Key Biscayne, Florida
|
|
Key Biscayne is a village located in Miami-Dade County, Florida. As of the 2000 census, the village had a total population of 10,507.
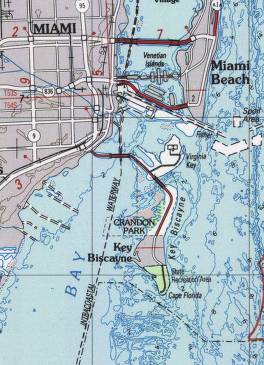
Key Biscayne is an island that lies south of Miami Beach and east of Miami. It and nearby Virginia Key form the first (northernmost) of the Florida Keys, a chain of islands off the South East coast of Florida, the last (southernmost) being Key West. Visitors can reach Key Biscayne from the mainland by driving over the Rickenbacker Causeway, a roadway and series of bridges that span Biscayne Bay. Key Biscayne is part of the same geological formation as the Florida Keys, which sit atop coral rock islands, as well as partly-submerged mangrove swamps.
The Key (from the Spanish word cayo, for "island") is connected to Miami via the Rickenbacker Causeway, originally built in 1947. Because of its low elevation and direct exposure to the Atlantic Ocean, it is usually among the first Miami areas to be evacuated before an oncoming hurricane.
The Key is home to Bill Baggs Cape Florida State Park and, along with parts of Biscayne Bay, forms Biscayne National Park.
Since 1985, a major professional tennis tournament for both men and women has been held annually in Key Biscayne. Currently known as the NASDAQ-100 Open, the event was formerly the Lipton Tennis Championships from 1985 to 1999 and the Ericsson Open from 1999 to 2002.
| Contents |
Geography
FLMap-doton-KeyBiscayne.PNG
Location of Key Biscayne, Florida
Key Biscayne is located at 25°41'25" North, 80°9'54" West (25.690329, -80.165118)Template:GR.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area of 3.6 km² (1.4 mi²). 3.3 km² (1.3 mi²) of it is land and 0.3 km² (0.1 mi²) of it is water. The total area is 8.63% water.
History
Native Americans of the Tequesta tribe were the first inhabitants of Key Biscayne, arriving by dugout canoe. They used the island as a base for fishing, collecting shellfish and hunting for sea turtle eggs. Juan Ponce de Leon charted Key Biscayne on his first mission to the New World in 1513. He christened the island Santa Marta and claimed it for the Spanish Crown. The island served as a source of fresh water for Spanish ships but the island was not colonized by the Spanish Empire perhaps because of the treacherous reefs, constantly shifting sandbars and unpredictability of tropical storms.
After Florida became a U.S. territory in 1821, the federal government built the Cape Florida lighthouse at the southern tip of Key Biscayne in 1825. On July 23, 1836, the lighthouse was attacked and burned by Native Americans of the Seminole tribe during the Second Seminole War. An assistant lighthouse keeper was killed and the lighthouse was abandoned until the end of the war in 1842.
In 1846, US Congress appropriated $23,000 to rebuild the lighthouse and work was completed in 1847. In 1861, Confederate militants sabotaged the lighthouse so that it could not guide Union sailors during the blockade of Confederate Florida. The lighthouse was repaired and re-lit again in 1866.
Early in the 20th Century, two-thirds of Key Biscayne was farmed as the largest coconut plantation in the continental United States. It wasn't until the construction of the seven-mile Rickenbacker Causeway in 1947 that the island became a convenient place to live. The Mackle Construction Company built hundreds of ranch and cottage homes for returning Korean War veterans in the 1950s. Fishing, boating and beachcombing were popular pastimes for the working class residents of the new suburban island community.
President Richard Nixon purchased the first of his three waterfront Mackle homes in 1969 to be close to his close friend and confidant, Bebe Rebozo. Bebe Rebozo, owner of the Key Biscayne Bank, was indicted for laundering a $100,000 donation from Howard Hughes to the Nixon election campaign. Plans for the Watergate break-in at Democratic headquarters were discussed at the Key Biscayne Nixon compound and, as the Watergate scandal unfolded, Nixon spent more time in seclusion there. Nixon visited Key Biscayne more than 50 times between 1969 and 1973. The U.S. Department of Defense spent $400,000 constructing a helicopter landing pad in Biscayne Bay adjacent to the Nixon compound and when Nixon sold his property, including the helicopter pad, there were public accusations that he enriched himself at taxpayer expense.
In 1992, Hurricane Andrew destroyed many homes and businesses on Key Biscayne but uninhabited Bill Baggs Cape Florida State Park received the brunt of the storm. Fear of hurricanes did not deter construction of several large resort hotels, condominium complexes and shopping centers on the island as the once bucolic island life continued to accelerate at a frenetic pace. Key Biscayne increasingly caters to an elite population of business moguls, high-income professionals, and a significant influx of Latin American tourists and part-time residents fleeing political and economic instability in their home countries.
Demographics
As of the censusTemplate:GR of 2000, there are 10,507 people, 4,259 households, and 2,900 families residing in the village. The population density is 3,169.4/km² (8,225.0/mi²). There are 6,378 housing units at an average density of 1,923.9/km² (4,992.8/mi²). The racial makeup of the village is 95.46% White, 0.46% African American, 0.14% Native American, 0.92% Asian, 0.00% Pacific Islander, 1.49% from other races, and 1.52% from two or more races. 49.79% of the population are Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There are 4,259 households out of which 32.3% have children under the age of 18 living with them, 58.0% are married couples living together, 7.7% have a female householder with no husband present, and 31.9% are non-families. 27.9% of all households are made up of individuals and 9.5% have someone living alone who is 65 years of age or older. The average household size is 2.47 and the average family size is 2.99.
In the village the population is spread out with 24.2% under the age of 18, 4.6% from 18 to 24, 29.6% from 25 to 44, 26.0% from 45 to 64, and 15.6% who are 65 years of age or older. The median age is 40 years. For every 100 females there are 88.4 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there are 84.8 males.
The median income for a household in the village is $86,599, and the median income for a family is $107,610. Males have a median income of $86,322 versus $46,765 for females. The per capita income for the village is $54,213. 8.3% of the population and 5.7% of families are below the poverty line. Out of the total population, 9.2% of those under the age of 18 and 3.6% of those 65 and older are living below the poverty line.
External links
- Village of Key Biscayne website (http://keybiscayne.fl.gov/)
- Key-Biscayne.com (http://www.key-biscayne.com/)
| Edit (http://en.wikipedia.org/w/wiki.phtml?title=Template:Florida_Keys&action=edit) | Florida Keys |
|---|---|
| Upper keys | Key Largo, Islamorada, Tavernier, Plantation Key, Matecumbe Key |
| Middle keys | Craig Key, Fiesta Key, Long Key, Conch Key, Duck Key, Grassy Key, Deer Key, Vaca Key, Marathon Key, Boot Key |
| Lower keys | Bahia Honda, West Summerland Key, No Name Key, Big Pine Key, Torch Key, Little Torch Key, Ramrod Key, Summerland Key, Cudjoe Key, Sugarloaf Key, Saddlebunch Keys, Big Coppitt Key, Boca Chica, Key West |
| Outlying islands | Dry Tortugas, Marquesas Keys |
| Areas | Florida Bay, Dry Tortugas National Park, Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary, National Key Deer Sanctuary, Biscayne Bay, Biscayne National Park |
| Other topics | Overseas Highway, Overseas Railway, Seven Mile Bridge, Key Deer, Conch Republic, Monroe County, Hurricane Georges, 1935 Hurricane, Theater of the Sea |