Skype
|
|
Skype (pronounced to rhyme with ripe) is a peer-to-peer internet telephony (VoIP) network, founded by Niklas Zennström and Janus Friis, the creators of Kazaa. The network is provided by all combined users of the free desktop software application. Skype users can speak to other Skype users for free, call traditional telephone numbers for a fee (SkypeOut), receive calls from traditional phones (SkypeIn), and receive voicemail messages.
| Contents |
Features
The basic computer-to-computer service allows users to speak, to send text messages or to send files to one another from their computers via the Internet at no cost. Conferences of up to five users are supported. SkypeOut is a paid feature of the Skype internet telephony service, which allows Skype users to call virtually any non-PC-based landline or mobile phone in the world.
Unlike international long-distance calls made from conventional phones, which are rated according to the relative distance between countries, SkypeOut bills all calls according to the relative size of the country, the volume of calls made from and to a given country, and how any country's government restricts international calls (this may explain the high cost per minute of calls placed to countries such as Cuba or North Korea). This rating method is used due to the fact that calls are rated the same regardless of place of origin. This way, a SkypeOut user will be billed the same for a called place to a phone number in London, whether the user is calling from his/her PC in London itself, or from an internet cafe in Sydney.
SkypeIn allows Skype users to receive calls on their computers dialled by regular phone subscribers to regular phone numbers. Beta released March 10, 2005, SkypeIn permits users to subscribe to numbers in UK, USA, France, Hong Kong, Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden. Cost is 30 Euro (about 36 dollars) for a 12-month subscription, or 10 Euro (about 12 dollars) for a three-month subscription.
Voicemail was also released on March 10, 2005. This service allows callers to leave voice-mail messages for Skype users who are not online, on another call or otherwise indisposed. This can be purchased separately or it is bundled with SkypeIn.
Skype Version 1.2 for Windows was released in March 23, 2005. Its most significant new feature is the provision of centrally-stored contact lists so that a user's contact information is available from any computer that is connected to Skype (in other previous versions, contact information was stored on the local computer).
Versions now exist for Microsoft Windows (Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows CE (Pocket PC)), Mac OS X and GNU/Linux.
Technology
Each Skype user must have the Skype software running on his computer. This software is available for free and can be downloaded from the company website.
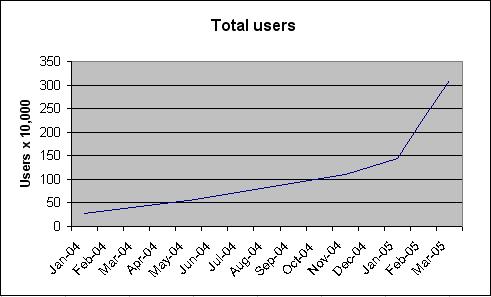
The main difference between Skype and other VoIP clients is that it operates on a peer-to-peer model rather than the more traditional server-client model. The Skype user directory is entirely decentralised and distributed among the nodes in the network, which means the network can scale very easily to large sizes (currently just over forty million users) without a complex and costly centralised infrastructure.
Skype also routes calls through other peers on the network, which allows it to traverse Symmetric NATs and firewalls, unlike most other VoIP programs (notably those based on the SIP protocol, see article (http://www.toyz.org/mrblog/archives/00000097.html)). This, however, puts extra burden on those who connect to the Internet without NAT, as their computers and network bandwidth may be used to route the calls of other users. The selection of intermediary computers is fully automatic, with individual users having no option to disable such use of their resources. This fact is not clearly communicated, however, and seems to contradict the license agreement which would limit Skype’s utilisation of the user’s “processor and bandwidth [to the] purpose of facilitating the communication between [the user] and other Skype Software users” (section 4.1).
The Skype code is closed and the protocol is proprietary. However the Skype client's application programming interface (API) exposes the network to software developers. The Skype API allows other programs to use the Skype network to get "white pages" information and manage calls.
Security
Since a Skype connection may be routed through an intermediate peer, 256-bit AES encryption actively encodes the data stream of each call, file transfer or instant message. Skype uses 1536-bit RSA (2048-bit RSA for customers who have purchased any "paid services" such as voicemail) to negotiate pairwise symmetric AES keys over an authenticated channel. The Skype server certifies each user's public key at log in.
Since the Skype code is not public source, the security of the software cannot be readily established. When run, Skype binds to three ports on the user's computer and directly manipulates Windows XP's built-in firewall to accommodate these network bindings.
History
- April 23 2003 Skype.com and Skype.net domain names registered
- August 29 2003 First public beta version released
- June 15 2004 Beta release of version 0.98.0.28 with first support for SkypeOut. Credits by voucher only.
- June 27 2004 SkypeOut credits first available for purchase on Skype website.
- July 27 2004 Release of Version 1.0 for Windows
- October 20 2004 First time 1 million Skype users are online at once
- February 14 2005 First reached 2 million online
- March 10 2005 SkypeIn Public Beta starts
- March 11 2005 Skype press release reports 1 million Skype-out users and 29 million registered users
- March 11 2005 Software has been downloaded 84 million times and 5.98 billion talk minutes served
- April 15 2005 Downloaded more than 100 million times
- May 18 2005 Three million online at once
Skype Business Ecology
Skype has partnered with online web properties including Tom.com, PcHomeOnline, Daum and Livedoor and hardware manufacturers including Plantronics, Logitech, Motorola, VTech, RTX and Siemens. Another boost to the distribution of Skype came in November 2004 when Kazaa bundled Skype with version 3.0 of its software.
Usage
Missing image
New-users-daily-skype.JPG
Image:New-users-daily-skype.JPG
iLBC CODEC
What is iLBC?
- iLBC (internet Low Bitrate Codec) is a FREE speech codec suitable for robust voice communication over IP. The codec is designed for narrowband speech and results in a payload bit rate of 13.33 kbit/s with an encoding frame length of 30 ms and 15.20 kbps with an encoding length of 20 ms. The iLBC codec enables graceful speech quality degradation in the case of lost frames, which occurs in connection with lost or delayed IP packets.
Features
- Bitrate 13.33 kbps (399 bits, packetized in 50 bytes) for the frame size of 30 ms and 15.2 kbps (303 bits, packetized in 38 bytes) for the frame size of 20 ms
- Basic quality higher then G.729A, high robustness to packet loss
- Computational complexity in a range of G.729A
- Royalty Free Codec
This is the codec used by Skype
Source: http://www.voip-info.org/wiki-iLBC
See also
External links
- Official Skype Website (http://www.skype.com)
- SkypeOut Call Charges (http://www.skype.com/products/skypeout/rates/all_rates.html)
- Official Skype Discussion forums (http://forum.skype.com/bb/)
- An Analysis of the Skype Peer-to-Peer Internet Telephony Protocol (http://arxiv.org/abs/cs.NI/0412017)
- Look2Skype.com - Outlook Skype Add-in. Skype Contacts from Outlook (http://www.look2skype.com/)
- Opinion piece advocating Skype and similar technologies (http://www.webcogs.com/the_future_of_phone_calls_is_now.aspx)
- Jyve.com Portal to Everything Skype - Community, Language Learning, Yellow Pages (http://www.Jyve.com)
- SAM - Skype Answering Machine (http://www.freewebs.com/skypeansweringmachine/)
- SomeoneNew.com - Skype Dating site - search for Skype users with common interests (http://www.someonenew.com)
- Skype Headset Reviews - Helps users to identify which headset is most suitable for them (http://www.skype-headset-reviews.com/)
- Skype Journal (http://www.skypejournal.com)
- Skype Journal's Guide: Learning Skype’s Plug-In Architecture (http://www.skypejournal.com/blog/archives/2005/04/skype_journal_g.php) - an ebook tutorial for programming the Skype API
- SummitCircle.com - Find Skype phones, add-ons and communities. (http://www.SummitCircle.com/)
- WigiWigi.com - True real-time video over ip for skype (http://www.wigiwigi.com)
- YapperNut.com - Telephone Gateway that Connects a Regular Telephone to Skype (http://www.yappernut.com/)cs:Skype
de:Skype eo:Skype es:Skype fr:Skype he:סקייפ id:Skype it:Skype ja:Skype ku:Skype lt:Skype nl:Skype pl:Skype pt:Skype fi:Skype sv:Skype zh:skype