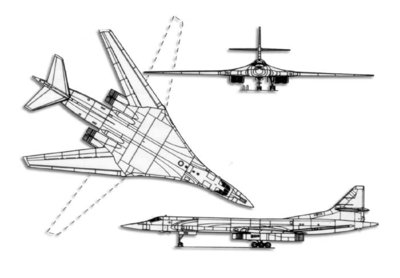
Tupolev Tu-160
|
|
The Tupolev Tu-160 (NATO reporting name Blackjack) is a supersonic, swing-wing heavy bomber designed in the Soviet Union. It was the last Soviet strategic bomber design, and the heaviest combat aircraft ever built. Introduced in 1987, small numbers remain in service in Russia.
| Contents |
History
The first competition for a supersonic strategic heavy bomber was launched in the Soviet Union in 1967. The new plane was to have a cruise speed of over Mach 3, in response to the U.S. XB-70 Valkyrie. It soon became apparent that such an aircraft would be too expensive and difficult to build, so it was decided to reduce demands (in the U.S., the XB-70 project had already been abandoned).
In 1972 the Soviet Union launched a new multi-mission bomber competition to create a new supersonic, swing-wing heavy bomber with Mach 2.3 maximum speed, in response to the U.S. Air Force B-1B Lancer bomber project. The Tupolev design, dubbed Aircraft 160M, with a lengthened flying wing layout and incorporating some elements of the Tu-144, was the OKB's entry in the competition, which also included the Myasishchev M-18 and a Sukhoi T4MS design. Myasishchev's version, proposing a swing-wing aircraft, was considered to be the most successful, although the Tupolev organization was regarded as having the greatest potential for completing this complex project. Consequently, Tupolev was assigned in 1973 the development a new aircraft based on the Myasishchev design.
Tu_16019.jpg
Although the B-1A was cancelled in 1977, work on the new Soviet bomber continued, and in the same year, the design was accepted by the government committee. The prototype was photographed by an airline passenger at a Zhukovski airfield in November 1981, about a month before the aircraft's first flight on 18 December 1981. Production was authorized, beginning at Kazan Aviation Association in 1984. Production of the aircraft, designated Tu-160 (factory designation "aircraft 70" or "product K"), was originally intended to total 100 aircraft, although only 35 had been produced, including three prototypes. One aircraft (the second serial aircraft) was lost in flight testing in 1987 (the crew was saved). Production slowed due to lack of funds, and ceased in 1994, although some uncompleted aircraft remained.
The Tu-160 was first presented to the public on a parade in 1989. In 1989–1990 it also set 44 world speed flight records in its weight class. Squadron deployments to Long Range Aviation began in April 1987. Until 1991 19 of those aircraft served in the 184th Guards Heavy Bomber Regiment in Pryluki in Ukrainian Socialist Republic, replacing Tu-16 and Tu-22M3. After the fall of the Soviet Union those aircraft became Ukrainian property, although in 1999 a deal between Russia and Ukraine led to eight of those aircraft being returned to Russia in exchange for a reduction in Ukraine's energy debts. Ukraine, which has officially renounced nuclear weapons, has destroyed the other Blackjacks in its possession, except for one airframe retained for static display.
After the fall of the Soviet Union, Russia organized the second Tu-160 unit, the 121st Guards Heavy Bomber Regiment basing in Engels, in 1992. By 1994 it received only six Tu-160. Between 1999 and 2000 it received also eight formerly Ukrainian planes. In 2000, one additional aircraft was completed in a factory and given to the regiment.
There are currently 15 Tu-160s in service, with another three new-built aircraft either complete or nearing completion at the Kazan Aircraft Plant. As of 2001, six additional Tu-160 served as experimental aircraft in Zhukovski (four of them airworthy) and seven remained in Ukraine, phased out of service.
Tu_16029.jpg
Description
The Tu-160 bears a strong resemblance to the North American B-1B Lancer, although it is significantly larger and faster.
The Blackjack has a similar blended wing profile and variable-geometry wings, with sweep ranging from 20° to 65°. Full-span slats are used on the leading edges, with double-slotted flaps on the trailing edges. The Tu-160 has a fly-by-wire control system.
It is powered by four NK-32 afterburning turbofan engines, the most powerful ever fitted to a combat aircraft. Unlike the B-1B, which abandoned the Mach 2+ requirement of the original B-1A, it retains variable intakes, and is capable of slightly over Mach 2 at altitude.
The Tu-160 has a maximum fuel capacity of 130 tons, giving it a flight endurance of around 15 hours. It has a probe and drogue in-flight refueling system for extended-range missions.
Although the Tu-160 was designed for reduced detectability to both radar and infrared, it is not a stealth aircraft, and has a higher radar cross section (RCS) than the B-1B. The Blackjack has an attack radar ("Obzor-K", NATO "Clam Pipe") in a slightly upturned dielectric radome, plus a separate "Sopka" terrain-following radar, which provides fully automatic terrain-following flight at low level. The Tu-160 has an electro-optical bombsight, and comprehensive active and passive ECM systems.
The Tu-160 has a crew of four (pilot, co-pilot, weapons systems officer, and defensive systems operator) in K-36DM ejection seats. The pilot has a fighter-style control stick, but controls are traditional dials. There is no HUD, nor are CRT multi-function displays provided. A crew rest area, a toilet, and a galley are provided for long flights.
Weapons are carried in two internal bays, each capable of holding 20,000 kg (44,400 lb) of free-fall weapons or a rotary launcher for nuclear missiles. No defensive weapons are provided, making it the first unarmed post–World War II Soviet bomber.
Tu_160.jpg
Variants
A demilitarized, commercial version of the Blackjack, dubbed Tu-160KS, was displayed at an air show in Singapore in 1994 carrying a model of the Russian Buran space shuttle. In 1995 Tupolev announced a partnership with the German firm OHB-System to produce the aircraft as a carrier for the launch vehicle, but the German government subsequently withdrew funding in 1998. Development reportedly continues, although funding in the CIS is scarce.
Several other variants have been proposed, but not built, including:
- Tu-160M: a stretched bomber carrying two long-range, hypersonic Kh-90 (3M25 Meteorit-A) missiles
- Tu-160P (Tu-161): a very long-range escort fighter/interceptor
- Tu-160PP: an electronic warfare aircraft carrying stand-off jamming and ECM gear
- Tu-160R: a strategic reconnaissance platform
- Tu-170: a conventional bomber (conceived in order to avoid SALT-2 limits)
Specifications
General characteristics
- Crew: 4 (pilot, co-pilot, bombardier, defensive systems operator)
- Length: 54.1 m (177 ft 6 in)
- Wingspan: 55.70 m (189 ft 9 in) spread (20° sweep); 35.60 m (116 ft 9.75 in) maximum sweep (65°)
- Height: 13.10 m (43 ft 0 in)
- Wing area: 400 m² (4,310 ft²) spread; 360 m² (3,875 ft²) swept
- Empty: 110,000 kg (242,500 lb)
- Loaded: 267,600 kg (590,000 lb)
- Maximum takeoff: 275,000 kg (606,000 lb)
- Powerplant: 4× Samara/Trud NK-321 turbofans, 14,000 kgf (137 kN or 30,900 lbf) thrust each
- 25,000 kgf (245 kN (55,100 lbf) thrust each with afterburner
Performance
- Maximum speed: 2,220 km/h (1,380 mph) (Mach 2.05) at high altitude
- Range: 12,300 km (7,640 mi) unrefulled
- Service ceiling: 15,000 m (49,200 ft)
- Rate of climb: 4,200 m/min (13,780 ft/min)
- Wing loading: 743 kg/m² (152 lb/ft²) with wings fully swept
Armament
- 2 internal bays for 40,000 kg (88,200 lb) of ordnance, options include
- 2 internal rotary launchers each holding 6× Kh-55SM (AS-15 "Kent") cruise missiles (primary armament) or 12× Kh-15 (AS-16 "Kickback") short-range nuclear missiles
Related content
Related development
Similar aircraft
Designation Series
Related lists
|
Lists of Aircraft | Aircraft manufacturers | Aircraft engines | Aircraft engine manufacturers Airports | Airlines | Air forces | Aircraft weapons | Missiles | Timeline of aviation |