Talk:Astrology
|
|
| Contents |
What astrologers "don't know" about the span of each constellation
The "boundaries" of each constellation were decided in 1930, so seeing as to how astrology is thousands of years older than that, the argument that "they don't know" these totally modern, artificially drawn boundaries is completely bogus. I'd edit it out but I'm afraid my dial-up connection would cut off at least half of this humonguous article.Doovinator 00:46, 19 Feb 2005 (UTC)
- Why would you edit it out? I assume you're talking about the part in The case against astrology. Since people actually use that as an argument against the usefulness of astrology, it's our job to document that as part of The case against.
- Also, you complain that the modern boundaries are "artificially drawn". Firstly, the ancient boundaries were artificially drawn too. Secondly, we call the same set of stars "Virgo" that we did back then. If the sun is actually inside that group of stars for 44° of arc, how is that bogus? I can't vouch for the actual arc lengths, but the argument sounds logical to me. Foobaz·✐ 01:49, 19 Feb 2005 (UTC)
- In the original scheme the "boundaries" came first, like longitude lines. The constellations were the stars which happened to be in "x" area of the sky, not the other way around. It's as if we'd been defining "America" as "a land mass between 30 and 165 west longitude", and a geographical commission came along and declared the actual boundaries to be thus-and-so and therefore everyone who came before is "wrong". The definition has changed, not actual boundaries. All astrologers are fully aware of the "boundaries" of the constellations as defined in 1930, but this has nothing whatever to do with astrological "signs". If the sun is in the area of the sky where it habitually resides in the last month of summer, then it's in the astrological sign "Virgo". After it has passed through that area, the days start getting shorter and it's in the astrological sign "Libra". The stars are convenient markers for these areas of the sky, but nothing more. Astronomy is a completely different science, and has a different jargon.Doovinator 22:17, 19 Feb 2005 (UTC)
- Doovinator is right. Astrology divides the zodiac in twelve equal parts, and this matches roughly with the existing constellations (not through coincidence). The one legitimate point of dissenssion within the astrological community is whether to stick to a calendar zodiac or to follow the precession of the equinoxes (which leads to nearly a full sign's worth of difference nowadays). The term "sign" is also used to mean 30° (360° divided in 12).
- Urhixidur 03:10, 2005 Feb 20 (UTC)
This discussion is very confused. Nobody seem to "get it." Here are a few simple facts: The zodiac used by Western astrologers has been unchanged since at least ancent Greece, when it was agreed among Western astrologers that the ecliptic (which has nothing to do with stars millions of light-years away) is the basis of the twelve zodiacal divisions. Not the constellations! Critics of astrology persist in insisting that the "constellations" should be the basis of the zodiac, but they are not. Astrology uses a local system, namely, a system based entirely on our own solar system. The zodiac used in astrology is the relation between the earth and the sun. It is twelve evenly divided sections of the ecliptic beginning at the Vernal Equinox (beginning of the sign, not the constellation, Aries) when spring begins and the days and nights are pretty evenly divided (hence the name Equinox) and extending to the Summer Solstice (beginning of the sign, not the constellation, Cancer) when the days are longest and nights shortest in the Northern Hemisphere and then to the Autumnal Equinox (beginning of the sign, not the constellation Libra) when again there is an equality and then on to the Winter Solstice (beginning of the sign, not the constellation, Capricorn). All this is very clear. It is only the names of these divisions which are confusing because there happen to be constellations of stars with the same names, now out of synch with the signs although they were in synch with them millennia ago, presumably when they were first named. But when it is realized that the twelve ecliptical divisions are really twleve even divisions of the orbit of the earth around the sun, based upon the entirely measurable seasons of the year, we see that astrology is local, centered in our solar system. The twelve signs used by Western astrologers are twelve "fields" within the earth's orbit. Why they work, no one knows (nor does anyone know the ultimate "why" about much of anything in science), but it is dishonest to imply that they must rely upon remote constellations to have any efficacy. I myself decided upon them, rather than the so-called "sidereal" zodiac based on the constellations, after long and careful observation, comparing the positions of planets and the sun in the two systems.
List of Astrologers
I noticed this page is getting big; it will surely expand — it needs to be reworked from top to bottom, a lot of things haven't been said, don't know if I have the energy for it, but together I'm sure we will — so I've moved the list (which should also be expanded) to List of astrologers. I'm not very fond of lists, since Categories are a much more organized way of presenting the same skeleton, but they have the advantage of serving as a checklist for articles that need to be written, whereas Categories only include articles that have already been written. Ideally, though, the better list will be Category:Astrologers. At any rate, this sets "Astrology" on the same footing as "Physics" or "Medicine", which don't list every doctor or physicist on the article page; it does astrology no service to look like we're saying "See, look how many people were astrologers." — Bill 12:36, 23 Oct 2004 (UTC)
PROOF for Isidore of Seville
Press CONTROL + F and search for "Seville"
- Though Seville eventually came to reject natal astrology, he was always a major proponent of medical astrology/mundane astrology as is laid out in these pages:
- [1] (http://www.nickcampion.com/nc/history/articles/astrology_b4_the_normans.htm)
- [2] (http://explorers.whyte.com/astrol.htm)
- [3] (http://www.new-library.com/zoller/features/rz-article-medicine.shtml)
- [4] (http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/08186a.htm)
"The "De natura rerum" a manual of elementary physics, was composed at the request of King Sisebut, to whom it is dedicated. It treats of astronomy*, geography, and miscellanea. It is one of Isidore's best known books and enjoyed a wide popularity during the Middle Ages." -- previous page newadvent.org
* As any educated person knows there was no distinction between astrology and astronomy in those days -- it just does not list it as astrolomy, that is the mixture of astronomy/astrology.
- [5] (http://gfisher.org/chapter_9.htm)
"In his later life, Pierre d'Ailly was much concerned with defending astrology/astronomy from charges that it was inconsistent with Christianity. As a basis, he took the attitude endorsed long before by Isidore of Seville (c. 560-636) that one can distinguish between natural astrology* and superstitious astrology, and that it is the former which is consistent with Christianity, while the latter is not."
* Natural astrology being medical astrology and mundane astrology which was used and written about widely during his time, not the use of astrology for personal/predictive reasons, which many of the relgious believed would be somehow tampering with God's will.
- [6] (http://www.isidore-of-seville.com/astdiv/)
- I see no proof in any of this, nor do CAPITAL LETTERS make it one....
- Your main thesis is flawed: "any educated person" — thank you — and see my transcription of Isidore (http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Isidore/home.html) — knows no such thing. The line was vague and lots of people crossed over it in one direction or the other; but in general, "natural astrology" refers to what we call astronomy, "superstitious astrology" to predictive astrology. I'll concede to you the very grey area of what we now call meteorology and where it impinges on physiology: the ancients, almost uniformly, did view the weather as having something to do with the farther heavens, and there was general agreement that weather affected physiology (see for example Vitruvius on the siting of towns (http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Vitruvius/1.html#4) — where clicking on the section numbers sends you to the Latin if you need it).
- And before we go any further, in case you were tempted, it is pointless dismissing me as personally against astrology in any way. I've spent a good deal of time studying it, learned how to cast a chart 30 years ago, for a while even making some money casting charts, have a fair library of astrological material, and view astrology as valuable both in itself as a psychological descriptor and as part of the arsenal of "any educated person" in the fields of literary criticism or Antiquity. I've done statistical studies on some facets of astrology (one of them coming up in favor of a correlation between being an organist and having Mars conjunct Uranus: at 3σ level of significance!) I am still — as you can see — fascinated by the subject; see for example my chart of Nero (http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Suetonius/12Caesars/Nero*.html#noteA).
- Now that we've got that out of the way.... Of your 6 refs, two are quite irrelevant: #4 is the Catholic Encyclopedia on Isidore, breathing not a word about astrology (which I'm perfectly willing to admit means nothing, given the recent opposition of the church to astrology: 19th-century and very straight-laced; but still, there is nothing about astrology there, for whatever reason). #6 is merely the astrology section of Tim Spaulding's site, which he named "Isidore-of-Seville" in honor of the great man because he was a polymath or an encyclopedist. Nowhere there is Isidore brought up in connection with astrology.
- #1, #2, and #5 are very tertiary sources, all probably paraphrasing the same secondary source, notice the very similar turns of phrase; none of them states unambiguously that Isidore was an astrologer. #1 views Isidore — again, for what that's worth, these are people like you and me writing modern opinions — as against astrology, not for it. #2 mentions Isidore incidentally except for repeating that he was in favor of medical astrology. #5 is the most incidental repeat of the same thing.
- #3 is better, since it actually quotes Isidore, even kindly footnoting the reference, although not linking it: IV.13.4 is here (http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/L/Roman/Texts/Isidore/4*.html#13.4) — on my own site, natch; if Isidore's astrologer-ness boils down to that, it's very weak indeed.
- What is needed is some kind of proof that Isidore wrote about astrology per se, or practiced it. Again, this has nothing to do with being for or against astrology, or for or against Isidore, or Roman Catholicism: just a concern for facts. We wouldn't call Vanna White an "American politician" because she must surely have made some loose political statement like the rest of us all — nor even more politically active actors; we shouldn't call Isidore an astrologer if he wasn't one. — Bill 11:47, 23 Oct 2004 (UTC)
- Right. The issue is whether or not he was an "astrologer", did he do astrology-predictions or alchemy and all the rest of it. Educated people do not know that astronomy and astrology were one in the same. Humanity has been looking up at and studying the stars from the very beginning: astronomy is our oldest science. Many Middle Ages astronomer's were definately not astrologers, they considered astrology to be not in keeping with their Christian/Islamic/Jewish teachings. They were studing "the heavens" as a way to understand the universe of their God. Isidore wrote an encyclopedia, and in that encyclopedia, he tried to list all the endevors's of humanity, just like Wikipedia does today. What one may find in the Etymologiae concerning astrology is not proof that he was an astrologer: it simply does not fit his job description: it isn't what he did, (at least, not so far as history has recorded). func(talk) 20:35, 23 Oct 2004 (UTC)
Neo-Platonic astrology
Neo-Platonic astrology as a study case
Moved the following from the article as it is too much of an essay style for an encyclopedia. Someone needs to re work this into a history of the idea. Lumos3 23:56, 15 Nov 2004 (UTC)
Neo-Platonic astrology as a study case The case of Platonic and Neo-Platonic astrology should be of particular interest. Here one can easily observe both the strong motivations towards the establishment of an astrological science, and the collapse of the bulk of these motivations in the post-Galilean world.
We shall begin by following a line of thought that was very strong in many parts of the classical world. So strong, it was the reason for the deportation of Anaxagoras from Athens (he was advocating that the stars were nothing but “hot stones in the sky”), and the Epicureans made the fight against this view the main point of their moral philosophy.
So, imagine you live in a society with a technology that is less than modern: no cars, planes, etc. The only things you would observe that have the capacity to move on their own are living things. Hence only living things have what Aristotle calls (potential) "innate movement". But all living things decease (given enough time). All? Well, look at the sky - there you will find heavenly bodies moving perpetually in well-ordered paths. If living things are the only candidates for self-induced movement, then the heavenly bodies must be alive. They are also perpetual, hence immortal. They also seem to be moving in a nice circular fashion; hence they must be highly intelligent sentient beings (circles being the most perfect of geometric forms). What would you call a super-intelligent, immortal sentient being?
A god.
So the heavenly bodies are gods. That's well enough. But there are two other things you should notice about these gods:
- 1 They seem to be unbound by earthly physics: they float high above, unaffected by gravity, and they also move in circular motion - a type of motion that is not very common down here on earth. So the rules that work in the heavens are not the same as the terrestrial laws of physics.
- 2 We already know that the heavens directly affect our lives. Think about the weather: rain, snow, light, heat, cold, clouds... the different seasons... all these things govern our lives (esp. if we live in an agricultural society).
Let us sum things up. We have seen that:
- Heavenly things govern life here on earth.
- Heavenly things do not abide by earthly laws.
- Heavenly things are gods.
It should be strongly emphasized that this view holds strongly as well in monotheistic cultures, and is in fact firmly embedded into classical Christianity, Judaism and Islam. Although they are no longer deemed to be actual gods, the heavenly bodies are still highly regarded in classical monotheistic religious philosophies, and are often looked upon as angels or some other instrument of the one god.
It is very easy to see how Astrology and Alchemy stem from this view. It would be only rational to try and consult the heavenly bodies - concerning almost everything – from the conception of babies to the signing of political and commercial treaties – hence Astrology. It would also be very tempting to utilize the forces governing the heavens down here. If you could “make” Mars work for you, you would be free from the confines of terrestrial physics – hence Alchemy.
It is also very easy to see why the Galilean views were so intimidating in the eyes of many renaissance scientists and policy-makers: Galileo’s observations were deadly to the dichotomy between earth and the heavens. He was showing that the stars were merely natural phenomena, rather then super-natural super-intelligent perpetually unchanging beings.
So, in the classical world, the case for astrology was almost trivial. The connections between heaven and earth are everywhere you look, and the heavens are clearly something supernatural. In the post Galilean world, however, advocates for Astrology face an excruciating task. The easy-to-observe influences of heaven are dealt with within the framework of sciences e.g. Meteorology and Solar Astronomy. Further influences are no longer deemed trivial, and are usually very hard to show.
Remarks in the last paragraph
It is very easy to see how Astrology and Alchemy stem from this view. It would be only rational to try and consult the heavenly bodies - concerning almost everything – from the conception of babies to the signing of political and commercial treaties – hy and astrology were one in the same. Humanity has been looking up at and studying the stars from the very beginning: astronomy is our oldest science. Many Middle Ages astronomer's were definately not astrologers, they considered astrology to be not in keeping with their Christian/Islamic/Jewish teachings. They were studing "the heavens" as a way to understand the universe of their God. Isidore wrote an encyclopedia, and in that encyclopedia, he tried to list all the endevors's of humanity, just like Wikipedia does today. What one may find in the Etymologiae concerning astrology is not proof that he was an astrologer: it simply does not fit his job description: it isn't what he did, (at least, not so far as history has recorded). func(talk) 20:35, 23 Oct 2004 (UTC)
Article is nearly 32K
A warning has appeared when the edit box is opened that this article is now nearly 32K bytes long and needs to be split up into smaller articles. I suggest that the Cases for and against sections plus the Astrology and science section be moved into a new article called something like - The validity of astrology . A short summary of this would remain in the main astrology article. Any comments Lumos3 17:13, 3 Dec 2004 (UTC)
- Make sub-articles. ConfessedSockPuppetJunior 06:29, 14 Dec 2004 (UTC)
- Observing that many sections were exact duplicates of things in other articles, I deleted a lot of sections and made them into links saying "See (such-and-such)". That takes care of the 32 KB warning. Hope these edits aren't too drastic. I just thought it would be better not to have the exact same information duplicated in more than one article. --Slartibartfast 01:05, 8 Feb 2005 (UTC)
unclear text
what does this mean? I cant make sense out of it. do they influence or not?
- Many of those who practice astrology believe that the positions of certain celestial bodies either influence, or correlate with but do not influence, people's personality traits, important events in their lives, and even physical characteristics.
Knightt 21:46, 17 Dec 2004 (UTC)
- Opinions differ. Most reasonable people believe heavenly bodies neither influence nor correlate with mundane events. Some astrologers believe they correlate with human activities because they influence them; some other astrologers believe they correlate with human activiities for some other reason. - Nunh-huh 01:55, 18 Dec 2004 (UTC)
The case against Astrology - Distance + life prediction
I'm tempted to just delete the recent edits to the case against astrology, as both points are based on a misunderstanding of astrological practice, and I'm not sure that scientists make these criticisms. Before you accuse me of bias, I am not an astrologer, and I do not believe in astrological practice. That having been said, let me address the two points. The first point - distance is not taken into account - is invalid. While the typical chart has no indication of distance built in, the different aspects are given degrees of importance. For instance, many astrologers believe that the Sun is the most major aspect, and the moon is the second most major aspect. The second point - about a life predictive system - is also misguided. No astrologer makes the claim that the predictions of astrology are immutable. In fact, astrologers say that astrology describes influences, which if properly understood can help the person being analyzed change the future! These criticisms are strawmen, and I think it does the argument against astrology a disservice to keep them. I will be deleting them in a few days unless someone can convince me otherwise. Cardshark
- Hello. Some comments. Yes some specialists in paranormal stuff do this kind of comments. (See French book Henri Broch - Au coeur du paranormal). About distances. Indeed astrology mentiones some aspects related to distances. But, and that is the point, in such a case it means distances matters for astrologer and this criteria must be mentioned for all objects officially considered in astrology (it is not the case) but also... plainly all objects in universe. Mentionning one or two (or 10000) distances is not enough. To be precise all the signes would have to be charted in terms of distances for each of the stars making them up. In other word this point is a consistency one. About life predictive system: No astrologer makes the claim that the predictions of astrology are immutable. The very point. Either your are predicting something whatsoever and it has to be observable as predicted, or your are just speculating and you can be ignored. Actually the problem is mixed up in your comment: the concept of prediction is misunderstood in astrology (and many other domains). Astrologer hides behind a smoke screen the fact that their predictions (whatsoever: facts or influence which is wordable as probability) are not observable, therefore even less "verifiable" and utlimately are not prediction at all. I think those two points are rather informative because they are true, verifiable, and unlike for example precession of the equinoxes, any one can understand them. So no: certainly not delete! Rewrite if you please for sure. Gtabary 11:33, 17 Jan 2005 (UTC)
- You said - " The very point. Either your are predicting something whatsoever and it has to be observable as predicted, or your are just speculating and you can be ignored. " I'm sorry, but with all due respect, this is a ridiculous argument. For example, a geneticist may be able to tell you that you have a 10% chance of dying of a heart attack based on your genetic makeup, but that by changing your eating habits, you can lower your risk of that heart attack. Is the prediction useless because it is not immutable? Obviously not. The prediction is very helpful because by altering your lifestyle, you can affect your life in a positive way. Furthermore, the argument is a straw man defense because it argues against a position that astrologers do not advocate. It doesn't help the argument against astrology at all, rather it weakens it. Unless you can demonstrate that astrologers hold this view, and that some sort of qualified person such as a scientist argues against astrology based on this view, it has no place in the article. I'll give it a couple more days for further discussion, and then I will remove it from the article. Cardshark
- I am going to prove you incorrect, will you feel ridiculous ? (Ok just teasing there :-) . Probably better not to use ridiculous.) A geneticist may be able to tell you that you have a 10% chance of dying of a heart attack and, that's the catch, those 10% are repetedly observable at the scale of a population, over a 50 years period, statisticaly . Summary: a probabilistic prediction is done AND the prediction is observable. That's where para-science life-prediction predictions fails: Even with long time and an important sample to analyse, none of the predictions are observable. Astrologer do pretend to have a kind of prediction system be it absolute or probabilistic. If it's neither absolute nor porbabilistic, that's not prediction but speculation. That is technically the answer to your question. Note the orginal point of the paragraph is still unchanged and valid: knowing the future is meaningless if you can't change it; knowing the future is meaningless if you can change it because then you don't know the future; not knowing the future is... not knowing the future. I don't understand the use of straw man: Please explain me what else astrology pretend to do but to kind of predict (even only probabilisticaly) the future ? I'll suggest an other wording of the paragraph in some time. Gtabary 11:42, 20 Jan 2005 (UTC)
- Well, saying "If they believe this, they're wrong because.... and if they believe that, they're wrong because..." is the classic example of the straw man argument. Click the link, and read the section labeled "rhetorical use", it gives a thorough definition. Furthermore, I stand by the analogy that I made to genetics. Your paragraph said that either there was no point of knowing the future because it was immutable, or the prediction was just speculation and therefore useless. If an astrologer said you have a tendency to be obese, and you should watch your diet, that is not a useless prediction. If your argument is that astrology is not a science, and therefore it's predictions are wrong (and therefore useless), that topic is very well covered elsewhere in the article, and your paragraph was redundant (and less well-reasoned than others on the page). Furthermore, since astrologers do not claim to make immutable predictions, at least half your argument was a straw man. (sign please)
(Reset indent). Hi again. I read the straw man article. Interesting. Though unlike what you think orginial paragraph do not qualify as a straw man argument. Here is why.
What orginal paragraph does is quite different: It takes what astrology is reported to be - Many of those who practice astrology believe that the positions of certain celestial bodies either influence, or correlate with but do not influence, people's personality traits, important events in their lives, and even physical characteristics. which the single point for strology to be - and refutes it. Name it future prediction, probablities, influences it boils down to the same: predict somehow, something. There is no presenting whith (cf straw man) distortion, portion, fiction. Therefore there is no straw man stuff. End of story.
Now about the if a then wrong, or b then wrong and a = non b; then all wrong invalidity and "classicality". Sory but if a is wrong as well as b is, well, all is wrong. And in our case indeed both are wrong.
The analogy with genetics do not stand because... The geneticist do not have to observe his 10%, because the 10% are the result of observations. In other word the geneticist do not have to prove existance of facts for the facts are the base of the affirmations. Astrology still have to exibit even only some facts to back up affirmations, or to be observable after affirmations. Shorthand: no need to prove what's already proven, plenty of need for what's never been.
It is very possible that other paragraphs cover better than my contrib, some aspect of this. Though I did not read this interesting paradox elsewhere, which stimulate thinking on a fairly correct ground.
I was thanking about a milder wording like: A paradox seams to arise in life predictive system: if one's able to know the future, it's thanks a degree of immutability. Depending on this degree one can wonder what is the point in knowing such future if it's not changable. In the extreme, a completly knowable future would leave us with no interest in knowing it at all.
Don't forget to sign comments. :-)
Gtabary 16:01, 20 Jan 2005 (UTC)
- I tried to make my last edit more balanced, shortend, including your main point, immutability and is there more to stimulate thoughts as opposed to claim invalidity. Gtabary 14:31, 25 Jan 2005 (UTC)
Sorry, but this is extremely long winded. The case against astrology is that there is no scientific basis for it. That is all that needs to be said in this section.
Combining "Skeptics View..."/"Case Against..." Sections
Okay, just had an edit reverted. I think we should combine these two sections or subsections, and do the same for "Astrologers View..." and "Case For..." sections as well.
This should make it easier for scientists here to make a short and convincing argument against astology without having to get into an edit war with people who disagree. This section could link to another article as well. The page if 35k and I think this section needs to be first on the chopping block.
- In view of the unwieldy size of this article I suggest that the Cases for and against sections plus the Astrology and science section be moved into a new article called something like - The validity of astrology . A short summary of this would remain in the main astrology article. - Reposted from section on articles size above.Lumos3 21:32, 23 Apr 2005 (UTC)
- I have just done the above, moved the entire discussion on astrology's validity to a new article, see Validity of astrology. In order to keep the balance of the main article I have added the robust warning on astrology from the 1911 Britannica astrology article to the introduction. Lumos3 22:56, 23 Apr 2005 (UTC)
- Nice. Can I go and fix that now please?? Dave 06:35, 24 Apr 2005
- Please do 219.162.148.31 , I agree it needs a lot of work to make the arguments on both sides logical. You might like to get a Wikipedia user name if you will be doing a lot of editing. There's no charge and you will be able to keep track of all your edits that way and build up a creditable record as an editor. Lumos3 11:13, 24 Apr 2005 (UTC)
The Planets
I notice there are no pages giving the astrological meanings of the planets. Something I hope to remedy, calling them Sun (astrology) etc, and them linking them to this article.Squiquifox 00:36, 1 Feb 2005 (UTC)
A horoscope for Wikipedia
The Wikipedia article states that the project went public on January 15 , 2001 - but doesn’t mention a time of day. Has anyone constructed a horoscope for the project? It would be interesting to see one posted here. Lumos3 20:29, 5 Feb 2005 (UTC)
- The history of Wikipedia article doesn't state a time of day either, but it mentions that the server was located in San Diego. I'm not sure what a "real astrologer" would use for Wikipedia's "birth chart", but I made an image of a chart for January 15, 2001 at 12:00 PM (noon) in San Diego using the astrology program Kepler. You (or anyone else) can do whatever you want with it. Also, if we ever find out a more definite "birth" time, I can make another one.
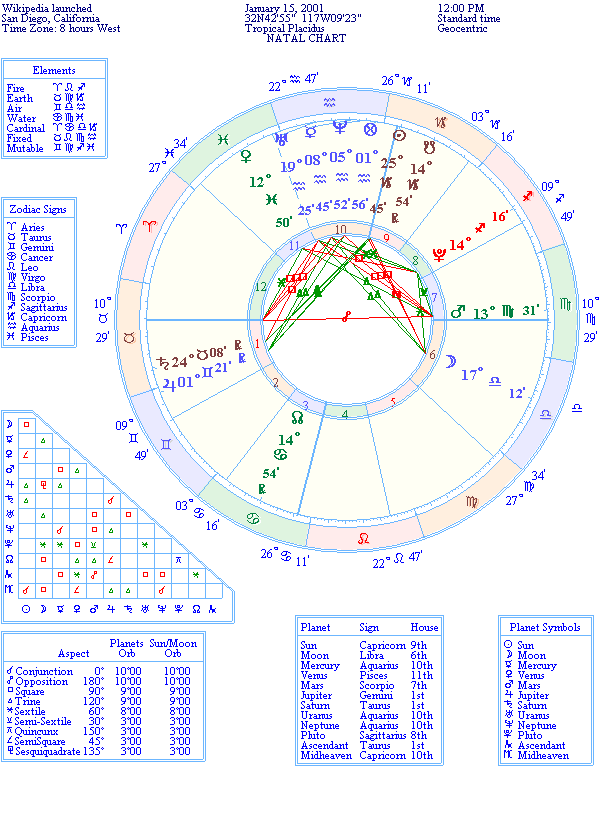
- --Slartibartfast 00:07, 8 Feb 2005 (UTC)
- Would any skilled astrology like to have a go at interpretation of this chart and post it here? Lumos3 21:44, 23 Apr 2005 (UTC)
Why I removed the "constellations of the zodiac and the parts of the body" section
This is because the signs in astrology are associated with so many tons of other things besides body parts - for instance, gemstones, metals, animals, plants, etc., etc., etc. - that I don't see any reason why the associations with body parts need to be singled out and spotlighted in the main article. --Slartibartfast 01:01, 8 Feb 2005 (UTC)
Free natal reports
I noticed that there were no free natal report links here , so I added them . I didnt find any good free Chinese & Jewish natal link . So still searching for it .farhansher
Explanation of restored sections
I discovered templates, and made a few, so that now, people viewing (for instance) the astrological sign keywords text will all see the same text - whether they're viewing it from zodiac, astrology, or astrological sign - and any improvements/edits to that text will affect all pages which contain it. More details, if desired, are on my Talk (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User_talk:Slartibartfast) page.
- --Slartibartfast 11:56, 9 Feb 2005 (UTC)
Numerology and Astrology
It says that "Zero is ruled by the planet Pluto, which gives it many transforming and regenerating qualities. It has a lot of depth and intensity, which makes it a transcendental number indeed." -- But 0 isn't a transcendental number at all.
Removed strange accusation of astronomers
I removed the suggestion that the constellations were redrawn to discredit astrologers. The 1930 convention had two main purposes: 1. Establishing one set of commonly agreed upon constellations. 2. Eliminating 'blank spaces' between constellations. This was done to facilitate astronomy, enabling astronomers to easily indicate a given sector of the sky. If there is any credible sources claiming otherwise, please link to them.
If the astronomers of 1930 wanted to discredit astrology that badly, they may have selected the far simpler course of merely pointing out that the signs of astrology bear little resemblance to the actual positions of heavenly bodies. --Spazzm 00:47, 2005 Feb 24 (UTC)
I'm going to remove the notion that the ecliptic didn't cross Ophiuchus before 1930, since it is clearly contradicted by this: Ophiuchus
The story seems to be that before 1930, the area that now only belongs to Ophiuchus belonged to two or more constellations. In order to formalize it, astronomers had to choose one. If they choose one of the astrological signs, they would avoid angering astrologers. If they choose Ophiuchus, one of the most important documents in astronomy, Kepler's "De stella nova in pede Serpentarii" (On the New Star in Ophiuchus's Foot) would still be meaningful to future astronomers. They would also honor Kepler and Ptolemy who first described the constellation over 1700 years earlier. It comes as no surprise that they acted as they did. --Spazzm 01:18, 2005 Feb 24 (UTC)
I removed some of the more blatant misrepresentations as well: Ophiuchus was intersected by the ecliptic before 1930. It is not a 'very small part' of Ophiuchus that lies across the ecliptic - the Sun is in Ophiuchus from 2005-11-30 to 2005-12-18, ca. 19 days. As a comparision it is in Cancer from 2005-07-21 to 2005-08-11, ca. 22 days. (According to Celestia). The constellations were not clear and agreed upon before 1930 - the area in question, that now belongs to the foot of Ophiuchus, belonged to more than one constellation. Ophiuchus was not extended, it was Scorpius that was diminished. --Spazzm 01:45, 2005 Feb 24 (UTC)
New articles on Jewish, Christian and Muslim views
Many Jewish authorities had views on astrology, especially Maimonides, but there is no systematic discussion on this issue. I thus am working on a new article, Jewish views on Astrology. My current sources include the Talmud (I own the Soncino version); the Jewish Encyclopedia, The Encyclopedia Judaica, the collected works of Rabbi Aryeh Kaplan, as well as other sources. I have now written text that includes the basis of Jewish views of astrology, based on mitzvot in the Torah, and it discusses the various ways in which these mitzvot have been interpreted. I then summarize the views of Nahmanides, Maimonides and Gersonides, and offer brief views from Reform and Conservative Jews, and from two Orthodox rabbis who have written on this issue, Rabbis Barry Freundel and Nachum Amsel. I will create the new article later tonight, and I hope we can bring in more sourced material and discussions. RK
We should begin a stub on Christian views of astrology, and Muslim views of Astrology. I know that astrology has been popular in many Christian communities over the past 2,000 years, and as such deserves serious discussion. (At the moment, I have no idea how astrology has been received in the Islamic world.) RK 18:19, Mar 2, 2005 (UTC)
Case for astrology? Text is very off-topic
I see that over time many proponents of astrology have added their views here, but I am truly puzzled by the section on the Case for astrology. It contains absolutely zero data for astrology, in any shape or form. The fact that tides affect many living organisms has nothing to do with astrology, stars, or anything supernatural. If there are actually people who use this as evidence for astrology, then they are using the word "astrology" in a way that has nothing to do with the contents of this article. The only "evidence" I have even heard of for astrology isn't even discussed in this article; that evidence is the first report on the so-called Mars effect, which has since been discredited. RK 20:41, Mar 13, 2005 (UTC)
- I'm not the right person add a pro-astrology section. There used to be a longer section, but it contained incoherent rambling, strange accusations and outright misrepresentations. It has been pruned down a bit since then, I'm glad to say. --Spazzm 23:47, 2005 Mar 13 (UTC)
- The section needs a better topic sentence to the effect that the gravitational influence of celestial bodies on the Earth may affect our perception of tides and theoretically our character. This is quite tenuous obviously. The only bodies that produce a tidal effect on the Earth are the Moon and Sun and of course astrology isn't limited to these two. Even if we accept tidal influence from other bodies you still have to make the leap and accept that this correlates to personality and life probabilities. I have read that statistically significant differences in life outcomes occur in people born at different times of year (likelihood of being in accident, obesity etc.) but this is much better explained by seasonal variation than astrology. Marskell 14:15, 17 Mar 2005 (UTC)
It seems plain to me that if astrology is real, then it is supernatural. Attempts to find scientific justifications for it are simply wrong-headed Pmurray bigpond.com 05:57, 9 Jun 2005 (UTC)
Rudolf Steiner
Hello Astrology Buffs,
I have included Rudolf Steiner's birth data in his article and was wondering if someone who has more know how and time than me would be kind enough to run it up on software and post the diagram on his article. I am worried that if it isn't done someone who poo poos astrology will take the information out. I had to search far and wide for that data, and it would be a shame if it was deleted.
Also, someone made a post that 0 is not transcendental. I beg to differ. If mankind had not discovered 0 then we would would not be nearly as progressed as we currently are technologically. If that is not transcendantal, I don't know what is.
Regards, --TracyRenee 22:17, 15 Mar 2005 (UTC)
PS. Sorry that I don't contribute more, but I have so much to do and so little time. I am currently studying for my accuntancy exams as well as working full time as well as pursuing my writing.
- Zero is not a Transcendental number: "[...] a transcendental number is any irrational number that is not an algebraic number [...]"
- Zero can't be transcendental because it's not irrational; it can be perfectly described by the sum of a finite number of fractions.
- If we accept that a transcendental number is any number that is necessary for our current level of technology, well then all numbers are transcendental. --Spazzm 00:45, 2005 Mar 16 (UTC)
Numerology and Astrology
Spazzm,
You obviously know much more about mathematics than I do. When I said that Zero is transcendantal, I was speaking metaphorically and did not know that there is an actual term called transcental to describe numbers. I stand corrected. Feel free to edit the word and use a word that you feel is more appropriate.
--TracyRenee 13:54, 17 Mar 2005 (UTC)
- Thanks, TracyRenee. I see that in the meantime the passage in question has been moved to a different article. --Spazzm 03:58, 2005 Mar 19 (UTC)
Removed quoted book review of Seymour's book
I removed the quoted book review because the legality of quoting almost the whole review is rather questionable. Also it was far too long. --Spazzm 03:57, 2005 Mar 19 (UTC)
this all seems very confused
surely an article about Astrology should mostly be concerned with history and the various methods used to determine predictions, rather than an elaborate and confusing argument about falsifiability and "pseudoscience"?
- Great idea. Since there are so many different traditions and methods in astrology, perhaps it would be best to have detailed discussions on subpages, e.g. Western astrology? --Spazzm 00:36, 2005 Mar 26 (UTC)
The "see also" section...
...is absurdly huge. "See also" is not intended to be a complete index to every topic related to this one; it should restrict itself to articles that notably contribute to the context of the topic (that is, things like anaretic degree are just too minor), it should not duplicate section article links (like astrology and alchemy), it should not mention topics that do not establish a relationship (tropical year) or are covered in the article itself (birthday through natal chart), it should not duplicate lists (people in list of astrologers don't need separate mention in the "see also", unless they were defining to the field, in which case they should be in the article to begin with).
A complete list of astrology-related articles is what Category:Astrology is intended to cover. In short: if you need a table to lay out the "see also" section, you're doing something wrong. Consider coalescing topics in new lists (I think List of astrological factors has merit).
I've weeded a lot, adding Category:Astrology or Category:Astrological factors to the linked article while I was at it. But there's just too much! Please help out in trimming the list down and properly categorizing the items. JRM 13:11, 2005 Apr 24 (UTC)
History mini-section
This small section includes a link to the "Jewish views" article, but I don't think that it's particuarlly noteworthy for this small section. I don't think that a significant percentage of people reading that section are interested in what Jewish people happen to think about astrology. Nor would that be an appropriate place to link to "Muslim views on astrology," or Hindu, Christian, Peruvian, etc. For now I'm moving the link to the "see also" section. At some point, someone may want to make a section, and possibly an article, on various culture's views on astrology, which could then link to all those sorts of articles. But at any rate, that sort of thing is only tangentally related to the history of astrolgy, so I'm moving it.
--Blackcats 22:11, 15 May 2005 (UTC)
Re-directs
I looked at this page two months ago and in stopping by it today I notice the bulk of material has been re-directed (history of astrology and validity of astrology). The page as it stands looks bad and reads bad. After the intro there is a series of series of choppy, meandering level 2 headlines. "Validity of astrology" particularly has little logical basis as an outside article and should be re-included here. I will re-merge this in a day or two unless someone has a good argument why not. Marskell 23:35, 19 May 2005 (UTC)
- See the discussion on splitting off the Validity of Astrology section to another page above (Combining "Sceptics View..."/"Case Against..." Sections). The article was over large and growing and was getting the 35K warning mesage. The idea was to keep the arguments in the Validity article and a concise description of Astrology in the main one and I think this is basically sound. I agree both articles still need a lot of work to improve them. Wikipedia's structure allows subordinate articles to be spun off in this way without loosing coherence. Lumos3 14:02, 20 May 2005 (UTC)
Astrology as a descriptive language for the mind
It might be intersting to point out that "star-signs" is probably the most widely used classification of personality types.
