Methionine
|
|
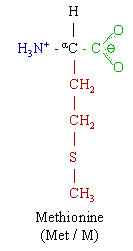 |
Methionine (Met, M. C5H11NO2S) is a essential nonpolar amino acid, and a lipotropic.
Methionine and cysteine are the only sulfur containing proteinogenic amino acids. The methionine derivative S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) serves as a methyl donor. Methionine plays a role in cysteine, carnitine and taurine synthesis by the transsulfuration pathway, lecithin production, the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and other phospholipids. Improper conversion of methionine can lead to atherosclerosis. Methionine is a chelating agent.
Methionine is one of only two amino acids encoded by a single codon (AUG) in the standard genetic code (tryptophan, encoded by UGG, is the other). The codon AUG is also significant, in that it carries the "Start" message for a ribosome to begin protein translation from mRNA. Consequently, methionine is incorporated into the N-terminal position of all proteins in eukaryotes and archaea during translation, although it is usually removed by post-translational modification. Methionine can also occur at other positions in the protein.
- Chemical formula: NH2CH(C2H4SCH3)COOH
- Mass: 149.2
- pK1 (α-COOH): 2.13
- pK2 (α-NH3+): 9.28
- Protein Occurrence: 2.2%
See also
Formylmethioninede:Methionin es:Metionina fr:Méthionine it:Metionina nl:Methionine ja:メチオニン pl:Metionina ru:Метионин fi:Metioniini sv:Metionin
