Consumer theory
|
|
Consumer theory relates preferences, indifference curves and budget constraints to consumer demand curves.
| Contents |
Indifference curves and budget constraints
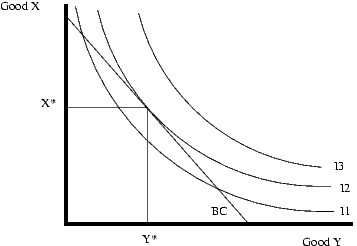
Using indifference curves and an assumption of constant prices and a fixed income in a two good world will give the following diagram. The consumer can choose any point on or below the budget constraint line BC. This line is diagonal since it comes from the equation <math>X \times px + Y \times py \leq Income<math>. In other words, the amount spent on both goods together is less than or equal to the income of the consumer. The consumer will choose the indifference curve with the highest utility that is within the budget constraint. I3 has all the points outside of their budget constraint so the best that they can do is I2. This will result in them purchasing X* of good X and Y* of good Y.
Price effects
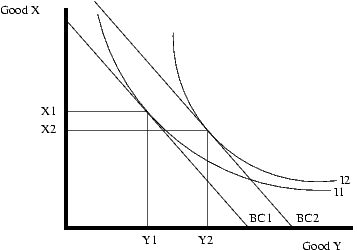
More usefully, this can now be used to predict the effect of various shifts in the constraint. The below graphic shows the effect of a price shift for good y. If the price of Y increases from where it is at BC2, the budget constraint will shift to BC1. Notice that since the price of X does not change, the consumer can still buy the same amount of X if they only choose to buy good X. On the other hand, if they choose to buy only good Y, they will be able to buy less of good Y since its price has increased.
To maximize the utility with the reduce budget constraint, BC1, the consumer will re-allocate consumption to reach the highest available indifference curve which BC1 can touch. As shown on the diagram below, that curve is I1, and therefore the amount of good Y bought will shift from Y2 to Y1, and the amount of good X bought to shift from X2 to X1. The opposite effect will occur if the price of Y decreases causing the shift from BC2 to BC3, and I2 to I3.
Missing image
Consumer_constraint_choice_price_shift.png
link to shifting price of good y and quanity of goods consumed as a result
If this shifts are repeated with many different prices for good Y, a demand curve for good Y can be constructed. If the price for good Y is fixed and the price for good X is varied, a demand curve for good X can be constructed. The below diagram shows this for good y.
Missing image
Found_demand.png
example of going from indifference curves to demand curve
Income effect
Another important item that can change is the income of the consumer. As long as the prices remain constant, changing the income will create a parallel shift of the budget constraint. Increasing the income will shift the budget constraint right since more of both can be bought, and decreasing income will shift it left.
Missing image
Consumer_constraint_choice_income_shift.png
link to shifting income of consumer and quntity of goods consumed as a result
Depending on the indifference curves the amount of a good bought can either increase, decrease or stay the same when income increases. In the diagram below, good Y is a normal good since the amount purchased increased as the budget constraint shifted from BC1 to the higher income BC2. Good X is an inferior good since the amount bought decreased as the income increases.
Substitution effect
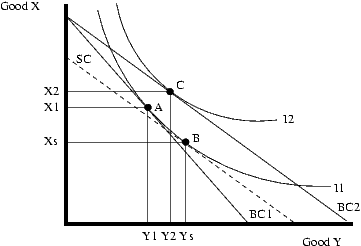
Every price change can be converted into an income effect and a substitution effect. The substitution effect is basically a price change that changes the slope of the budget constraint, but leaves the consumer on the same indifference curve. This effect will always cause the consumer to substitute away from the good that is becoming comparatively more expensive. If the good in question is a normal good, then the income effect will re-enforce the substitution effect. If the good is inferior, then the income effect will lessen the substitution effect. If the income effect is opposite and stronger than the substitution effect, the consumer will buy more of the good when it becomes more expensive. There is a generally agreed upon example of this happening, known as a Giffen good.
See also
|
Topics in microeconomics | Edit (http://en.wikipedia.org/w/wiki.phtml?title=MediaWiki:Microeconomics-footer&action=edit) |
| Scarcity | Opportunity cost | Supply and demand | Elasticity | Economic surplus | Aggregation of individual demand to total, or market, demand | Consumer theory | Production, costs, and pricing | Market form | Welfare economics | Market failure |