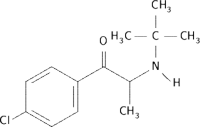
Bupropion
|
|
Bupropion | |
| (±)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-2-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-1-propanone | |
| Empiric formula | C13H18ClNO |
| Molecular weight | 239.74 |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half life | 20 hours |
| Excretion | Urine |
| ATC code | N07BA02 |
| Pregnancy category | B (USA) ? (Aus) |
Bupropion (amfebutamone) is an antidepressant of the aminoketone class, chemically unrelated to tricyclics or SSRIs. It is similar in structure to the stimulant cathinone, and to phenethylamines in general.
| Contents |
History
Bupropion was first synthesized by Burroughs Research in 1966, and patented by Burroughs-Wellcome (later Glaxo-Wellcome) in 1974. It was approved by the FDA in 1985 and marketed under the name Wellbutrin as an antidepressant, but clinical trials indicated that incidence of seizure was two to four times greater than other antidepressants and the drug was quickly pulled from the market. Glaxo, realizing that seizure risk was a function of dosage, then developed and marketed a sustained-release (SR) version of Wellbutrin which, when ingested, releases bupropion hydrochloride at a constant, gradual rate into the body. Because of this altered mechanism of delivery, incidence of seizure with Wellbutrin-SR is comparable to, and in some cases, lower than that of other antidepressants.
In 1997, bupropion HCl was approved by the FDA for use as a smoking cessation aid. Because the name Wellbutrin was still associated with high seizure risk, the drug was subsequently marketed by Glaxo under the name Zyban to help people stop smoking tobacco by reducing the severity of withdrawal symptoms. It can be used in combination with nicotine replacement therapies. Bupropion treatment course lasts for seven to twelve weeks, the patient halting the use of tobacco around ten days into the course.
It is contraindicated in people taking medication for seizure disorders (phenytoin, phenobarbital), with bulimia or anorexia, with kidney or liver dysfunctions, or people already taking any monoamine oxidase inhibitor. It can also cause problems with cold remedies, certain herbal supplements, creatine, cimetidine, ephedrine, and benzodiazepines.
Mode of action
Bupropion is a selective catecholamine (norepinephrine and dopamine) reuptake inhibitor. It has only a small effect on serotonin reuptake. It does not inhibit MAO. The actual mechanism behind bupropion's action is not known, but it is thought to be due to the effects on dopaminergic and noradrenergic mechanisms.
Pharmacokinetics
Bupropion is metabolised in the liver. It has at least three active metabolites; hydroxybupropion, threohydrobupropion and erythrohydrobupropion. These active metabolites are further metabolised to inactive metabolites and eliminated through excretion into the urine. The half-life of bupropion is 20 hours as is hydroxybupropion's. Threohydrobupropion's half-life is 37 hours and erythrohydrobupropion's 33 hours.
Pills
Wellbutrin pills are available in three forms: immediate release, sustained release (SR) and extended release (XL). Generic forms of immediate and sustained release are available.
| Brand Name | Dosage | Color |
| Wellbutrin | 75 mg | yellow-gold |
| Wellbutrin | 100 mg | red |
| Wellbutrin SR | 100 mg | blue |
| Wellbutrin SR | 150 mg | purple |
| Wellbutrin SR | 200 mg | pink |
| Wellbutrin XL | 150 mg | white |
| Wellbutrin XL | 300 mg | white |
| Zyban | ??? mg | ??? |
| Zyban SR | 150 mg | purple |
Side effects
Common side effects include dry mouth, tremors, anxiety, loss of appetite, agitation, dizziness, headache, excessive sweating, increased risk of seizure, and insomnia. Bupropion causes less insomnia if it is taken just before going to bed.
External links
- Wellbutrin Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Studies, Metabolism - Bupropion - RxList Monographs (http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic/buprop_cp.htm)
- NAMI Wellbutrin (http://www.nami.org/Template.cfm?Section=About_Medications&template=/ContentManagement/ContentDisplay.cfm&ContentID=7388)
- Bupropion: What Mechanism of Action? (http://www.preskorn.com/columns/0001.html)
- Discovery Health Channel: Drug Reference Center: bupropion (oral) (http://health.discovery.com/encyclopedias/reference/drug.jsp?drug=47395)