Marquesas Islands
|
|
| |||
| National motto: Mau‘u‘u ha‘e iti | |||
| Official languages | French, Tahitian | ||
| Political status | Dependent territory, administrative division of French Polynesia | ||
| Capital | Tai o Hae | ||
| Largest City | Tai o Hae | ||
| Area | 1,274 km² ( 492 sq. mi.) | ||
| Population | 8,712 6.84/km² | ||
| Currency | CFP franc | ||
| Time zone | UTC -9.5 | ||
| Internet TLD | .pf | ||
| Calling Code | 689 | ||
The Marquesas Islands are a group of islands in French Polynesia. In French they are known as the Īles Marquises, and in Marquesan they are known variously as Te Henua (K)enana (North Marquesan) and Te Fenua `Enata (South Marquesan), which means "The Land of Men". (See also: Names of the Marquesas Islands.)
| Contents |
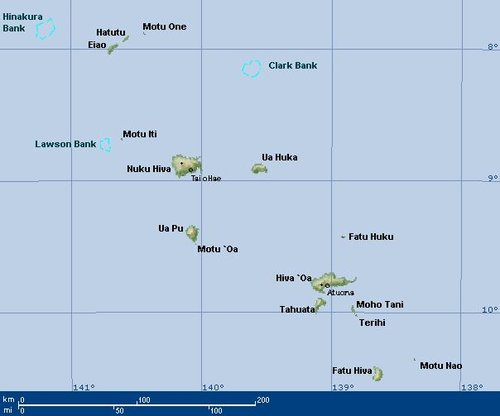
Islands of the Marquesas
Northern Marquesas
Southern Marquesas
Seamounts in the Marquesas
There are also a number of seamounts or shoals, mostly located in the area of the northern Marquesas. Among these are:
- See related articles: Names of the Marquesas Islands Marquesas geology
Government of the Marquesas
The center of government is Tai o Ha`e on Nuku Hiva, although the former capital, Atuona, on Hiva `Oa, still serves as the administrative center for the southern islands.
See related article: Marquesas Islands Government
Language of the Marquesas
See related article: Marquesan Language(s)
History of the Marquesas
The first recorded settlers of the Marquesas were Polynesians, who, from archaęological evidence, are believed to have arrived before 100 CE. Ethnological and linguistic evidence suggests that they likely arrived from the region of Samoa.
The islands were given their name by Įlvaro de Mendańa de Neira who reached them in 1595, visiting first Fatu Hiva and then Tahuata before continuing on to the Solomon Islands.
The American navigator Capt. Joseph Ingraham first visited the northern Marquesas in 1791, giving them the name Washington Islands. In 1813, Commodore David Porter claimed Nuku Hiva for the United States, but the United States Congress never ratified that claim, and in 1842, France, following a successful military operation on behalf of a native chief (named Iotete) who claimed to be king of the whole of the island of Tahuata, took possession of the whole group, establishing a settlement (abandoned in 1859) on Nuku Hiva. French control over the group was reestablished in 1870, and later incorporated into the territory of French Polynesia.
The Marquesas Islands suffered the greatest population decline as a result of diseases brought by European and American explorers, reducing the estimated sixteenth century population of over 100,000 inhabitants, to about 20,000 by the middle of the nineteenth century, and to just over 2,000 by the beginning of the 1900s. During the course of the twentieth century, the population increased to about 8,500 by 2002, not including the Marquesan community residing on Tahiti.
- See related article: Marquesas history
Demographics of the Marquesas
The population of the Marquesas Islands at the 2002 census was 8,712 inhabitants, which is on the rise, but still far lower than 16th century estimates which put the population at over 100,000. Much of the population was wiped out by Small pox between 1600 and 1900, when the population was counted at just under 2,000.
See related article: Marquesan Demographics
Communications in the Marquesas
Airports
There are four airports in the Marquesas, one each on the islands of Nuku Hiva, Ua Pu, Ua Huka, and Hiva Oa.
Telecommunications
The Marquesas are served by telephone as well as by radio and television mainly from Tahiti.
Culture of the Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands were once a major center of eastern Polynesian civilization.
See related article: Marquesan culture
Geography of the Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands are the furthest island group in the world from any continent, lying between 400 and 600 miles (600 and 1,000 km) south of the equator and approximately 1,000 miles (1,600 km) northeast of Tahiti. They fall naturally into two geographical divisions: the northern group, consisting of Eļao, Hatutu (Hatutaa), Motu One, and the islands centered around the large island of Nuku Hiva: Motu Iti (Hatu Iti), Ua Pou, Motu `Oa and Ua Huka, and the southern group of Fatu Uku, Tahuata, Moho Tani (Motane), Terihi, Fatu Hiva and Motu Nao (Thomasset Rock), clustered around the main island of Hiva `Oa.
With a combined land area of 1,274 km² (492 sq. miles), the Marquesas are among the largest island groups of French Polynesia, Nuku Hiva being the second largest island in the entire territory, after Tahiti.
See related article: Marquesas geography
Geology of the Marquesas
With the exception of Motu One, all of the Marquesas Islands are high islands. Motu One is a low island, comprised of two small sand banks awash on a coral reef. Unlike the majority of the islands of French Polynesia, the Marquesas are not surrounded by protective fringing reefs. Except for at Motu One, and in bays and other protected areas, the only coral in the Marquesas is found in a rather strange place: on the top of the island of Fatu Huku.
The South Equatorial Current lashes the islands mercilessly, which has led to sea-caves dotting the islands' shores. Except for where the valleys empty into the small bays, the islands are remarkable for their mountain ridges, which end abruptly as cliffs where they meet the sea.
See related article: Marquesas geology
Rainforest_Fatu_Hiva.jpg
Biology of the Marquesas
The ecosystem of the Marquesas has been devastated in some areas by the activities of feral livestock. As a first step in preserving what remains, the Marquesan Nature Reserves were created in 1992.
See related articles: Marquesas zoology, Marquesas botany
The Marquesas Islands in Western Culture and Civilization
Famous French painter Paul Gauguin and Belgian singer Jacques Brel spent the last years of their lives in the Marquesas, and are buried there. Brel composed a famous song, Les Marquises, about the Marquesas Islands, his last home.
The Marquesas provided inspiration to American novelist Herman Melville, whose experiences in the Marquesas formed the basis for his novel Typee.
Robert Louis Stevenson visited the Marquesas in 1888, and wrote about his experiences and impressions there in 1900, in a book called In the South Seas (http://www.sharebook.co.kr/stevenson/sseas10.htm).
Thor Heyerdahl wrote his book Fatu Hiva during a year-long stay on that island.
The island group is also mentioned in passing in the Crosby, Stills & Nash (and Young) song, The Southern Cross.
The Marquesas Islands temporarily received an international spotlight in the United States when the reality TV show Survivor: Marquesas was filmed there. It was the fourth installment of the TV series Survivor.
See also
External links
- Finding French Polynesia (http://www.southpacific.org/text/finding_tahiti.html)
- The Marquesas Online (http://www.marquises.pf/2index.htm)
- Effects of the 1946 Aleutian Tsunami on the Marquesas Is. (http://www.usc.edu/dept/tsunamis/1946/)
- Flora of the Marquesas Islands (http://ravenel.si.edu/botany/pacificislandbiodiversity/marquesasflora/)
- History of the Marquesas Islands (http://www.ms-starship.com/sciencenew/marquesas.htm)
- Satellite Images of the Marquesas Islands (http://rove.to/marquesas-islands/)
- Encarta Map (http://encarta.msn.com/encnet/features/mapcenter/map.aspx?refid=701514510)
- WorldAtlas.com's map of the Marquesas--includes most of the islands (http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/oceania/lgcolor/mqcolor.htm)
- Administrative divisions of the Marquesas Islands (http://www.polynesie-francaise.gouv.fr/hc/iles-marquises/index.asp)
- Pacific Islands Travel's Marquesas Page (http://www.pacificislandtravel.com/fr_polynesia/about_destin/marquesas_isl.html)
- Marquesas Islands Homepage (http://gaste.free.fr/les_Marquises/marquises.htm)
- http://cecile.barbet.free.fr/ (in French) (http://cecile.barbet.free.fr/)
de:Marquesas es:Islas Marquesas fr:Īles Marquises he:איי מרקיז lt:Markizų salos nl:Marquesaseilanden pl:Markizy