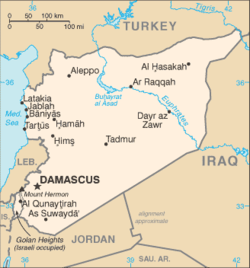
Geography of Syria
|
|
| Syria | |
| Continent | Asia |
| Region | Southwest Asia |
| Coordinates | Template:Coor dm |
| Area | Ranked 87 185,180 km includes 1,295 km² of Israeli-occupied territory {{{miles area}}} miles² |
| Coastline | 193 km; / {{{miles coastline}}} miles² |
| Borders | 2,253 km
Iraq 605 km, Israel 76 km, Jordan 375 km, Lebanon 375 km, Turkey 822 km |
| Highest point | Mount Hermon 2,814 m |
| Lowest point | unnamed location near Lake Tiberias (Sea of Galilee) -200 m |
| Longest river | Euphrates |
| Largest lake | Lake Assad |
Syria is a country in Southwest Asia, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Lebanon and Turkey. Considered to be one of the fifteen states that comprise the so-called "Cradle of Humanity."
Area:
total:
185,180 km^2
land:
184,050 km^2
water:
1,130 km^2
note:
Land boundaries:
total:
2,253 km
border countries:
Iraq 605 km, Israel 76 km, Jordan 375 km, Lebanon 375 km, Turkey 822 km
Coastline: 193 km
Maritime claims:
contiguous zone:
41 nautical miles
territorial sea:
35 nautical miles
Climate: Orographic lift over Ansariyah Mountains brings rainfall to the coastal plain and valleys. Otherwise mostly desert; hot, dry, sunny summers (June to August) and mild, rainy winters (December to February) along coast; cold weather with snow or sleet periodically hitting Damascus.
Terrain: semiarid; Ansariyah Mountains in the west,then a narrow coastal plain progressing to desert plateau that covers most of the country. In the north, the Taurus Mountains separate Syria from Turkey, and in the southwest, the Anti-Lebanon Mountains form the border of Syria and Lebanon. The Orontes River flows northward in a valley east of the Ansariyah mountains, and the Euphrates River flows from southeast Turkey on its way to the Persian Gulf.
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
unnamed location near Lake Tiberias (Sea of Galilee) -200 m
highest point:
Mount Hermon 2,814 m
Natural resources: petroleum, phosphates, chrome and manganese ores, textiles, cotton, asphalt, iron ore, rock salt, marble, gypsum, hydropower
Land use:
arable land:
28%
permanent crops:
4%
permanent pastures:
43%
forests and woodland:
3%
other:
22% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 9,060 km^2 (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: dust storms, sandstorms
Environment - current issues: deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification; water pollution from dumping of raw sewage and wastes from petroleum refining; inadequate supplies of potable water
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Environmental Modification
Geography - note: there are 42 Israeli settlements and civilian land use sites in the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights (August 1999 est.)
- See also : Syriafr:Géographie de la Syrie