Pome
|
|
In botany, a pome (after the French name for an apple, pomme) is a type of fruit, produced by flowering plants in the subfamily Maloideae of the family Rosaceae.
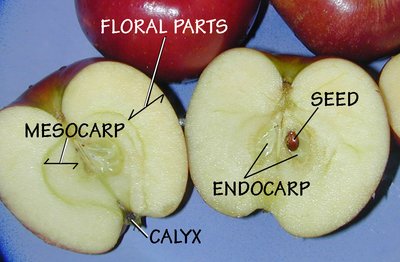
A pome is an accessory fruit composed of five or more carpels in which the exocarp forms an inconspicuous layer, the mesocarp is usually fleshy, and the endocarp forms a leathery case around the seed. However, outside of the exocarp is the most edible part of this fruit, derived from the floral tube (torus and other parts). In this fruit, the exocarp roughly outlines what is commonly called the core. The shriveled remains of the sepals, style and stamens can be seen at the end of a pome opposite the stem.
The best-known example of a pome is the apple. Other examples of pomes are produced by cotoneaster, hawthorn, loquat, medlar, pear, quince, rowan and whitebeam.