Terpene
|
|
Terpenes are a class of hydrocarbons, produced by many plants, particularly conifers. They are major components of resin, and of turpentine produced from resin. The name "terpene" comes from "turpentine".
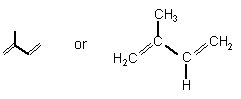
Terpenes are derived from isoprene C5H8 units and have the basic formula of multiples of it, i.e., (C5H8)n. This is called the isoprene rule. The isoprene units can be arranged in a linear way or forming rings. One can consider isoprene as one of nature's preferred building blocks.
Myrcen.png
Terpenes can be classified according to the number of isoprene units that they contain:
- Monoterpenes, C10H16, 2 isoprene units
- Sesquiterpenes, C15H24, 3 isoprene units
- Diterpenes, C20H32, 4 isoprene units
- Triterpenes, C30H48, 6 isoprene units
- Tetraterpenes, C40H60, 8 isoprene units
- Polyterpenes with a large number of isoprene units
Cadinene.png
The important plant photosynthetic pigment carotene is a tetraterpene. Rubber is essentially a polyterpene. Other important terpenes include:
If terpenes are further modified, for instance by adding hydroxyl groups or moving or removing a methyl group, the resulting compounds are called terpenoids. (Some authors also call these compounds terpenes.)
External links
- Institute of Chemistry - terpenes (http://www.chemie.fu-berlin.de/chemistry/oc/terpene/terpene_en.html)
- Structures of alpha pinene and beta pinene (http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iubmb/enzyme/glossary/pinene.html)de:Terpene