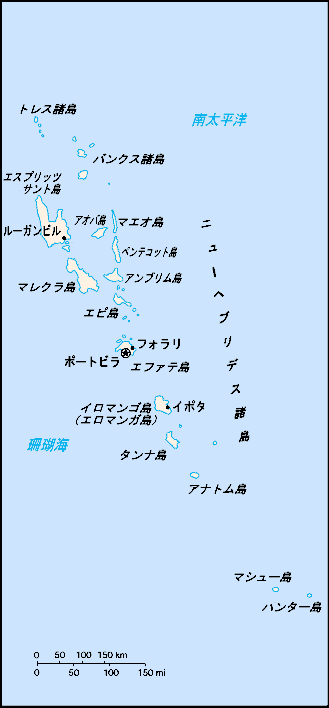
Geography of Vanuatu
|
|
Vanuatu, formerly called New Hebrides, is a group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean, about three-quarters of the way from Hawaii to Australia. Vanuatu's immediate neighbours include the Solomon Islands and New Caledonia.
Geographic coordinates: Template:Coor dm
Map references: Oceania
Area:
total:
14,760 sq km
land:
14,760 sq km
water:
0 sq km
note:
includes more than 80 islands
Area - comparative: slightly larger than Connecticut
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 2,528 km
Maritime claims:
measured from claimed archipelagic baselines
contiguous zone:
24 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
territorial sea:
12 nm
Climate: tropical; moderated by southeast trade winds
Terrain: mostly mountains of volcanic origin; narrow coastal plains
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Tabwemasana 1,877 m
Natural resources: manganese, hardwood forests, fish
Land use:
arable land:
2%
permanent crops:
10%
permanent pastures:
2%
forests and woodland:
75%
other:
11% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: NA sq km
Natural hazards: tropical cyclones or typhoons (January to April); volcanism causes minor earthquakes
Environment - current issues: a majority of the population does not have access to a potable and reliable supply of water; deforestation
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements