Geography of Lithuania
|
|
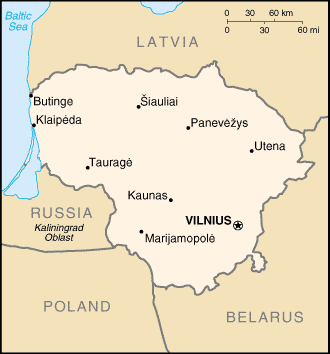
The largest and most populous of the Baltic states, Lithuania is has 60 miles of sandy coastline, of which only 24 miles face the open Baltic Sea. Lithuania's major warm-water port of Klaipeda lies at the narrow mouth of Curonian Lagoon, a shallow lagoon extending south to Kaliningrad and separated from the Baltic sea by Curonian Spit, where Kursiu Nerija National Park was established for its remarkable sand dunes.
The Neman River and some of its tributaries are used for internal shipping (in 2000, 89 inland ships carried 900,000 tons of cargo, which is less than 1% of the total goods traffic). Between 56.27 and 53.53 latitude and 20.56 and 26.50 longitude, Lithuania is glacially flat, except for morainic hills in the western uplands and eastern highlands no higher than 300 meters. The terrain is marked by numerous small lakes and swamps, and a mixed forest zone covers 30% of the country. The growing season lasts 169 days in the east and 202 days in the west, with most farmland consisting of sandy- or clay-loam soils. Limestone, clay, sand, and gravel are Lithuania's primary natural resources, but the coastal shelf offers perhaps 1.6 million m³ (10 million barrels) of oil deposits, and the southeast could provide high yields of iron ore and granite. According to some geographers, the Geographical Center of Europe is just north of Lithuania's capital, Vilnius.
Location: Northeastern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, between Latvia and Russia
Geographic coordinates: Template:Coor dm
Map references: Europe
Area:
total:
65,200 kmē
land:
65,200 kmē
water:
0 kmē
Area - comparative: slightly larger than West Virginia
Land boundaries:
total:
1,273 km
border countries:
Belarus 502 km, Latvia 453 km, Poland 91 km, Russia (Kaliningrad) 227 km
Coastline: 99 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea:
12 nautical miles
Climate: transitional, between maritime and continental; wet, moderate winters and summers
Terrain: lowland, many scattered small lakes, fertile soil
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
Baltic Sea 0 m
highest point:
Juozapines/Kalnas 292 m
Natural resources: peat, arable land
Land use:
arable land:
35%
permanent crops:
12%
permanent pastures:
7%
forests and woodland:
31%
other:
15% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 430 kmē (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: NA
Environment - current issues: contamination of soil and groundwater with petroleum products and chemicals at military bases
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
Related article
External link
- Kursiu Nerija National Park (http://www.nerija.lt/en/info)lt:Lietuvos geografija