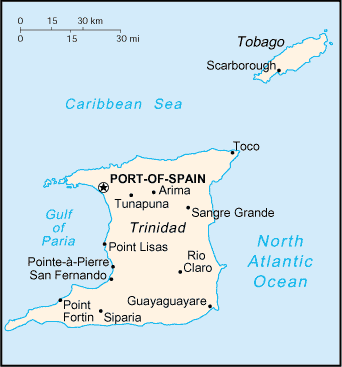
Geography of Trinidad and Tobago
|
|
Location: Caribbean, islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Venezuela
Geographic coordinates: Template:Coor dm
Map references: Central America and the Caribbean
Area:
total:
5,128 sq km
land:
5,128 sq km
water:
0 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly smaller than Delaware
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 362 km
Maritime claims:
contiguous zone:
24 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm or to the outer edge of the continental margin
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
territorial sea:
12 nm
Climate: tropical; rainy season (June to December)
Terrain: mostly plains with some hills and low mountains
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
Caribbean Sea 0 m
highest point:
El Cerro del Aripo 940 m
Natural resources: petroleum, natural gas, asphalt
Land use:
arable land:
15%
permanent crops:
9%
permanent pastures:
2%
forests and woodland:
46% (Based on reported rates of deforestation this figure is actually likely to be closer to 35%)
other:
28% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 220 sq km (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: outside usual path of hurricanes and other tropical storms
Environment - current issues: water pollution from agricultural chemicals, industrial wastes, and raw sewage; oil pollution of beaches; deforestation; soil erosion
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements