Law of cosines
|
|
In trigonometry, the law of cosines is a statement about arbitrary triangles which generalizes the Pythagorean theorem by correcting it with a term proportional to the cosine of the opposing angle. Let a, b, and c be the sides of the triangle and A, B, and C the angles opposite those sides. Then,
- <math>c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos C . \;<math>
This formula is useful for computing the third side of a triangle when two sides and their enclosed angles are known, and in computing the angles of a triangle if all three sides are known.
The law of cosines also shows that
- <math>c^2 = a^2 + b^2\;<math> if and only if <math>\cos C = 0 . \;<math>
The statement cos C = 0 implies that C is a right angle, since a and b are positive. In other words, this is the Pythagorean theorem and its converse. Although the law of cosines is a broader statement of the Pythagorean theorem, it isn't a proof of the Pythagorean theorem, because the law of cosines derivation given below depends on the Pythagorean theorem.
| Contents |
Proof
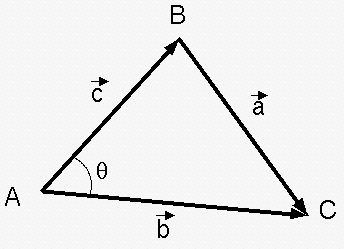
Using vectors and vector dot products, we can easily prove the law of cosines. If we have a triangle with vertices A, B, and C whose sides are the vectors a, b, and c, we know that:
- <math>\mathbf{a = b - c} \;<math>
and
- <math>\mathbf{(b - c)\cdot (b - c) = b\cdot b - 2 b\cdot c + c\cdot c}. \;<math>
Using the dot product, we simplify the above into
- <math>\mathbf{|a|^2 = |b|^2 + |c|^2 - 2 |b||c|}\cos \theta. \;<math>
Alternate proof (for acute angles)
Law_of_cosines_proof.png
Triangle
Let a, b, and c be the sides of the triangle and A, B, and C the angles opposite those sides. Draw a line from angle B that makes a right angle with the opposite side b. If the length of that line is x, then sin C = x/a, which implies x = a sin C.
That is, the length of this line is a sin C. Similarly, the length of the part of b that connects the foot point of the new line and angle C is a cos C. The remaining length of b is b − a cos C. This makes two right triangles, one with legs a sin C and b − a cos C and hypotenuse c. Therefore, according to the Pythagorean theorem:
- <math>c^2 = (a \sin C)^2 + (b - a \cos C)^2\,<math>
- <math>= a^2 \sin^2 C + b^2 - 2 ab \cos C + a^2 \cos^2 C\,<math>
- <math>= a^2 (\sin^2 C + \cos^2 C) + b^2 - 2ab \cos C\,<math>
- <math>=a^2+b^2-2ab\cos C\,<math>
because
- <math>\sin^2 C + \cos^2 C=1.\,<math>
Transposing
By transposing
- <math>c^2=a^2+b^2-2ab\cos C,\,<math>
we can find C:
- <math>cos C= \frac{a^2+b^2-c^2}{2ab}<math>
See also
External link
- Several derivations of the Cosine Law, including Euclid's (http://www.cut-the-knot.org/pythagoras/cosine.shtml)da:Cosinusrelation
de:Kosinussatz es:Teorema del coseno fr:Théorème d'Al-Kashi ko:코사인 법칙 it:Legge del coseno he:משפט הקוסינוסים nl:Cosinusregel ja:余弦定理 pl:Twierdzenie cosinusów ru:Теорема косинусов sl:Kosinusni izrek uk:Теорема косинусів zh:余弦定理