spacecraft info (http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/database/MasterCatalog?sc=1964-016D)
| Previous mission: none |
Zond program | Next mission: Zond 2 |