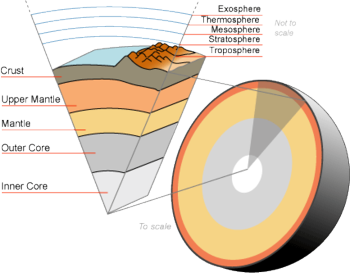
Crust (geology)
|
|
In geology, a crust is the outer layer of a planet, part of its lithosphere. Planetary crusts are generally composed of a less dense material than that of its deeper layers. The crust of the Earth is composed mainly of basalt and granite. It is cooler, harder and stronger than the deeper layers of the mantle and core.
On partially-molten planets, such as Earth, the lithosphere is floating on fluid interior layers. Because of the partially-fluid upper mantle, or asthenosphere, underneath, floating lithospheres are often broken into tectonic plates that move. On Earth, the crust beneath the oceans is different from that of the continents. The oceanic crust (sima) is 5 to 10 km thick and is composed primarily of a dark, dense rock called basalt. The continental crust (sial) is 20-70 km deep and is composed mainly of a light-colored, less dense rock called granite.