Burkina Faso
|
|
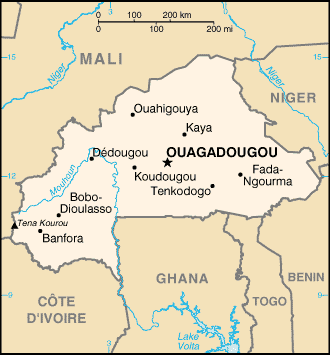
Burkina Faso is a landlocked nation of western Africa. It is surrounded by six countries. Mali to the north, Niger to the east, Benin to the south east, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Côte d'Ivoire to the south west.
| |||||
| Motto: Unité, Progrès, Justice (French: Unity, Progress, Justice) | |||||
| Anthem: Une Seule Nuit (One Single Night) | |||||
| |||||
| Capital | Ouagadougou Template:Coor dm | ||||
| Largest city | Ouagadougou | ||||
| Official languages | French | ||||
| Government | Parliamentary system Blaise Compaoré Paramanga Ernest Yonli | ||||
| Independence - Date | From France August 5, 1960 | ||||
| Area • Total • Water (%) | 274,200 km² (72nd) 0.1% | ||||
| Population • 2005 est. • 2003 census • Density | 13,925,313 (63rd) 13,228,460 51/km² (119) | ||||
| GDP (PPP) • Total • Per capita | 2005 estimate 16,9161 (115) 1,326 (170) | ||||
| Currency | CFA franc (XOF)
| ||||
| Time zone • Summer (DST) | GMT (UTC) not observed (UTC) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .bf | ||||
| Calling code | +226
| ||||
| 1 The data here is an estimation for the year 2005 produced by the International Monetary Fund in April 2005. | |||||
Formerly called Upper Volta, it was renamed on August 4, 1984 by President Thomas Sankara to mean "the land of upright people" (or "upright land") in Mossi and Dioula, the major native languages of the country. Independence from France came in 1960. Governmental instability during the 1970s and 1980s was followed by multiparty elections in the early 1990s. Several hundred thousand farm workers migrate south every year to Côte d'Ivoire and Ghana.
The inhabitants of Burkina Faso are called Burkinabe. The capital is Ouagadougou, referred to by locals as "Ouaga."
| Contents |
History
- Main article: History of Burkina Faso
Prehistory
Like all of the west of Africa, Burkina Faso was populated early, notably by hunter-gatherers in the north-western part of the country (12 000 to 5000 BC), and whose tools (scrapers, chisels and arrowheads) were discovered in 1973. Settlements appeared between 3600 and 2600 BC with farmers, the traces of whose structures leave the impression of relatively permanent buildings. The use of iron, ceramics and polished stone developed between 1500 and 1000 BC, as well as a preoccupation with spiritual matters, as shown by the burial remains which have been discovered.
Relics of the Dogon are found in the centre-north, north and north west region. They left the area between the 15th and 16th centuries BC to settle in the cliffs of Bandiagara. Elsewhere, the remains of high walls are localised in the south west of Burkina Faso (as well as in the Côte d'Ivoire), but the people who built them have not yet been definitely identified.
Burkina Faso was an important economic region for the Songhai Empire during the 15th and 16th centuries.
From colony to independence
In 1896, the Mossi kingdom of Ouagadougou became a French protectorate after being defeated by French forces. In 1898, the majority of the region corresponding to Burkina Faso today was conquered. In 1904, these territories were integrated into French West Africa in the heart of the Upper-Senegal-Niger (Haut-Sénégal-Niger) colony.
Its inhabitants participated in the First World War in the heart of the battalions of the Senegalise Infantry (Tirailleurs sénégalais). It was originally administered as part of Côte d'Ivoire colony, but became a separate colony in 1919. On March 1 1919, François Charles Alexis Édouard Hesling became the first governor of the new colony of Upper-Volta, which was broken up September 5 1932, being shared between the Côte dIvoire, Mali and Niger.
On September 4 1947 Upper-Volta was recreated with its 1932 boundaries. On December 11 1958, it achieved self-government, and became a republic and member of the Franco-African Community (La Communauté Franco-Africaine). Full independence was attained in 1960. Its first military coup occurred in 1966, then returned to civilian rule in 1978. There was another coup, led by Saye Zerbo in 1980, which in turn was overthrown in 1982. A counter-coup was launched in 1983, which left Captain Thomas Sankara in charge. The current president is Blaise Compaoré, who came to power in 1987 after a coup d'état that killed Thomas Sankara.
Politics
Template:Election burkina The constitution of June 2 1991 established a semi-presidential government with a parliament (Assemblée) which can be dissolved by the President of the Republic, who is elected for a term of 5 years. The year 2000 saw a constitutional amendment reducing the presidential term from 7 to 5 years, enforceable as from 2005, when new presidential elections will be held. Another change according to the amendment would prevent sitting president Blaise Compaore from being re-elected. However, since Compaore was elected in 1998, it is not clear, whether the amendment will be applied retroactively or not, and it now appears that President Compaore will run for re-election. The political opposition is very divided, and he is the heavy favorite to win re-election. The parliament consists of two chambers: the lower house (l'Assemblée Nationale) and the upper house (la Chambre des Représentants). There is also a constitutional chamber, composed of ten members, and an economic and social council whose roles are purely consultative.
Provinces
Main article: Provinces of Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso is divided into 45 provinces: Balé, Bam, Banwa, Bazega, Bougouriba, Boulgou, Boulkiemde, Comoe, Ganzourgou, Gnagna, Gourma, Houet, Ioba, Kadiogo, Kenedougou, Komondjari, Kompienga, Kossi, Koulpelogo, Kouritenga, Kourweogo, Leraba, Loroum, Mouhoun, Namentenga, Nahouri, Nayala, Noumbiel, Oubritenga, Oudalan, Passore, Poni, Sanguie, Sanmatenga, Seno, Sissili, Soum, Sourou, Tapoa, Tuy, Yagha, Yatenga, Ziro, Zondoma, Zoundweogo
Geography
Main article: Geography of Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso is made up of two major types of countryside:
- The larger part of the country is covered by a peneplain which forms a gently undulating landscape with, in some areas, a few isolated hills, the last vestiges of a precambrian massif.
- The south-west of the country forms a sandstone massif, where the highest peak is found: Ténakourou (749 m, 2,450 ft). The massif is bordered by sheer cliffs up to 150 m (490 ft) high.
The average altitude is 400 m (1,300 ft) and the difference between the highest and lowest terrain is no greater than 600 m (2,000 ft). Burkina Faso is therefore a relatively flat country, with a very few localised exceptions.
Hydrography
The country owed its former name of Upper Volta to three rivers which cross it: le Mouhoun (formerly called the Black Volta), le Nakambé (the White Volta) and le Nazinon (the Red Volta). Le Mouhoun, along with la Comoé which flows to the south west, is the country's only river which flows year-round.
The basin of the Niger River also drains 27% of the country's surface. Its tributaries (le Béli, le Gorouol, le Goudébo and le Dargol) are seasonal streams, and only flow for 4 to 6 months a year but can cause large floods.
The country also contains numerous lakes. The principal lakes are Tingrela, Bam and Dem, and the large ponds of Oursi, Béli, Yomboli and Markoye.
Water shortages are often a problem, especially in the north of the county.
Climate
Burkina Faso has a primarily tropical climate with two very distinct seasons: the rainy season with between 600 and 900 mm (24-35 inches) of rainfall, and the dry season during which the harmattan blows, a hot dry wind from the Sahara. The rainy season lasts approximately 4 months, May/June to September, and is shorter in the north of the country.
Three large climatic zones can be defined:
The Sahel zone
The Sahel in the north receives less than 600 mm (24 inches) rainfall a year and high temperatures (15-45 degrees C, 60-110 deg F). A relatively dry tropical savanna, the Sahel extends beyond the borders of Burkina Faso, from the Horn of Africa to the Atlantic Ocean, and borders the Sahara to its north, and the fertile region of the Sudan to the South.
The Sudan-Sahel zone
Situated between 11°3' and 13°5' north latitude, the Sudan-Sahel region is a transitional temperate zone with regards to rainfall and temperature.
The Sudan-Guinea zone
Further to the south, the Sudan-Guinea zone receives more than 900 mm (35 inches) rain a year and cooler average temperatures.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso is one of the poorest countries in the world. This can be explained by its population growth and its arid soil. Agriculture represents 32% of its gross domestic product and occupies 80% of the working population. It consists mostly of livestock but also, especially in the south and southwest, of growing sorghum, millet, maize (corn), peanuts, rice and cotton.
Lack of work causes a high rate of emigration: for example, three million people from Burkina Faso live in Côte d'Ivoire. According to the Central Bank of Western African States (La Banque Centrale des États de l'Afrique de l'Ouest), these migrants send tens of billions of CFA francs back to Burkina Faso each year. Since the 1967 expulsions from Ghana, this situation has provoked tensions in the destination countries. The most recent crisis occurred owing to the events of 2003 in Côte d'Ivoire, which led to the return of 300 000 migrants.
A large part of the economic activity of the country is funded by international aid.
There is mineral exploitation of copper, iron and, above all, gold.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Burkina Faso
Population growth rate: 2.71% (2000 est.)
Population estimates take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2000 est.): the 11,946,065 Burkinabe belong to two major West African cultural groups--the Voltaic and the Mande. The Voltaic are far more numerous and include the Mossi, who make up about one-half of the population. Additionally, about 5,000 Europeans live in Burkina Faso.
The population is concentrated in the south and center of the country, sometimes exceeding 48 per square kilometer (125/sq. mi.). This high population density, causes annual migrations of hundreds of thousands, for seasonal employment.
Besides traditional African religions, Islam and Christianity are also practiced.
Schooling is free but not compulsory, and only about 29% of Burkina's primary school-age children receive a basic education, few Burkinabe have had formal education. Institutions of higher education include The University of Ouagadougou, and The Polytechnical University in Bobo-Dioulasso.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Burkina Faso
see also: List of writers from Burkina Faso, Music of Burkina Faso and Cinema of Burkina Faso.
Education
Main article: Education in Burkina Faso
Education in Burkina Faso is structured primary, secondary, and higher education. Education is technically free and officially mandatory until the age of 16, however only about 29% of Burkina's primary school-age children actually receive a basic education, few adult Burkinabe have had formal education. Institutions of higher education include The University of Ouagadougou, and The Polytechnical University in Bobo-Dioulasso.
Miscellaneous topics
- Music of Burkina Faso
- Communications in Burkina Faso
- Transportation in Burkina Faso
- Military of Burkina Faso
- Foreign relations of Burkina Faso
- Holidays in Burkina Faso
- Ambassadors to Burkina Faso
- List of cities in Burkina Faso
External links
Template:Portal Template:Commonscat Template:Wiktionary
Government
- Premier Ministère (http://www.primature.gov.bf/) official government portal (in French)
- Embassy of Burkina Faso in Washington, DC (http://www.burkinaembassy-usa.org/) government information and links
News
- allAfrica - Burkina Faso (http://allafrica.com/burkinafaso/) news headline links
Overviews
- BBC News - Country Profile: Burkina Faso (http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/africa/country_profiles/1032616.stm)
- CIA World Factbook - Burkina Faso (http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/uv.html)
Directories
- LookSmart - Burkina Faso (http://search.looksmart.com/p/browse/us1/us317836/us317916/us559898/us559899/us10065674/us559905) directory category
- Open Directory Project - Burkina Faso (http://dmoz.org/Regional/Africa/Burkina_Faso/) directory category
- Stanford University - Africa South of the Sahara: Burkina Faso (http://www-sul.stanford.edu/depts/ssrg/africa/burkina.html) directory category
- University of Pennsylvania - African Country Studies: Burkina Faso (http://www.sas.upenn.edu/African_Studies/Country_Specific/Burkina.html)
- Yahoo! - Burkina Faso (http://dir.yahoo.com/Regional/Countries/Burkina_Faso/) directory category
Tourism
Other
- Burkina Faso Official wikipedia (French only) (http://www.thomassankara.net/wiki/)
- History of Burkina Faso (French only) (http://www.burkinbila.net/modules.php?name=Burkina)
- Fotos from Burkina Faso (http://www.helge.at/photos/burkina2003/)
- OuagaNet.com: A portal site about Burkina Faso English/French (http://www.ouaganet.com/)
- Burkina Faso map and information page by World Atlas (http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/africa/bf.htm)
| Countries in Africa | ||
|
Algeria | Angola | Benin | Botswana | Burkina Faso | Burundi | Cameroon | Cape Verde | Central African Republic | Chad | Comoros | Democratic Republic of the Congo | Republic of the Congo | Côte d'Ivoire | Djibouti | Egypt | Equatorial Guinea | Eritrea | Ethiopia | Gabon | The Gambia | Ghana | Guinea | Guinea-Bissau | Kenya | Lesotho | Liberia | Libya | Madagascar | Malawi | Mali | Mauritania | Mauritius | Morocco | Mozambique | Namibia | Niger | Nigeria | Rwanda | São Tomé and Príncipe | Senegal | Seychelles | Sierra Leone | Somalia | Somaliland | South Africa | Sudan | Swaziland | Tanzania | Togo | Tunisia | Uganda | Zambia | Zimbabwe | Western Sahara | ||
| Dependencies: Canary Islands | Ceuta and Melilla | Madeira Islands | Mayotte | Réunion | Saint Helena and dependencies | ||
bn:বুর্কিনা ফাসো ca:Burkina Faso cs:Burkina Faso da:Burkina Faso de:Burkina Faso et:Burkina Faso es:Burkina Faso eo:Burkino fr:Burkina Faso gd:Burkina Faso gl:Burquina Faso - Burkina Faso ko:부르키나파소 ht:Boukina Faso io:Burkina-Faso id:Burkina Faso ia:Burkina Faso it:Burkina Faso he:בורקינה פאסו ks:बुर्कीना-फासो lv:Burkinafaso lt:Burkina Fasas ms:Burkina Faso na:Burkina Faso nl:Burkina Faso nn:Burkina Faso nds:Burkina Faso ja:ブルキナファソ no:Burkina Faso pl:Burkina Faso pt:Burkina Faso ro:Burkina Faso ru:Буркина-Фасо sa:बुर्कीना-फासो sq:Burkina Faso scn:Burchina Fasu sk:Burkina sl:Burkina Faso fi:Burkina Faso sv:Burkina Faso tr:Burkina Faso uk:Буркіна Фасо zh:布吉納法索