Geography of Iraq
|
|
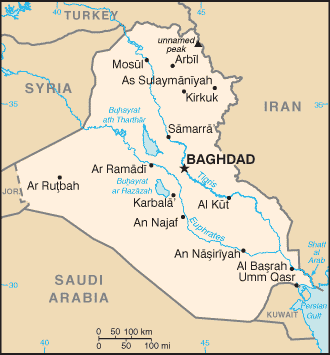
Iraq is bordered by Kuwait, Iran, Turkey, Syria, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia. The country slopes from mountains over 3,000 meters (10,000 ft) above sea level along the border with Iran and Turkey to the remnants of sea-level, reedy marshes in the southeast. Much of the land is desert or wasteland.
The mountains in the northeast are an extension of the alpine system that runs eastward from the Balkans into southern Turkey, northern Iraq, Iran, and Afghanistan, terminating in the Himalayas.
Average temperatures range from higher than 48 °C (120 °F) in July and August to below freezing in January. Most of the rainfall occurs from December through April and averages between 100 and 180 millimeters (4 to 7 in) annually. The mountainous region of northern Iraq receives appreciably more precipitation than the central or southern desert region.
Location: Southwest Asia, bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iran and Kuwait
Map references: Southwest Asia
Geographic coordinates: Template:Coor dm
Area:
total: 437,072 km²
land: 432,162 km²
water: 4,910 km²
Land boundaries:
total: 3,631 km
border countries: Iran 1,458 km, Jordan 181 km, Kuwait 242 km, Saudi Arabia 814 km, Syria 605 km, Turkey 331 km
Coastline: 58 km
Maritime claims:
continental shelf: not specified
territorial sea: 12 nautical miles (22.2 km)
Climate: mostly desert; mild to cool winters with dry, hot, cloudless summers; northern mountainous regions along Iranian and Turkish borders experience cold winters with occasionally heavy snows that melt in early spring, sometimes causing extensive flooding in central and southern Iraq
Terrain: mostly broad plains; reedy marshes along Iranian border in south with large flooded areas; mountains along borders with Iran and Turkey
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Persian Gulf 0 m
highest point: Haji Ibrahim 3,600 m
Natural resources: petroleum, natural gas, phosphates, sulfur
Land use:
arable land: 12%
permanent crops: 0%
permanent pastures: 9%
forests and woodland: 0%
other: 79% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 25,500 km² (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: dust storms, sandstorms, floods
Environment - current issues: government water control projects have drained most of the inhabited marsh areas east of An Nasiriyah by drying up or diverting the feeder streams and rivers; a once sizable population of Shi'a Muslims, who have inhabited these areas for thousands of years, has been displaced; furthermore, the destruction of the natural habitat poses serious threats to the area's wildlife populations; inadequate supplies of potable water; development of Tigris-Euphrates Rivers system contingent upon agreements with upstream riparian Turkey; air and water pollution; soil degradation (salination) and erosion; desertification
Environment - international agreements:
party to: Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban
signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification
- Major ecoregions : PA1303 | PA1320
- Minor ecoregions : PA0446 | PA1320 | PA0812 | PA1207 | PA1305 | PA1328 | PA0906 | PA1325 | PA1323