Lens (vision)
|
|
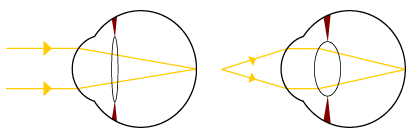 Light from a single point of a distant object and light from a single point of a near object being brought to a focus by changing the curvature of the lens. |
The lens or crystalline lens is a component of the eye. In concert with the cornea, it refracts light, focussing it onto the retina.
|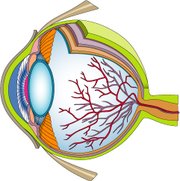
Color Cross Section Illustration of the Human Eye courtesy of Classroom Clip Art (http://classroomclipart.com)
The lens is clear and flexible; its curvature is controlled by ciliary muscles. By changing the curvature of the lens, one can focus the eye on objects at different distances from it.
The lens is about 5 mm wide and has a diameter of about 9 mm for an adult human (though these figures can vary). The lens is included into the capsular bag, maintained by the zonules of Zinn.
Diseases of the eye
- A cataract is when the normally transparent crystalline lens develops opacities and leads to blurry vision.
See also
Anatomy Clipart and Pictures
- Clip Art (http://classroomclipart.com)
- Anatomy Clip Art (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Anatomy)
- Anatomy Clip Art (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Clipart/Anatomy)
- Anatomy Animations (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Animations/Anatomy)
- Anatomy Illustrations (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Illustrations/Anatomy)
| Sensory system - Visual system - Eye | Edit (https://academickids.com/encyclopedia/index.php?title=Template:eye&action=edit) |
| Optic disc - Retina - Cornea - Iris - Pupil - Lens - Macula - Sclera - Optic fovea - Blind spot - Vitreous humour - Aqueous humour - Choroid - Ciliary body - Conjunctiva - Angle structure - Tapetum lucidum |
| Sensory system - Visual system |
|
Eye - Optic nerve - Optic chiasm - Optic tract - Lateral geniculate nucleus - Optic radiations - Visual cortex |
