The Crossing
|
|
The Crossing is a term used in Egypt to refer to the west to east crossing of the Suez Canal by the Egyptian army at the start of the Yom Kippur War in 1973. It is also a term used by some Israelis to refer to the east to west counter-attack crossing of the Suez Canal by the Israeli army led by General Ariel Sharon later in that war.
New Egyptian president Anwar Sadat's regime was quite unstable and threatened by student demonstrations. They were unable to force through economic reforms that they felt were necessary to Egypt's survival.
In an attempt to restore Egyptian morale and secure the regime's position President Sadat decided to attempt to defeat Israel on the battlefield. Egypt had, for many years, suffered repeated defeat at the hands of the Israelis, most dramatically in the Six-Day War of 1967 where much of the Egyptian military had been destroyed and the Sinai peninsula across the Suez Canal had been taken by Israel.
President Sadat hoped to overwhelm the Israeli forces stationed there. His Soviet advisors thought otherwise and argued that it would take many days of fighting and a 50% casualty rate for Egypt to capture the canal, but he decided to proceed anyway.
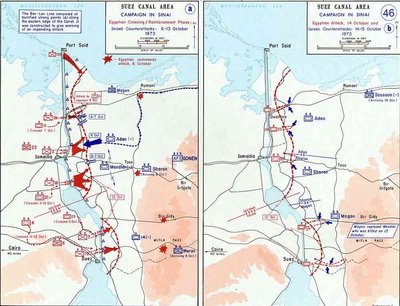
Egypt, in cooperation with Syria, launched the attack on October 6, 1973. Initially, it was a spectacular success. Within hours over 80 000 Egyptian soldiers crossed the canal. The Israelis had constructed a massive line of fortifications along the canal called the Bar Lev Line, which they considered impregnable. The heart of these defences were massive sand banks with a series of 43 manned installations. The Israelis had calculated that blasting through the sand barriers would take several hours, however the Egyptians solved this problem by using pressurized water to quickly erode the hills. The Israeli's back-up plan had been to redirect the nearby oil pipeline into the canal and set it alight. However, the night before Egyptian saboteurs had managed to disable the pipeline. In the initial attack only 200 Egyptians lost their lives. It was the first Arab victory over the Israelis in a generation. Behind the initial defensive line the Israelis had a large armoured reserve. These were immediately dispatched to contain the breach. However they were sent without air support and the tanks were picked apart by the anti-tank guns the Egyptians had rushed across the canal. The Egyptian forces rushed north into the Sinai.
After the assault Egyptian forces dug-in and tried to hold defensive positions in the Sinai. This proved unsuccessful because Israeli forces forced them to either retreat or surrender in the northern areas near the canal, and in the southern areas, under General Ariel Sharon the Israelis were able to counter-attack and cross the Suez Canal on its western bank into Egypt's heartland and head for its capital Cairo. This was the first time in history that the IDF had waged war on African soil. President Sadat almost lost his gamble. Only because of threats from the Soviet Union to mobilize its forces, and the arguments of the UN and the United States, did Israel stop its march on Cairo and accede to negotiate with Egypt.
Egypt's crossing had achieved President Sadat's aims, although in somewhat unexpected ways. It had forced the two superpowers to once again focus more intensely on the Middle East. Egypt's initial short-term victory also greatly reinforced President Sadat's domestic position. For the rest of his life he was referred to as "The Hero of the Crossing," and this status let his often corrupt and incompetent regime persist until 1981. The attack, combined with pressure from the United States, also brought Israel to the negotiating table and in 1977 the Camp David Accords, a comprehensive Israeli-Egyptian peace treaty, was signed, which among other things saw the Sinai eventually returned to Egypt in return for Egypt's official recognition of the State of Israel and the establishment of normal diplomatic relations with Israel, and a commitment to live in peace with the Jewish state.