Antique province
|
|
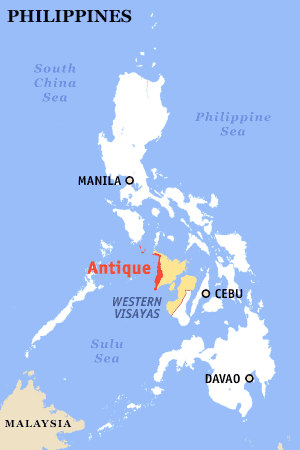
Antique P is a province of the Philippines located in the Western Visayas region. Its capital is San Jose and is located at the western portion of Panay island, bordering Aklan, Capiz, and Iloilo to the east. Antique faces the Sulu Sea to the west.
2000 census—471,088 (26th smallest)
Density—187 per km² (46th highest)
Highly urbanized cities—0
Component cities—0
Municipalities—18
Barangays—590
Congressional districts—1
Antique was one of the three old sakups (districts) of Panay before the Spanish colonizers arrived in the islands. The Antique was then known as Hantik, which was named from the large red ants found on the island, called lantik-lantik. (See History section below.)
| Contents |
People and Culture
Economy
Geography
Political
Antique is subdivided into 18 municipalities.
Municipalities
Physical
Antique is mostly isolated from the rest of the island of Panay by the Cordilleras of the island. The province's borders with its three neighbors lie on the divide of this mountain range. Antique faces the northern portions of the Sulu Sea to the west. The Semirara Islands, located between Panay and Mindoro are part of Antique.
History
Early History: The Legend of Maragtas. Historians believe that the earliest people who settled on the island of Panay were tribal Negritos or Atis. The popular folk legend, Maragtas, gives an account of the early events in the province. The legend states that in 1212, ten Malay datus escaped persecution from Sri-Vishaya, a Hindu-Malay empire that existed at that time in Borneo and Sumatra. These datus, led by Datu Puti, sailed with their families and communities from Borneo northward and landed on Panay.
There, they met the Negrito chieftain, Marikudo. They bought the island from the chieftain for a golden saduk (headpiece or helmet), and a golden necklace, among other gifts. The Negritos then retreated to the mountains, while the Borneans settled in the lowlands. Today, the landing is commemorated every year in Antique in the Binirayan festival.
The island of Panay was then divided into three sakups (districts). These are Hantik, Aklan, and Irong-Irong. Aklan became the present-day Aklan and Capiz, Irong-Irong became Iloilo, and Hantik (also called Hamtik or Hamtic) became Antique. Hantik was named for the large red ants found on the island called lantik-lantik.
The sakup of Hantik was given to Datu Sumakwel, one of the ten datus, and who, according to tradition, was the oldest and wisest of them. The three sakups were later governed as a political unit called the Confederation of Madia-as, also under Datu Sumakwel.
Datu Sumakwel founded the town of Malandog, considered to be the first Malay settlement in the country. Malandog is now a barangay in the present-day municipality of Hamtic, which was named after the historic sakup.
The Spanish Period. ...
External links
- Official Website of the Provincial Government of Antique
References
- Vanzi, Sol Jose. “The Many Facets of Antique.” Philippine Headline News Online. [1] (http://www.newsflash.org/2003/05/ht/ht003434.htm)
- Website of the Provincial Government of Antique (old) [2] (http://www.geocities.com/antiquegov)
- The Antique Circle USA. [3] (http://members.tripod.com/ACUSA_1/home_eng/antique_circle_u2.htm)
| Regions and Provinces of Visayas | |
| Western Visayas: | Aklan | Antique | Capiz | Guimaras | Iloilo | Negros Occidental |
| Central Visayas: | Bohol | Cebu | Negros Oriental | Siquijor |
| Eastern Visayas: | Biliran | Eastern Samar | Leyte | Northern Samar | Samar | Southern Leyte |

