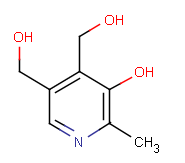
Vitamin B6
|
|
The two major forms of vitamin B6 are pyridoxine and pyridoxamine. In the liver they are converted to pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) which is a cofactor in many reactions of amino acid metabolism. PLP also is necessary for the enzymatic reaction governing the release of glucose from glycogen.
Pyroluria is one potential cause of vitamin B6 deficiency. An overdose of pyridoxine can cause a temporary deadening of certain nerves such as the proprioceptory nerves; causing a feeling of dissembodiment common with the loss of proprioception.
External links
- Facts about Vitamin B6 (http://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/cc/vitb6.html) from NIH Office of Dietary SupplementsTemplate:Biochem-stub
de:Pyridoxin fa:ویتامین ب۶ fr:Vitamine B6 it:Vitamina B6 he:ויטמין B6 lb:Pyridoxin lt:Piridoksinas nl:Pyridoxine ja:ビタミンB6 pl:Witamina B6