Frequency
|
|
- For other uses, see Frequency (disambiguation).
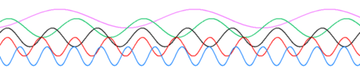 Sine waves of various frequencies; the lower waves have higher frequencies than those above.
Sine waves of various frequencies; the lower waves have higher frequencies than those above.
Frequency is the measurement of the number of times that a repeated event occurs per unit time. To calculate the frequency, one fixes a time interval, counts the number of occurrences of the event within that interval, and then divides this count by the length of the time interval.
In SI units, the result is measured in hertz (Hz) after the German physicist, Heinrich Rudolf Hertz. 1 Hz means that an event repeats once per second. Other units that have been used to measure frequency include: cycles per second, revolutions per minute (rpm). Heart rate is measured in beats per minute.
An alternative method to calculate frequency is to measure the time between two consecutive occurrences of the event (the period) and then compute the frequency as the reciprocal of this time:
- <math>f = \frac{1}{T}<math>
where T is the period.
| Contents |
Frequency of waves
Measuring the frequency of sound, electromagnetic waves (such as radio or light), electrical signals, or other waves, the frequency in hertz is the number of cycles of the repetitive waveform per second. If the wave is a sound, frequency is what characterizes its pitch.
Frequency has an inverse relationship to the concept of wavelength. The frequency f is equal to the speed v of the wave divided by the wavelength λ (lambda) of the wave:
- <math>f = \frac{v}{\lambda}<math>
In the special case of electromagnetic waves moving through a vacuum, then v = c, where c is the speed of light in a vacuum, and this expression becomes:
- <math>f = \frac{c}{\lambda}<math>
NOTE: When waves travel from one medium to another, their frequency remains more or less the same - only their wavelength and/or speed changes.
Examples
- The frequency of the standard pitch tone A above middle C is nowadays set at 440 Hz that is 440 cycles per second (or slightly higher) and known as concert pitch, after which an orchestra is tuned.
- A baby can hear tones with oscillations up to approximately 20,000 Hz, but these frequencies become impossible to hear at maturity.
- In Europe the frequency of the alternating current is 50 Hz (close to the tone G), with 230 V of rated voltage.
- In North America the frequency of the alternating current is 60 Hz (close to the tone B flat), with 117 V of rated voltage.
See also
wave, period, wavelength, amplitude, cutoff frequency
cent (music), angular frequency, simple harmonic motion
pitch, music note, tuning, electromagnetic spectrum, piano key frequencies
frequency spectrum
External links
- Conversion: frequency to wavelength and back (http://www.sengpielaudio.com/calculator-wavelength.htm)
- Conversion: period, cycle duration, periodic time to frequency (http://www.sengpielaudio.com/calculator-period.htm)
- TNFL, The Nordic Frequency List: Extensive collection of Scandinavian frequencies (http://w1.647.telia.com/~u64705175/lista.htm)bg:Честота
ca:Freqüència cs:Frekvence da:Frekvens de:Frequenz el:Συχνότητα es:Frecuencia eo:Frekvenco fa:بسامد fr:Fréquence id:Frekuensi it:Frequenza he:תדירות hu:Frekvencia nl:Frequentie ja:周波数 no:Frekvens pl:Częstotliwość pt:Frequência ru:Частота sk:Frekvencia sl:Frekvenca fi:Taajuus sv:Frekvens ta:அதிர்வெண் vi:Tần số tr:Frekans zh:頻率
