Treaty of Trianon
|
|
Trianon1.jpg
The Treaty of Trianon was an agreement that regulated the situation of the new Hungarian state that replaced the Kingdom of Hungary, part of the former Austro-Hungarian monarchy, after World War I. It was signed on June 4, 1920, at the Grand Trianon Palace at Versailles, France.
The main parties to the Treaty were the winning powers, their allied countries, and the losing side. The winning powers included the United States, Britain, France and Italy; their allies were Romania, Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia; and the losing side was the former Austro-Hungarian monarchy, represented by Hungary.
| Contents |
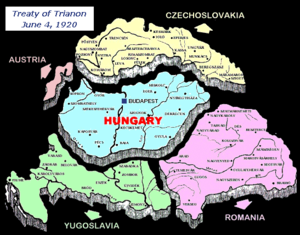
Frontiers of Hungary
Hungary became an independent state in 1918, with temporary borders defined in November–December 1918. Compared with the former Kingdom of Hungary (part of Austria-Hungary), the borders of independent Hungary didnt include:
- a part of Transylvania, which became part of Romania.
- Slovakia, which became part of Czechoslovakia.
- Croatia, Slavonia, Vojvodina and Bosnia, which joined the newly formed Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, along with the Hungarian cities of Pécs, Mohács, Baja and Szigetvár.
The final borders of Hungary were defined by the Treaty of Trianon in 1920. Compared with the borders set eighteen months previously, the Trianon borders of Hungary didn't include:
- the rest of Transylvania, which became part of Romania.
- Carpathian Ruthenia, which had become part of Czechoslovakia, pursuant to the Treaty of Saint-Germain in 1919.
- most of Burgenland, which had gone to Austria, also pursuant to the Treaty of Saint-Germain; the district of Sopron opted to remain with Hungary after a plebiscite held in December 1921.
By the Treaty of Trianon, the cities of Pécs, Mohács, Baja and Szigetvár, which were on the Yugoslav side of the border after November 1918, were restored to Hungary.
Compared with the former Kingdom of Hungary, the population of post-Trianon Hungary was reduced from 19 million to 7 million and its land area reduced by two-thirds.
After 1918, Hungary did not have access to the sea, which the former Kingdom had had through Croatia for over 800 years.
With the help of Nazi Germany and Adolf Hitler, Hungary expanded its borders towards neighbouring countries at the outset of World War II, under the Munich Agreement (1938), the two Vienna Awards (1938 and 1940), following the dissolution of Czechoslovakia (occupation of northern Carpathian Ruthenia and eastern Slovakia) and following German aggression against Yugoslavia. This territorial expansion was short-lived, since the post-war boundaries agreed on at the Treaty of Paris in 1947 were nearly identical with those of 1920.
Consequences of the treaty
Demographic consequences
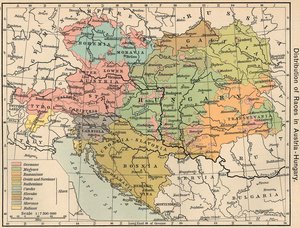
According to the census of 1910, the largest ethnic group in the Kingdom of Hungary was the Magyars (usually called "Hungarians" in English), who were approximately 48% of the entire population. Some demographers, however, believe that the 1910 census overstated the percentage of Magyars, arguing that there were different results in previous censuses of the Kingdom and subsequent censuses in the new states. The provinces Hungary lost in the treaty had a majority population of non-Magyars, but also a significant Magyar minority.
The number of Hungarians in the provinces based on census data of 1910:
- In Slovakia: 885,000 - 30%
- In Transylvania (now in Romania): 1,662,000 - 32%
- In Vojvodina (now in Serbia and Montenegro): 420,000 - 28%
- In Transcarpathia (now in Ukraine): 183,000 - 30%
- In Croatia: 121,000 - 3.5%
- In Slovenia: 20,800 - 1.6%
- In Burgenland (now in Austria): 26,200 - 9%
The Hungarian population in all those regions decreased in percentage after that, although Magyars can still be found in these countries today.
On the other hand, a considerable number of other nationalities remained within the frontiers of the new Hungary, e.g. some 450,000 Slovaks (399,170 according to Hungarian sources, 450,000–550,000 according to Czechoslovak sources), some 800,000–900,000 Germans and some 82,000 Serbs and Croats (for lack of other information, the last figure is the official figure of 1930). The percentage of all non-Magyar nationalities very quickly decreased nearly to zero in the new Hungary (there are e.g. only some 17,000 Slovaks in Hungary today, which of 2,000 live in a small village called Pilisszentkereszt).
Other consequences
Economically, 61.4% of the arable land, 88% of the timber, 62.2% of the railroads, 64.5% of the hard surface roads, 83.1% of the pig iron output, 55.7% of the industrial plants and 67% of the credit and banking institutions of the former Kingdom of Hungary became part of other countries. Romania and Yugoslavia had to assume part of the financial obligations of Hungary on account of the territory placed under their sovereignty.
The military conditions were similar to those imposed to Germany by the Treaty of Versailles; the Hungarian army was to be restricted to 35,000 men and there was to be no conscription. Further provisions stated that in Hungary, no railway would be built with more than one track.
Hungary also renounced all privileges in territory outside Europe that belonged to the former Austro-Hungarian monarchy.
Articles 54–60 of the Treaty required Hungary to observe various rights of national minorities within its borders. Hungary has been accused of violating these provisions.
See also
External links
- Text of the Treaty (http://www.lib.byu.edu/~rdh/wwi/versa/tri1.htm)
- (Hungary's) Government Office for Hungarian Minorities Abroad (http://www.htmh.hu/index_en.html)
- Hungarian Railroad (http://www.mav.hu/) (in Hungarian)
- Map of Hungarian borders in November-December 1918 (http://terkepek.adatbank.transindex.ro/kepek/netre/167.gif)
- "The Treaty of Trianon and the Dismemberment of Hungary" (http://www.webenetics.com/hungary/trianon.htm)
- "The Obsolete Treaty of Trianon and its tragic consequences" (http://www1.minn.net/~graczar/FTR-208/lessons_of_trianon.htm)de:Vertrag von Trianon
es:Tratado de Trianon fr:Traité du Trianon ja:トリアノン条約 pl:Traktat w Trianon