USS Puritan (1882)
|
|
| |
| Career | 
|
|---|---|
| Ordered: | |
| Laid down: | |
| Launched: | 6 December 1882 |
| Commissioned: | 10 December 1896 |
| Decommissioned: | 23 April 1910 |
| Fate: | sold, 26 January 1922 |
| Struck: | 27 February 1918 |
| General Characteristics | |
| Displacement: | 3,265 tons |
| Length: | 351 ft |
| Beam: | 50 ft |
| Draft: | 20 ft |
| Propulsion: | |
| Speed: | |
| Range: | |
| Depth: | |
| Complement: | |
| Armament: | four 12 inch (305 mm) guns |
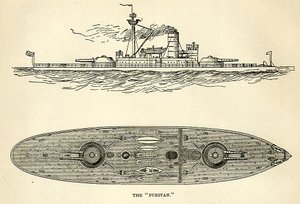
The second USS Puritan was a monitor in the United States Navy, constructed in 1882.
The never-completed Puritan of the American Civil War underwent the same extent of rebuilding as the four Miantonomohs under the direction of Secretary of the Navy George Robeson. The revised design of the “repaired” Puritan called for two turrets, and with her superstructure, tall stack, and military mast, she had the characteristics which identified the monitors built between 1889 and 1903. The new Puritan was built by John Roach & Son, Chester, Pennsylvania and completed by the New York Navy Yard, Brooklyn, New York. She was launched 6 December 1882 and commissioned 10 December 1896, Captain J. R. Bartlett in command.
By 1891, she had been equipped with four 12 inch (305 mm) guns in barbette turrets, with the plane of fire ten and a half feet (3.2 m) above the water. The armor belt was 5 feet 7 inches (1.7 m) deep, 14 inches (360 mm) amidships, with an armor deck of 2 inches (50 mm); barbettes, 14 inches (360 mm); and inclined turrets, 8 inches (200 mm). The original crew quarters were below deck, but these were given up to be additional crew quarters after new officers quarters were constructed in the superstructure.
Puritan had a busy career in 1898 during the Spanish-American War. Assigned to the Cuban blockade in April, she joined New York and Cincinnati in shelling Matanzas the 27th. At Key West in early May, she departed the 20th to join the force then building under Rear Admiral William T. Sampson to move against Santiago. Puritan linked up on the 22nd and Sampson moved his ships to Key Frances on the Nicholas Channel to execute his plan to contain the Spanish Fleet at Santiago. The success of Sampson’s squadron at Santiago 3 July resulted in almost complete destruction of the Spanish Fleet.
Following war-time service, Puritan served as a practice ship for the Naval Academy from 1899 to 1902. She decommissioned 16 April 1903 at Philadelphia but recommissioned 3 June to serve as a receiving ship at League Island. In 1904 she was loaned to the Naval Militia of Washington, D.C. and served with them until 14 September 1909. Puritan then moved to Norfolk, Virginia where she decommissioned 23 April 1910. She was struck from the Navy List 27 February 1918 and sold, 26 January 1922, to J. G. Hetner and W. F. Cutler of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
See USS Puritan for other ships of this name.
This article includes text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships.
