|
|
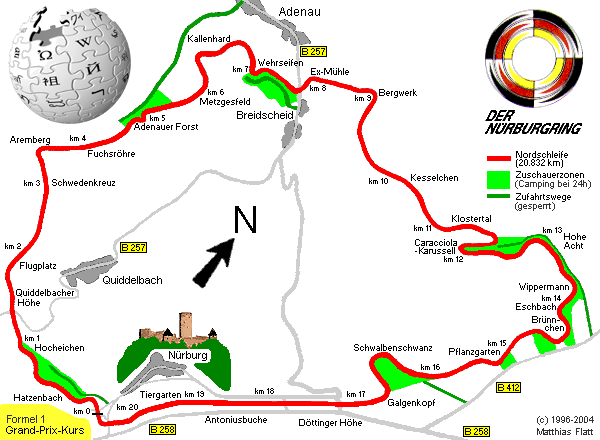
The Nürburgring (alternative spelling: Nuerburgring; known as simply "the Ring" by enthusiasts) is the name of a famous road circuit for autos or motorcycles in Germany, of which there are several configurations. Built around the village and medieval castle of Nürburg in the Eifel mountains, the older version of the Ring is widely considered the toughest and most demanding race track in the world, nicknamed The Green Hell by Jackie Stewart.
The original Nürburgring was meant to be a showcase for German automotive engineering and racing talent, and was built with both purposes in mind. Construction of the track, designed by the Eichler Engineering Firm from Ravensburg (led by Gustav Eichler), began in September 1925. There was then a single 28.265 km (17.5 mile) circuit of, on avarage, 8 to 9 metres in width and a total of 174 bends (but note that there is much disagreement on the total number of bends), which could be split into two sections: the Südschleife (Southern loop) of 7.747 km (4.8 miles) and the Nordschleife (Northern loop) of 22.810 km (14 miles), with both sections sharing two straights (one of which was the start-finish straight) of 2.292 km (1.4 miles) in length. The first World Cycling Championship race took place on June 19, 1927, and the first German Grand Prix a month later.
In 1929 the full Ring was used for the last time in major racing events, as future Grands Prix would be held only on the Nordschleife (though minor races used just the Südschleife). Many memorable pre-war races took place at the circuit, featuring the talents of early Ringmeister (Ringmasters) such as Rudolf Caracciola, Tazio Nuvolari and Bernd Rosemeyer.
After World War II, racing recommenced in the 1950s and the Nordschleife of the Nürburgring again became the popular venue for the German Grand Prix as part of the Formula One World Championship (with the exception of 1959 when it was held on the AVUS in Berlin). It featured a new generation of F1 Ringmeister, with racers like Alberto Ascari, Juan Manuel Fangio, Stirling Moss, John Surtees, Jackie Stewart and Jacky Ickx. By the late 1960s it was apparent that the track was becoming increasingly dangerous for the latest generation of F1 cars, and in 1970 the German GP was temporarily moved to Hockenheim while the Nordschleife was under reconstruction. Taking out some bumps and installing safety barriers (armco) did much to improve safety, but it was not enough in the long run. By 1976 the track, primarily due to its extraordinary length of over 20 kilometres, was unable to meet the ever-increasing safety requirements, and was also deemed unsuitable for the burgeoning television market. Niki Lauda proposed to the other drivers that year, that the circuit should be boycotted because of the saftey arrangements. The other drivers voted against the idea and the race went ahead. Lauda crashed his Ferrari and was badly burned, being saved by the combined actions of fellow drivers Arturo Merzario, Guy Edwards, Brett Lunger and Harald Ertl rather than by the ill-equipped fire marshals. For Formula One, that was the end of the old Nurburgring. It was never used for a Grand Prix again.
In 1981, work began on a 4.5 km (2.8 miles) replacement circuit built next to and partly over the old one, and it was completed in 1984. This new Nürburgring, called GP-Strecke, though in character a mere shadow of its older sibling, has seen the return of Formula One to the Ring, briefly in 1984 and 1985, but more permanently since the 1995, following the success of Michael Schumacher.
The former Südschleife is now mostly gone or converted to a normal public road, but the Nordschleife is currently a one-way public toll-road with no speed limit. At a slightly reduced length of 20.8 km (13 miles), bypassing the modern GP-Strecke, the Nordschleife is frequently closed off for testing purposes and touring car endurance racing, but at other times it is open to anyone with a road legal car or motorcycle. This Nürburgring is a popular attraction for many driving and riding enthusiasts in Europe and beyond, because of its history and the considerable challenge it still provides. Accidents are common, and everyone considering driving round the Nordschleife should familiarize themselves with rules that apply, as well as the "do's" and "don'ts".
Several touring car series are still competing on the Nordschleife, using either only the simple 20.8 km version with a separate small pit lane, or a combined 24.4km long track that uses a part of the modern F1 track plus its huge pit facilities. Entry level of competition is a regularity test for road legal cars. Two racing series (CHC and VLN) compete on 15 Saturdays each year, for several hours.
The annual highlight is the 24 hour race weekend in mid-June, featuring 220 cars (from small 100hp cars to 700hp Turbo Porsche or 500hp factory race cars of BMW, Opel, Audi), over 700 drivers (amateurs and professionals) and up to 220 000 spectators.
Because of its demanding layout, the Nordschleife is used by many auto manufacturers as a proving ground for car prototypes. Some of the most notable corporate "Ring Rats" are BMW, Porsche, Mercedes-Benz, Audi, Nissan, and starting in 2002, General Motors. GM's first wave of Nürburgring-honed vehicles includes the Cadillac CTS-V and the sixth-generation Chevrolet Corvette. Nissan's Japanese domestic market supercar, the Skyline GT-R, was tuned at Nurburgring and held the unofficial lap record for several years.
In recent years, the Nürburgring's allure has spread through its appearance in video games. Titles featuring the Green Hell include Sierra's Grand Prix Legends and two games for the Xbox: Project Gotham Racing 2 and Forza Motorsport. It also featured in the PlayStation 2 game Gran Turismo 4.
See also: List of Formula One circuits
External links
- Official website (English version) (http://213.239.207.198/nuerburgring.de/index.php?id=186&L=1)
- Ben Lovejoy's Ringers Site (www.nurburgring.co.uk) (http://www.nurburgring.org.uk)
- Site dedicated to the forgotten Südschleife (http://sudschleife.8200rpm.com)
- 24hour Race (http://adac.24h-rennen.de)
- Nürburgring Fan Project (www.nurburgring.de) (http://www.nurburgring.de)
- A description of the racing line (http://www.team-tschauder.de/nring/n-ring1.htm)
- Regularity test for road cars (GLP) (http://www.glp1.de)
- Rallye-like racing (CHC) (http://www.castrol-haugg-cup.com)
- Endurance Racing (VLN) (http://www.langstreckenpokal.de/index.htm)
- Report from 24 Hour Race (http://members.ozemail.com.au/%7Emotorweb/nurburgring/)bg:Нурбургринг
de:Nürburgring es:Nürburgring it:Nürburgring ja:ニュルブルクリンク sv:Nürburgring