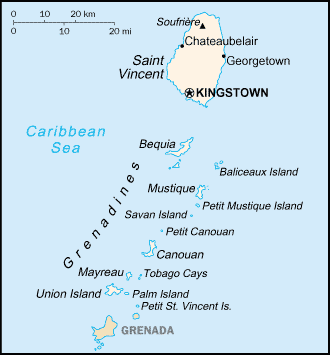
Geography of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
|
|
Location: Caribbean, islands in the Caribbean Sea, north of Trinidad and Tobago
Geographic coordinates: Template:Coor dm
Map references: Central America and the Caribbean
Area:
total:
389 kmē (Saint Vincent 344 kmē)
land:
389 kmē
water:
0 kmē
Area - comparative: twice the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 84 km
Maritime claims:
contiguous zone:
24 nautical miles (44 km)
continental shelf:
200 nautical miles (370 km)
exclusive economic zone:
200 nautical miles (370 km)
territorial sea:
12 nautical miles (22 km)
Climate: tropical; little seasonal temperature variation; rainy season (May to November)
Terrain: volcanic, mountainous
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
Caribbean Sea 0 m
highest point:
Soufriere 1,234 m
Natural resources: hydropower, cropland
Land use:
arable land:
10%
permanent crops:
18%
permanent pastures:
5%
forests and woodland:
36%
other:
31% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 10 kmē (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: hurricanes; Soufriere volcano on the island of Saint Vincent is a constant threat
Environment - current issues: pollution of coastal waters and shorelines from discharges by pleasure yachts and other effluents; in some areas, pollution is severe enough to make swimming prohibitive
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
Geography - note: the administration of the islands of the Grenadines group is divided between Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and Grenada
- See also : Saint Vincent and the Grenadines