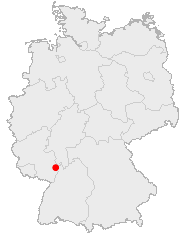
Ludwigshafen am Rhein
|
|
LudwigshafenPanorama.jpg
Ludwigshafen am Rhein is a city in Rheinland-Pfalz, Germany, with about 162,000 inhabitants. Ludwigshafen is located at the Rhine opposite Mannheim. It is known for its chemical industry (BASF). Among the cultural facilities ranks the renowned Wilhelm-Hack-Museum with its magnificent ceramic wall, which was arranged by the Catalan artist Joan Miró. Ludwigshafen is the birthplace of the world-famous German rock-climber Wolfgang Gullich.
| Contents |
History
Ostasieninstitut.jpg
The first settlement in the area of Modern Ludwigshafen was a fortress ("Die Rheinschanze") built by Kurfürst Friedrich IV on the other side of the Rhine River to protect the City of Mannheim. In 1808, Carl Hornig from Mannheim purchased the fortress from the French invaders and turned it into a resting place for French sailors that needed to pass from that area of the Rhine River. Hornig died in 1819, but Johann Heinrich Scharpff, the businessman from Speyer, continued Hornig's plans, which was turned over to his son-in-law, Philipp Markus Lichtenberger, in 1830.
The year 1843 was the birth of Ludwigshafen, when Lichtenberger sold this property to Bavaria (Bayern), and the military title of the fortress was removed. The Bavarian king, Ludwig I set forth plans to rename the settlement and to start construction of an urban area. On December 27, 1852, King Maximilian II granted Ludwigshafen Am Rhein political freedom.
| Facts and Figures | |
|---|---|
| State: | Rhineland-Palatinate |
| Area: | 42.24 square miles (109 km²) |
| German Population: | 133,788 |
| Non-German Population: | 33,029 |
| Total Population: | 166,816 |
| Postal Codes: | 67001-67071 (Old Postal Code: 6700) |
| Area Code: | 0621 and 06237 |
| Number of City Districts: | 10 |
| Website: | http://www.ludwigshafen.de/ |
| E-mail: | info@ludwigshafen.de (mailto:info@ludwigshafen.de) |
| Mayor: | Dr. Eva Lohse (CDU) |
| Party Majority: | CDU |
The year 1865 was an important date in the history of independent Ludwigshafen. After several discussions, BASF decides to move its factories from Mannheim to the Hemshof district, which belonged to Ludwigshafen. With more jobs available, the population of Ludwigshafen started to increase very rapidly, so that in 1899 the city was governing more than 62,000 residents (Compared to 1,500 in 1852).</p>
During World War II, Ludwigshafen suffered heavy damages, so that only 20% of the buildings were still habitable. After the War, in 1948, the “Pasadena Shares Committee” sent packages of blankets, clothing, food, and medicines to help the residents of post-war Ludwigshafen. Many friendships started to form, so that in 1956, Ludwigshafen Am Rhein and Pasadena, California became sister cities. Today, Ludwigshafen, with a population of more than 160,000 is one of Germany’s most prosperous industrial cities. It is an ideal gateway for trips to the Black Forest, Heidelberg, and the surrounding wine country in the German Palatinate.
Sister Cities
- Antwerp - http://www.antwerpen.be/
- Dessau - http://www.dessau.de/
- Havering - http://www.havering.gov.uk/
- Lorient - http://www.lorient.com/
- Pasadena - http://www.ci.pasadena.ca.us/
- Sumgait
Radio Stations
- bigFM (http://www.bigFM.de/)
- Radio-Regenbogen (http://www.regenbogenweb.de/)
- RPR1 (http://www.rpr1.de/)
- SWR1 (http://www.swr1.de/)
- SWR2 (http://www.swr2.de/)
- SWR3 (http://www.swr3.de/)
- SWR4 (http://www.swr4.de/)
External Links
- Official City Website (http://www.ludwigshafen.de/)
- Ludwigshafener Kongress- und Marketing-Gesellschaft mbH (in English) (http://www.lukom.com/html/english.html)
- Wilhelm-Hack-Museum (in German) (http://www.wilhelm-hack-museum.de/)
- BASF Website (in German & English) (http://www.basf.de/)de:Ludwigshafen am Rhein
fr:Ludwigshafen it:Ludwigshafen sul Reno nl:Ludwigshafen ja:ルートヴィッヒスハーフェン
sv:Ludwigshafen