Modern dance
|
|
Modern dance is a dance form developed in the early 20th century. Although the term Modern dances has also been applied to a category of 20th Century ballroom dances, Modern dance as a term usually refers to 20th century concert dance.
In the early 1900s a few dancers in the United States and Europe started to rebel against the rigid constraints of Classical Ballet. Shedding classical ballet technique, costume and shoes these early modern dance pioneers practiced free dance.
In America Loie Fuller, Isadora Duncan and Ruth St. Denis developed their own styles of free dance and laid the foundations of American modern dance with their choreography and teaching.
In Europe Rudolf Laban, Émile Jaques-Dalcroze and Francois Delsarte developed theories of human movement and methods of instruction that lead to the development of European modern and Expressionist dance.
| Contents |
|
1.1 Free dance |
History
Free dance
main article: Free dance
- 1891 - Loie Fuller (a burlesque skirt dancer) began experimenting with the effect that gas lighting had on her silk costumes. Fuller developed a form of natural movement and improvisation techniques that were used in conjunction with her revolutionary lighting equipment and translucent silk costumes.
- 1903 - Isadora Duncan developed a dance technique influenced by the philosophy of Friedrich Nietzsche and a belief that dance of the ancient Greeks (natural and free) was the dance of the future. Ducan developed a philosophy of dance based on natural and spiritual concepts and advocated for that acceptance of pure dance as a high art.
- 1905 - Ruth St. Denis influenced by the actress Sarah Bernhardt and Japanese dancer Sado Yacco, St. Denis developed her translations of Indian culture and mythology. Her performances quickly became popular and she toured extensively whilst researching Oriental culture and arts. .
Fuller, Duncan and St. Denis all toured Europe seeking a wider and more accepting audience for their work. Only Ruth St. Denis retuned to the United States to continue her work, Isadora Duncan died in Paris in 1927 and Fuller's work received little support outside Europe.
Early modern dance
In 1915 Ruth St. Denis founded the Denishawn school and dance company with her husband Ted Shawn. Whilst St. Denis was responsible for most of the creative work, Shawn was responsible for teaching technique and composition. Martha Graham, Doris Humphrey, and Charles Weidman where all pupils at the school and members of the dance company.
- 1923 Graham leaves Denishawn to work as a solo artist in the Greenwich Village Follies.
- 1928 Humphrey and Weidman leave Denishawn to found their own school and company (Humphrey-Weidman).
- 1933 Shawn founds his all male dance group Ted Shawn and His Men Dancers based at his Jacob's Pillow farm in Lee, Massachusetts.
After shedding the techniques and compositional methods of their teachers the early modern dancers developed their own methods and ideologies and dance techniques which became the foundation for modern dance practice.
- Martha Graham (and Louis Horst) -
- Helen Tamiris - originally trained in free movement (Irene Lewisohn) and ballet (Michel Fokine) Tamiris studied briefly with Isadora Duncan but disliked her emphasis on personal expression and lyrical movement. Tamiris believed that each dance must create its own expressive means and as such did not develop an individual style or technique. As a choreographer Tamiris made works based on American themes working in both concert dance and musical theatre.
- Lester Horton - choosing to work in California (three thousand miles away from the center of modern dance - New York), Horton developed his own approach that incorporated diverse elements including Native American dances and modern Jazz. Horton's dance technique (Lester Horton Technique) emphasises a whole body approach including; flexibility, strength, coordination, and body awareness to allow freedom of expression.
European modern and expressionist dance
see also: Expressionist dance and Ausdruckstanz
Dance as art
In 1927 newspapers regularly began assigning dance critics, such as Walter Terry, and Edwin Denby, who approached performances from the viewpoint of a movement specialist rather than as a reviewer of music or drama. Educators accepted modern dance into college and university curricula, first as a part of physical education, then as performing art. Many college teachers were trained at the Bennington Summer School of the Dance, which was established at Bennington College in 1934.
Development of Modern Dance
Whilst the founders on modern dance continued to make works based on ancient myths and legends following a narrative structure, their students the radical dancers saw dance as a potential agent of change. Disturbed by the great depression and the rising threat of fascism in Europe, they tried to raise consciousness by dramatizing the economic, social, ethnic and political crises of their time.
- Hanya Holm - A student of Mary Wigman and instructor at the Wigman School in Dresden Holm founded the New York Wigman School of Dance in 1931 (which became the Hanya Holm Studio in 1936) introducing Wigman technique, Laban's theories of spatial dynamics and later her own dance techniques to American modern dance. An accomplished choreographer she was a founding artist of the first American Dance Festival in Bennington (1934). Holm's dance work Metropolitan Daily was the first modern dance composition to be televised on NBC and her labanotation score for Kiss Me, Kate (1948), was the first choreography to be copyrighted in the United States. Holm choreographed extensively in the fields of concert dance and musical theatre.
- Anna Sokolow - a student of Martha Graham and Louis Horst, Sokolow created her own dance company (circa 1930). presenting dramatic contemporary imagery, Sokolow's compositions were generally abstract; revealing the full spectrum of human experience reflecting the tension and alienation of the time and the truth of human movement.
- José Limón - In 1946, after studying and performing with Doris Humphrey and Charles Weidman, Limón established his own company with Humphrey as Artistic Director. It was under her mentorship that Limón created his signature dance, The Moor’s Pavane (1949). Limón’s choreographic works and technique remain a strong influence on contemporary dance practice.
- Merce Cunningham - a former ballet student and performer with Martha Graham, he presented his first New York solo concert with John Cage in 1944. Influenced by Cage and embracing modernist ideology using postmodern processes, Cunningham introduced chance procedures and pure movement to choreography and Cunningham technique to the cannon of 20th century dance techniques. Cunningham set the seeds for postmodern dance with his non-linear, non-climactic, non-psychological abstract work. In these works each element is in, and of itself expressive, and what it communicates is (in large part) determined by the observer.
- Erick Hawkins - a student of George Balanchine Hawkins became a soloist and the first male dancer in Martha Graham's dance company. In 1951 Hawkins, interested in the new field of kinesiology, opened his own school and developed his own technique (Hawkins technique) a fore-runner of somatic dance techniques.
- Paul Taylor - a student of the Juilliard School of Music and the Connecticut College School of Dance. In 1952 his performance at the American Dance Festival attracted the attention of several major choreographers. Performing in the companies of Merce Cunningham, Martha Graham, and George Balanchine (in that order), he founded the Paul Taylor Dance Company in 1954. the use of everyday gestures and modernist ideology is characteristic of his choreography. Member of the Paul Taylor Dance Company included: Twyla Tharp, Laura Dean, Dan Wagoner, and Senta Driver.
- Alwin Nikolais - a student of Hanya Holm, not only pre-empted postmodern dance but also dance technology (as did Loie Fuller) before Judson Dance Theater in the 1960s. Nikolais use of multimedia in works such as Masks, Props, and Mobiles (1953), Totem (1960), and Count Down (1979) was unmatched by other choreographers. Often presenting his dancers in constrictive spaces and costumes with complicated sound and sets he focused their attention on the physical tasks of overcoming obstacles he placed in their way. Nikolais viewed the dancer not as an artist of self-expression, but as a talent who could investigate the properties of physical space and movement.
African-American modern dance
The development of Modern dance embraced the contributions of African-American dance artists regardless of whether they made pure modern dance works or blended modern dance with African and Caribbean influences.
- Katherine Dunham - African-American dancer, and anthropologist, originally a ballet dancer she founded her first company Ballet Negre in 1936 and later the Katherine Dunham Dance Company based in Chicago. Dunham opened a school in New York (1945) where she taught Katherine Dunham Technique, a blend of African and Caribbean movement (flexible torso and spine, articulated pelvis and isolation of the limbs and polyrhythmic movement) integrated with techniques of ballet and modern dance.
- Pearl Primus - a dancer, choreographer and anthropologist Primus drew on African and Caribbean dances to create strong dramatic works characterized by large leaps in the air. Primus often based her dances on the work of black writers and on racial and African-American issues. Primus created works based on Langston Hughes The Negro Speaks of Rivers (1944), and Lewis Allen's Strange Fruit (1945). Her dance company developed into the Pearl Primus Dance Language Institute which teaches her method of blending African-American, Caribbean, and African influences with modern dance and ballet techniques.
- Alvin Ailey- a student of Lester Horton (and later Martha Graham) Ailey spent several years working in both concert and theatre dance. in 1930 Ailey and a group of young African-American dancers perform as Alvin Ailey American Dance Theater in New York. Ailey drew upon his blood memories of Texas, the blues, spirituals and gospel as inspiration, his most popular and critically acclaimed work is Revelations (1960).
Legacy of Modern dance
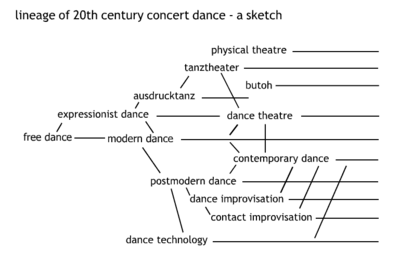
The legacy on Modern dance can be seen in lineage of 20th century concert dance forms. Although often producing divergent dance forms many seminal dance artists share a common heritage that can be traced back to free dance.
Postmodern and Contemporary dance
Both Postmodern dance and Contemporary dance built upon the foundations laid by Modern dance and form part of the greater category of 20th century concert dance. Where as Postmodern dance was a direct and opposite response to Modern dance, Contemporary dance draws on both modern and postmodern dance as a source of inspiration.
see also: Postmodern dance, Contemporary dance and 20th century concert dance
lineage 20th century concert dance
note: this sketch is provided for illustrative purposes only
teachers and students
This list illustrates the basic teacher / student links in modern dance. For more detailed information see the individual artists entries.
-
- Isadora Duncan - Duncan technique
-
- Ruth St. Denis
- Ted Shawn - Shawn Fundamentals
- Denishawn (school and company)
- Doris Humphrey and Charles Weidman - The Art of Making Dances (Humphrey)
- Humphrey-Weidman school - Humphrey-Weidman technique (fall and recovery)
- José Limón - Limón technique
- Humphrey-Weidman school - Humphrey-Weidman technique (fall and recovery)
- Martha Graham - Graham technique (and Louis Horst)
- Erick Hawkins (via George Balanchine) - Hawkins technique
- Anna Sokolow
- Merce Cunningham - Cunningham technique (also see Postmodern dance)
- Doris Humphrey and Charles Weidman - The Art of Making Dances (Humphrey)
-
-
- Rudolf Laban
- Kurt Jooss (see Ausdruckstanz)
- Pina Bausch (see Tanztheater)
- Mary Wigman (see Expressionist dance)
- Hanya Holm
- Alwin Nikolais - decentralization
- Hanya Holm
- Kurt Jooss (see Ausdruckstanz)
-
-
- Katherine Dunham Katherine Dunham Technique
-
-
Further information
Related articles
-
Further reading
- Adshead-Lansdale, J. (Ed) (1994) Dance History: An Introduction. Routledge. ISBN 041509030X
- Anderson, J. (1992) Ballet & Modern Dance: A Concise History. Independent Publishers Group. ISBN 0871271729
- Au, S. (2002) Ballet and Modern Dance (World of Art). Thames & Hudson. ISBN 0500203520
- Brown, J. Woodford, C, H. and Mindlin, N. (Eds) (1998) (The Vision of Modern Dance: In the Words of Its Creators). Independent Publishers Group. ISBN 0871272059
- Cheney, G. (1989) Basic Concepts in Modern Dance: A Creative Approach. Independent Publishers Group. ISBN 0916622762
- Daly, A. (2002) Done into Dance: Isadora Duncan in America. Wesleyan Univ Press. ISBN 0819565601
- De Mille, A. (1991) Martha : The Life and Work of Martha Graham. Random House. ASIN 0394556437
- Duncan, I. (1937) The technique of Isadora Duncan. Dance Horizons. ASIN 0871270285
- Foulkes, J, L. (2002) Modern Bodies: Dance and American Modernism from Martha Graham to Alvin Ailey. The University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 0807853674
- Graham, M. (1973) The Notebooks of Martha Graham. Harcourt. ASIN 0151672652
- Graham, M. (1992) Martha Graham: Blood Memory: An Autobiography. Pan Macmillan. ASIN 0333574419
- Hawkins, E. and Celichowska, R. (2000) The Erick Hawkins Modern Dance Technique. Independent Publishers Group. ISBN 087127213X
- Horosko, M (Ed) (2002) Martha Graham: The Evolution of Her Dance Theory and Training. University Press of Florida. ISBN 0813024730
- Humphrey, D. and Pollack, B. (Ed) (1991) The Art of Making Dances Princeton Book Co. ISBN 0871271583
- Hutchinson Guest, A. (1998) Shawn's Fundamentals of Dance (Language of Dance). Routledge. ISBN 2881242197
- Kriegsman, S, A.(1981) Modern Dance in America: the Bennington Years. G K Hall. ASIN 081618528X
- Lewis, D, D. (1999) The Illustrated Dance Technique of Jose Limon. Princeton Book Co. ISBN 0871272091
- Love, P. (1997)Modern Dance Terminology: The ABC's of Modern Dance as Defined by its Originators. Independent Publishers Group. ISBN 0871272067
- Mazo, J, H. (2000) Prime Movers: The Makers of Modern Dance in America. Independent Publishers Group. ISBN 0871272113
- Roseman, J, L. (2004) Dance Was Her Religion: The Spiritual Choreography of Isadora Duncan, Ruth St. Denis and Martha Graham. Hohm Press. ISBN 1890772380
- Sherman, J. (1983) Denishawn: The Enduring Influence. Twayne. ASIN 0805796029
- Terry, W. (1976) Ted Shawn, father of American dance : a biography. Dial Press. ASIN 0803785577
- -to be fixed -
- Moira Hodgson, Quintet: Five American Dance Companies (1977)
- Richard Long, The Black Tradition in Modern Dance (1989)
- Don McDonagh, The Complete Guide to Modern Dance (1976); The Rise and Fall of Modern Dance (1990)
- Sandra Minton, Modern Dance (1984)
Template:Modernismde:Modern Dance fy:Moderne dûns nl:Moderne dans pl:Taniec nowoczesny zh:現代舞