555 timer IC
|
|
The 555 is an integrated circuit (chip) implementing a variety of timer and multivibrator applications. The IC was was designed and invented by Hans R. Camezind. It was designed in 1970 and introduced in 1971 by Signetics (later acquired by Philips). The original name was the SE555/NE555 and was called "The IC Time Machine". It is still in wide use, thanks to its ease of use, low price and good stability. Still today, Samsung in Korea manufactures over 1 billion units per year (2003).
The 555 timer is one of the most popular and versatile integrated circuits ever produced. It includes 23 transistors, 2 diodes and 16 resistors on a silicon chip installed in an 8-pin mini dual-in-line package (DIP). The 556 is a 14-pin DIP that combines two 555s on a single chip. The 558 is a 16-pin DIP that combines four, slightly modified, 555s on a single chip (DIS & THR are connected internally, TR is falling edge sensitive instead of level sensitive). Also available are ultra-low power versions of the 555.
The 555 has three operating modes:
- Monostable mode: in this mode, the 555 functions as a "one-shot". Applications include timers, missing pulse detection, bouncefree switches, touch switches, etc.
- Astable mode: the 555 can operate as an oscillator. Uses include LED and lamp flashers, pulse generation, logic clocks, tone generation, security alarms, etc.
- Bistable mode: the 555 can operate as a flip flop, if the DIS pin is not connected and no capacitor is used. Uses include bouncefree latched switches, etc.
| Contents |
Usage
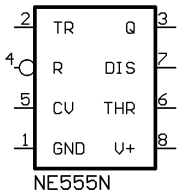
The connection of the pins is as follows:
| Nr. | Name | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | TR | A short pulse on the trigger starts the timer |
| 3 | Q | During a timing interval, the output stays at +VCC |
| 4 | R | A timing interval can be interrupted by applying a reset pulse |
| 5 | CV | Control voltage allows access to the internal voltage divider (2/3 VCC) |
| 6 | THR | The threshold at which the interval ends |
| 7 | DIS | Connected to a capacitor whose discharge time will influence the timing interval |
| 8 | V+, VCC | The positive supply voltage which must be between 5 and 15 V |
Using simply a capacitor and a resistor, the timing interval, i.e. the time during which the output stays low, can be adjusted to the need of the specific application. An example configuration is shown below:
555-schem-2.png
Example 555 schematic
Example 555 schematic
The interval time t is given by
- <math>t = RC<math>
which is the time it takes to charge C to 63% of the applied voltage (exact figure: (1-1/e)V). See RC circuit for an explanation of this effect.
Specifications
These specifications apply to the NE555. Other 555 timers can have better specifications depending on the grade (military, medical, etc).
| Supply voltage (VCC) | 4.5 to 15 V |
| Supply current (VCC = +5 V) | 3 to 6 mA |
| Supply current (VCC = +15 V) | 10 to 15 mA |
| Output current (maximum) | 200 mA |
| Power dissipation | 600 mW |
| Operating temperature | 0 to 70° C |
Derivatives
Photo555.jpg
Many pin-compatible variants, including CMOS versions, have been built by various companies. The 555 is also known under the following type numbers:
| Manufacturer | Model |
|---|---|
| ECG Philips | ECG955M |
| Exar | XR-555 |
| Fairchild | NE555/KA555 |
| Harris | HA555 |
| Intersil | SE555/NE555 |
| Lithic Systems | LC555 |
| Maxim | ICM7555 |
| Motorola | MC1455/MC1555 |
| National | LM1455/LM555C |
| NTE Sylvania | NTE955M |
| Raytheon | RM555/RC555 |
| RCA | CA555/CA555C |
| Sanyo | LC7555 |
| Texas Instruments | SN52555/SN72555 |
External links
- 555 Timer Tutorial (http://www.uoguelph.ca/~antoon/gadgets/555/555.html)
- Data Sheet (Fairchild) (http://www.fairchildsemi.com/ds/NE/NE555.pdf)
- Java simulation (http://www.falstad.com/circuit/ex-555.html) of 555 oscillator circuit