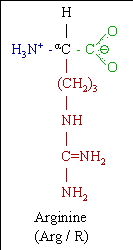
Arginine
|
|
Arginine is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. It has a guanidine side chain functional group. In non-hepatic tissues, arginine can be biosynthesized by the ornithine cycle (or urea cycle). Even so, arginine is often classed as one of the 10 essential amino acids. This need, evidently, is restricted to children.
Arginine molecule
- One letter symbol:R
- Three letter symbol:Arg
- Molecular Weight:174.2
- Isolectric point (pH):11.15
- Molecular Formula: C6H14N4O2
Physiology
Arginine is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids on Earth, and coded for by DNA. In non-hepatic tissues, arginine can be biosynthesized by the ornithine cycle. Even so, arginine is often classed as one of the 10 essential amino acids. This need evidently is restricted to children.
Arginine plays an important role in cell division, the healing of wounds, removing ammonia from the body, immune function, and the release of hormones. It can be found in many foods such as meat, poultry, dairy products, and fish. The body also uses arginine to produce nitric oxide, which relaxes blood vessels. For this reason, it has been used to treat cardiovascular disorders such as heart failure, intermittent claudication, impotence, female sexual dysfunction, and interstitial cystitis.
Arginine can be decarboxylated, yielding agmatine. Conversion by nitric oxide synthase to citrulline also yields the vasoactive mediator nitric oxide. Hence, its use is considered in many conditions where vasodilation is required.
Template:Biochem-stubde:Arginin es:Arginina eo:Arginino fr:Arginine it:Arginina nl:Arginine ja:アルギニン pl:Arginina ru:Аргинин sv:Arginin