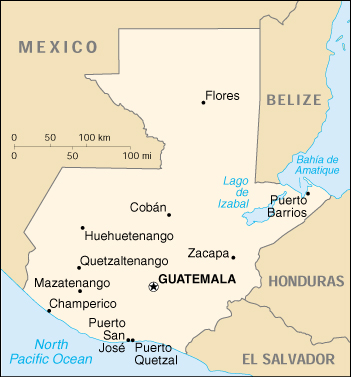
Geography of Guatemala
|
|
This article describes the geography of Guatemala.
- Location
- Central America, bordering the Caribbean Sea, between Honduras and Belize and bordering the North Pacific Ocean, between El Salvador and Mexico
- Geographic coordinates
- Template:Coor dm
- Map references
- Central America and the Caribbean
- Area
-
- Total: 108,890 km²
- Land: 108,430 km²
- Area - comparative
- Slightly smaller than Tennessee
- Land boundaries
-
- Total: 1,687 km
- Border countries: Belize 266 km, El Salvador 203 km, Honduras 256 km, Mexico 962 km
- Coastline
- 400 km
- Maritime claims
-
- Continental shelf: 200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
- Exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
- Territorial sea: 12 nm
- Climate
- Tropical; hot, humid in lowlands; cooler in highlands
- Terrain
- Mostly mountains with narrow coastal plains and rolling limestone plateau (Peten)
- Elevation extremes
-
- Lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
- Highest point: Volcan Tajumulco 4,211 m
- Natural resources
- Petroleum, nickel, rare woods, fish, chicle, hydropower
- Land use
-
- Arable land: 12%
- Permanent crops: 5%
- Permanent pastures: 24%
- Forests and woodland: 54%
- Other: 5% (1993 est.)
- Irrigated land
- 1,250 km² (1993 est.)
- Natural hazards
- Numerous volcanoes in mountains, with occasional violent earthquakes; Caribbean coast subject to hurricanes and other tropical storms
- Environment--current issues
- Deforestation; soil erosion; water pollution; Hurricane Mitch damage
- Environment--international agreements
-
- Party to: Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
- Signed, but not ratified: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol
- Geography--note
- No natural harbors on west coast