CERES
|
|
- For the first asteroid to be discovered, see 1 Ceres
- For the Melbourne community environment park, see the Centre for Education and Research in Environmental Strategies
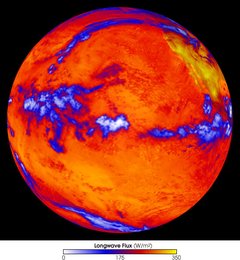
CERES (Clouds and the Earth's Radiant Energy System) is an on-going NASA metereological experiment in Earth orbit. It is designed to measure the Earth's radiation flux and provide estimates of cloud properties of the surface of the Earth.
The first set of CERES instruments was one of five payload scientific instruments launched by NASA into Earth orbit in 1999 on board the Terra satellite . A second set of CERES devices was launched in May 2002 as a payload of the Aqua satellite.
The CERES measurements allow the assessment of the role of cloud cover in radiative fluxes from the surface to the top of the atmosphere. One of the two instruments operates in cross track scan mode and essentially continues the measurements of the Earth Radiation Budget Experiment (ERBE) mission as well as the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM). The second instrument operates in biaxial scan mode and provides new angular flux information, which is considered useful in improving the accuracy of angular models used to derive the Earth's radiation balance.
External link
- Official NASA site (http://aqua.nasa.gov/)
- Visible Earth: Latest CERES images (http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/Sensors/Terra/CERES.html)