2C-T-7
|
|
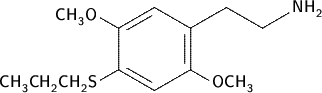
2C-T-7 (Sulfurous Samadhi) is a psychedelic phenethylamine presumably first synthesized in 1986 by Alexander Shulgin, sometimes used as an entheogen; it has structural and pharmacodynamic properties similar to the drugs Mescaline, MDMA, and 2C-B. In Shulgin's book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines I Have Known and Loved), the dosage range is listed as 10 to 30 mg. Chemically 2C-T-7 is 4-propylthio-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine, with the formula C12H21O2NS. 2C-T-7 has been sold on the street under the names "Blue Mystic" and "Tweetybird Mescaline".
Around the year 2000, 2C-T-7 began to change from an obscure chemical to a drug used at parties and clubs in North America and Europe as it became available through a number of grey-market commercial vendors. There have been at least three reported deaths related 2C-T-7 use, and in January of 2002, Rolling Stone Magazine published an article about 2C-T-7 entitled "The New (legal) Killer Drug".
On September 20, 2002, 2C-T-7 was classified as a Schedule I substance in the United States by an emergency ruling by the DEA.
Categorization
Template:Hallucinogenic phenethylamines
See also
External links
- PiHKAL #43 2C-T-7 (http://www.erowid.org/library/books_online/pihkal/pihkal043.shtml)
- Sulfurous Samadhi: An Investigation of 2C-T-2 & 2C-T-7 (http://www.erowid.org/chemicals/2ct7/article1/article1.shtml)