The Troubles
|
|
- "The Troubles" is a term used to describe two periods of violence in Ireland during the twentieth century. This article describes the latter; for the earlier Troubles, see Anglo-Irish War and Irish Civil War.
The Troubles is a generic term used to describe a period of sporadic communal violence involving paramilitary organisations, the police, the British Army and others in Northern Ireland from the late 1960s until the mid-1990s. (Another term, common among British commentators is the "Irish Problem", though this is seen as pejorative by many Irish people as it seems to absolve Britain of any blame for the conflict and portray it as a neutral party.) It could also be described as a many-sided conflict, a guerrilla war or even a civil war. The Provisional IRA maintained their violent campaign was armed resistance to British occupation; they are however described by many countries (including the UK) as a terrorist organisation. The Troubles were another chapter in the long-running hatred between Northern Ireland's Protestant and Roman Catholic communities. They were brought to an uneasy end by a peace process which included the declaration of ceasefires by some paramilitary organisations, the withdrawal of some troops from the streets and the creation of a new police force in a series of reforms, most notably the Belfast Agreement (commonly known as the Good Friday Agreement).
Though the number of active participants in the Troubles was small, and the paramilitary organisations that claimed to represent the communities were, in reality, unrepresentative of the general population, the Troubles touched the lives of most people within Northern Ireland on a daily basis, while occasionally spreading to Great Britain and the Republic of Ireland. Between three and four thousand people (many of them civilians) died as a result of the violence. Many had their political, social and communal attitudes and perspectives shaped by the Troubles.
Though not itself part of the Troubles, the Civil Rights campaign in the mid to late 1960s in Northern Ireland, which was largely modelled on the American Civil Rights campaigns of Martin Luther King and others in the United States, was seen by some in the Unionist community as the starting point for the Troubles. They argue that it led to a destabilisation of government and created a void filled later by paramilitary groups. Others, mainly though not exclusively nationalist, disagree, arguing that the Civil Rights campaign was a reaction to a corrupt system of government, the failure to reform the system causing the collapse in law and order that was the Troubles. All are agreed that the Troubles does include Bloody Sunday, Bloody Friday, Internment without trial, the suspension of the unionist-dominated Stormont Home Rule government, the campaigns of violence by the various paramilitary organisations, including the Dublin and Monaghan Bombings, the La Mon bombing, the killing of Lord Mountbatten and his family, the assassination of Sir Christopher Ewart-Biggs, the then British Ambassador to the Republic of Ireland, the attempted assassination of Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher and most of her cabinet in the Brighton hotel bombing, the assassination of Airey Neave and the attempted assassination of John David Taylor, the Enniskillen and Omagh bombings, the hunger strikers in the Maze prison, the creation of the Peace People organisation (which won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1976), the splits in the IRA and ultimately the Belfast Agreement.
Deaths_in_The_Troubles_by_area.PNG
| Contents |
Overview
The origin of the states
The origins of the Troubles are complex. What is clear is that its origins lie in the century long debate over whether Ireland, or part of Ireland, should be part of the United Kingdom. In 1920, after widespread political violence, the Government of Ireland Act partitioned the island of Ireland into two separate states, one of which was Northern Ireland. According to the majority of unionists, Northern Ireland, which remained a self governing region of the United Kingdom, was governed in accordance with "democratic" principles, the rule of law and in accordance with the will of a majority within its borders to remain part of the United Kingdom. Nationalists however saw the partition of Ireland as an illegal and immoral division of the island of Ireland against their will, and argued that the Northern Ireland state was neither legitimate nor democratic, but created with a deliberately designed unionist majority. Each side had their own soundbites to describe their perspective. Unionist Prime Minister of Northern Ireland Lord Brookborough talked of a "Protestant state for a Protestant people", while a later Republic of Ireland taoiseach (prime minister) Charles Haughey called Northern Ireland a "a failed political entity".
The 'four communities'
Four overlapping segments exist within Northern Ireland. The majority of the Protestant community are generally called Unionists and commit to supporting political parties like the Ulster Unionist Party (known for part of the 1970s and 1980s as the Official Unionist Party) or the more militant Protestant Democratic Unionist Party. The larger segment of the Catholic community are generally called simply Nationalist and supported at various times the Nationalist Party and since the 1970s the Social Democratic and Labour Party. Both communities had smaller, more radical elements who supported at various times what one IRA strategist called the "armalite and the ballot box" (ie, a combination of electoral politics and violence when necessary). More radical elements within the unionist community came to be called Loyalists while radical nationalists came to be described as Republicans. Each of the radical groups produced their own paramilitary organisations like the Provisional IRA, Official IRA, Continuity IRA, Real IRA, Irish National Liberation Army etc (republican), and the Ulster Defence Association, Ulster Freedom Fighters, Red Hand Commandos etc (loyalist). Most such groups had their own political organisations, while some of the groups had overlapping memberships. While the various political movements claimed to speak on behalf of the 'majority of the people', electoral votes throughout the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s returned majorities for Nationalist and Unionist parties at the expense of Republican and Loyalist ones, though the latter two did achieve occasional successes, notably the election of MPs in the constituencies of West Belfast and Fermanagh & South Tyrone. At its electoral highpoint during the troubles, in the 1981 Republic of Ireland general election, it won two seats out of one hundred and sixty six in parliament. Sinn Féin's major electoral successes only followed the ceasefire of the IRA in the 1990s.
Religion and class
For the most part a clear divide exists in terms of religion and some times a left-right divide between the various communities. Most though not all Protestants are Unionists, while most though not all Catholics are Nationalists. While the mainstream organisations representing Nationalists and Unionists tended to be quite conservative, more politically and religious radical groups emerged associated with Republicans and Loyalists, with Sinn Féin adopting a Marxist perspective of the 'Irish problem', defining it in terms of "class struggle". Loyalists in the 1970s even advocated forms of an "independent Ulster" which they compared to the apartheid-style regimes of Rhodesia and South Africa, in which one community's dominance could be ensured.
Except for Unionists, all other segments argued that the Northern Ireland of the 1960s needed change. Moderate Nationalists in the Civil Rights movement, under figures like John Hume, Gerry Fitt and Austin Currie advocated an end to the gerrymandering of local government wards to ensure Protestant victories on minority votes, and the end to discrimination over access to council housing. They pressed for wide reforms, whereas Unionists saw "concessions" as part of a process whereby nationalists would bring down Northern Ireland and force Irish unity. Republicans adopted a more violent approach to force more radical change, while Loyalists stepped up their violence to oppose it.
The Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC), the police force in Northern Ireland, was largely, though not totally, Protestant for a complex series of reasons. Catholics did not join in the numbers expected by the British when the force was first created. Those that did reported a 'hostile to Catholics' working environment, in which Unionist and Protestant organisations like the Orange Order and the Ulster Unionist Party had undue influence. Those Catholics who did join were often targeted as traitors by the various IRAs. Yet some Catholic police officers did play a part in the constabulary. One served as Chief Constable, while the current leader of the Social Democratic and Labour Party, Mark Durkan is himself the son of a Catholic RUC man.
The lack of Catholic officers was augmented by the role of constabulary played in policing, which involved, as is generally the case with policing, the maintenance of the status quo. The result was that critics of the Unionist and Loyalist communities saw the police force as the "Unionist police force for a Unionist state". Unlike its sister police force in the South, An Garda Síochána, which was mainly composed of ex-IRA men, the RUC failed to establish cross community trust, with each community blaming the other or the RUC for failings in policing.
A policing review, part of the Good Friday Agreement, has led to some reforms of policing, including more rigorous accountability, measures to increase the number of Catholic officers, and the renaming of the RUC to the Police Service of Northern Ireland to avoid using the word "Royal".
Timeline
to be completed . . .
Deaths related to conflict (1990-2004)
Number of deaths listed as "conflict-related (uncertain if conflict-related)" ( [1] (http://cain.ulst.ac.uk/issues/violence/violence.htm)).
| Year | Deaths |
|---|---|
| 2004 | 2 (2) |
| 2003 | 10 (2) |
| 2002 | 11 (4) |
| 2001 | 15 |
| 2000 | 19 |
| 1999 | 8 |
| 1998 | 53 |
| 1997 | 21 |
| 1996 | 17 |
| 1995 | 9 |
| 1994 | 60 |
| 1993 | 84 |
| 1992 | 85 |
| 1991 | 94 |
| 1990 | 76 |
Significant groups
Some significant groups are:
Nationalist or Republican political parties
- The Social Democratic and Labour Party (SDLP)
- Sinn Féin (President Gerry Adams) - This party has been described as having an "insight into the thinking of" the republican paramilitary group, the Provisional IRA.
Unionist or loyalist political parties
- The Ulster Unionist Party
- The Democratic Unionist Party (Leader Ian Paisley)
- The Progressive Unionist Party (Leader David Ervine) - This party has been described as having an "insight into the thinking of" the loyalist paramilitary group, the UVF.
- The UK Unionist Party (Leader Robert McCartney)
Other parties
- The Alliance Party of Northern Ireland
- The Northern Ireland Women's Coalition
- The Natural Law Party
- The Conservative Party
(The Labour Party does not organise in Northern Ireland. The Liberal Democrats are associated with the Alliance Party.)
Republican paramilitary groups
- The Provisional Irish Republican Army
- The Real Irish Republican Army
- The Continuity Irish Republican Army
- The Irish National Liberation Army
(See Irish Republican Army for a discussion of how some of these are related).
Loyalist paramilitary groups
Bloody Sunday
The Bloody Sunday in 1972 was one of the key events during The Troubles. From 1971 until 1975, under the Special Powers Act there was Internment (see Long Kesh).
Current situation as of 2004
Currently, the governments of Ireland and the United Kingdom are working together closely to seek a solution and have been doing so for some time. It is widely held by many in both Britain and Northern Ireland that The Troubles came to an end in the mid-nineties with the various paramilitary cease-fires that were established. The period that came after The Troubles was the Northern Ireland peace process, the Good Friday Agreement.
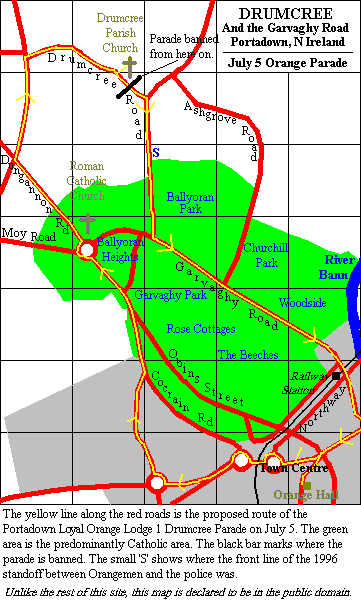
There are however continuing inter-communal tensions that tend to arise in particular during the "Marching Season" when Nationalists try to prevent Loyalists marches, held to commemorate William of Orange's victory in the Battle of the Boyne, through their neighbourhoods. This has been ongoing for at least a century. One particular flashpoint that has caused repeated strife is the Garvagy Road area in Drumcree.
It is also reported that punishment beatings by IRA related groups continue. In response, the UUP recently called for the Provisional IRA to be disbanded. Also of note is the recent internecine feuds within individual Loyalist paramilitary groups and between separate Loyalist paramilitary groups .