4179 Toutatis
|
|
| Discovery A (http://cfa-www.harvard.edu/iau/lists/NumberedMPs.html) | |
|---|---|
| Discoverer | Christian Pollas |
| Discovery date | January 4, 1989 |
| Alternate designations | 1934 CT; 1989 AC B (http://cfa-www.harvard.edu/iau/MPDes.html) |
| Category | Apollo, Alinda, Mars-crosser |
| Orbital elements C (http://asteroid.lowell.edu/) Epoch October 22, 2004 (JD 2453300.5) | |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.635 |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 377.326 Gm (2.522 AU) |
| Perihelion (q) | 137.739 Gm (0.921 AU) |
| Aphelion (Q) | 616.914 Gm (4.124 AU) |
| Orbital period (P) | 1463.140 d (4.01 a) |
| Mean orbital speed | 16.69 km/s |
| Inclination (i) | 0.446° |
| Longitude of the ascending node (Ω) | 122.777° |
| Argument of perihelion (ω) | 280.059° |
| Mean anomaly (M) | 358.877° |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 4.5×2.4×1.9 km |
| Mass | 5.0×1013 kg |
| Density | 2.1 g/cm³ |
| Surface gravity | 0.0010 m/s² |
| Escape velocity | 0.0019 km/s |
| Rotation period | 5.41+7.35 d |
| Spectral class | S |
| Absolute magnitude | 15.30 |
| Albedo | 0.13 |
| Mean surface temperature | ~174 K |
The asteroid 4179 Toutatis (too-ta'-tis) is an Apollo, an Alinda and a Mars-crosser asteroid with a chaotic orbit produced by a 3:1 resonance with the planet Jupiter. Due to its very low orbital inclination (0.47°) and its orbital period of very nearly 4 years, Toutatis makes frequent close approaches to Earth, with a minimum distance at present of just 0.006 AU (2.3 times as far as the Moon). The approach on September 29, 2004 was particularly close, at 0.0104 AU (within 4 lunar distances) from Earth, presenting a good opportunity for observation. The next approach after that will be November 9, 2008 at 0.0503 AU.
Its rotation combines two separate periodic motions into a non-periodic result; to someone on the surface of Toutatis the Sun would seem to rise and set in apparently random locations and at random times at the asteroid's horizon.
It was discovered on January 4, 1989 by Christian Pollas and was named after the Celtic deity Toutatis, a Gallic war god.
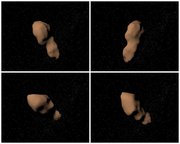
Radar imagery has shown that Toutatis is a highly irregular body consisting of two distinct "lobes", with maximum widths of about 4.6 km and 2.4 km respectively. It is hypothesized that Toutatis formed from two originally separate bodies which coalesced at some point, with the resultant asteroid being compared to a "rubble pile".
Just how close is that?
To put the September 29, 2004 approach in perspective, imagine the asteroid and the Earth as two race cars, on two racetracks that represent their two orbits. The asteroid's track is about the length of the Indianapolis Motor Speedway, but wider: 1.5 km long and 1.2 km wide. Earth's track would be a circle 600 m (650 yards) in diameter located inside the asteroid's track, intersecting it near one end. At this scale, when the two speeding cars reach the intersection, they would pass within 3.2 m (10.2 ft, or two-thirds of a car-length) of each other, and could theoretically pass within 1.8 m (6 ft) of each other.
The analogy breaks down, however, when one notes that the real "tracks" (representing the orbits) are not fixed in space and could be perturbed in the future.
Related topics
External links
- Toutatis Home Page (http://www.astrosurf.com/maury/asteroides/toutatis.html) - by one of the asteroid's discoverers
- Space.com: Video of Toutatis's close approach to Earth, 29 Sept, 2004 (http://space.com/scienceastronomy/toutatis_video_040929.html)
- Interesting views of asteroid (http://www.solarviews.com/eng/toutatis.htm)
| The minor planets |
| Vulcanoids | Main belt | Groups and families | Near-Earth objects | Jupiter Trojans |
| Centaurs | Trans-Neptunians | Damocloids | Comets | Kuiper belt | Oort cloud |
| (For other objects and regions, see: Binary asteroids, Asteroid moons and the Solar system) |
| (For a complete listing, see: List of asteroids. For pronunciation, see: Pronunciation of asteroid names.) |
de:Toutatis (Asteroid) et:4179 Toutatis es:(4179) Tutatis fr:(4179) Toutatis nl:4179 Toutatis pl:Toutatis (planetoida)