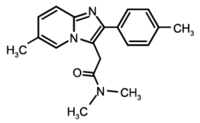
Zolpidem
|
|
| N,N,6-trimethyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)- imidazo(1,2-a)pyridine-3-acetamide | |
| CAS number 82626-48-0 | ATC code N05CF02 |
| Chemical formula | C19H21N3O |
| Molecular weight | 307.395 |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Elimination half-life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Pregnancy category | ? |
| Legal status | Schedule IV (USA) |
| Routes of administration | Oral: 3.75, 7.5 mg and 10mg tablets |
Zolpidem is a prescription drug used for the short-term treatment of insomnia (sleeping pill). It works quickly (usually within 15 minutes) and has a short half-life (2-3 hours), but will last longer in patients with hepatic failure. Some trade names of zolpidem are Ambien®, Stilnox® or Stilnoct®.
It activates the same neuronal receptors as the benzodiazepines, but has a different chemical structure than these drugs, and is actually classified as an imidazopyridine. Zolpidem works by enhancing the effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain.
Larger doses of the drug can result in a variety of unwanted side effects: hallucinations, delusions, poor motor coordination, increased appetite, increased sex drive, poor judgement, and, following use, inability to remember events that took place while under the influence of the drug. Some users take zolpidem recreationally for these side effects. Zolpidem can also become psychologically addictive if taken for extended periods of time, due to dependence on its ability to put one to sleep or to the unique sense of euphoria it can produce. Under the influence of the drug it is common to take more zolpidem than is necessary. Users are advised to keep additional zolpidem away to avoid this risk.